Endocrine Review
... b. Prepares the uterus for embryo implantation c. Helps maintain pregnancy Thymus Gland 1. Located in the chest 2. Large size in children, decreases in size with age 3. Thought to play a role in growth and development, but this has not been confirmed 4. Part of the immune system; produces T cells (l ...
... b. Prepares the uterus for embryo implantation c. Helps maintain pregnancy Thymus Gland 1. Located in the chest 2. Large size in children, decreases in size with age 3. Thought to play a role in growth and development, but this has not been confirmed 4. Part of the immune system; produces T cells (l ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... Alpha cells secrete glucagon when blood glucose levels drop. Beta cells secrete insulin when blood glucose levels are elevated. Delta cells are stimulated by high levels of nutrients in the ...
... Alpha cells secrete glucagon when blood glucose levels drop. Beta cells secrete insulin when blood glucose levels are elevated. Delta cells are stimulated by high levels of nutrients in the ...
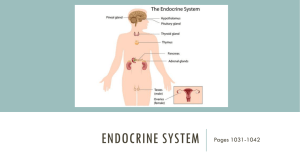
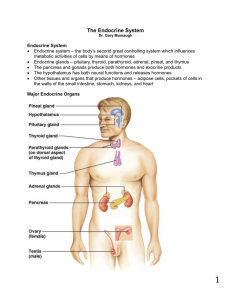
The Endocrine System
... into two distinct parts, the outer region of the adrenal called the adrenal cortex and the small inner section called the adrenal medulla. All adrenal hormones are ruled by adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary. 1. The adrenal cortex - produces and secretes three kinds of s ...
... into two distinct parts, the outer region of the adrenal called the adrenal cortex and the small inner section called the adrenal medulla. All adrenal hormones are ruled by adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary. 1. The adrenal cortex - produces and secretes three kinds of s ...
20 Endocrine System - Orange Coast College
... Functions principally in association with the lymphatic system to regulate and maintain body immunity. Produces complementary hormones thymopoietin and ...
... Functions principally in association with the lymphatic system to regulate and maintain body immunity. Produces complementary hormones thymopoietin and ...
chapt14-endocrine system
... The testes and ovaries produce the sex hormones which maintain the sex organs and secondary sexual characteristics. Male testes produce androgens (such as testosterone) that are similar to anabolic steroids taken to increase athletic performance. Female ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone. Thy ...
... The testes and ovaries produce the sex hormones which maintain the sex organs and secondary sexual characteristics. Male testes produce androgens (such as testosterone) that are similar to anabolic steroids taken to increase athletic performance. Female ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone. Thy ...
Endocrine System
... fully functional • Onset of puberty usually occurs between the ages of 9 and 15 & begins about one year earlier in females than in males • Puberty begins when hypothalamus signals pituitary to produce increased levels of ...
... fully functional • Onset of puberty usually occurs between the ages of 9 and 15 & begins about one year earlier in females than in males • Puberty begins when hypothalamus signals pituitary to produce increased levels of ...
Thyroid hormones
... TSH on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland (respectively) have become abnormal and no longer are sensitive to the negative feedback they continue to secrete TRH or TSH continuous stimulation of the thyroid gland with excess thyroid hormones being formed • symptoms of hyperthyroidism ...
... TSH on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland (respectively) have become abnormal and no longer are sensitive to the negative feedback they continue to secrete TRH or TSH continuous stimulation of the thyroid gland with excess thyroid hormones being formed • symptoms of hyperthyroidism ...
NEUROENDOCRINE Endocrine system glands
... Produces several hormones amongst which are thymosin, thymopoietin, and IGF-1. Stimulates the maturation of T- lymphocytes Largest size occurs at puberty and thereafter diminishes in size as one gets older. By the age of 50 it is ~ ¼ its original size. ...
... Produces several hormones amongst which are thymosin, thymopoietin, and IGF-1. Stimulates the maturation of T- lymphocytes Largest size occurs at puberty and thereafter diminishes in size as one gets older. By the age of 50 it is ~ ¼ its original size. ...
Hormones of the Body
... • This gland has both endocrine and exocrine functions… we’ll only cover the endocrine portion now (exocrine is for digestion) ...
... • This gland has both endocrine and exocrine functions… we’ll only cover the endocrine portion now (exocrine is for digestion) ...
The Endocrine System - Mediapolis Community School
... Lutenizing hormone (LH)- also called gonadotropins because they exert their actions on the gonads (reproductive organs.) ...
... Lutenizing hormone (LH)- also called gonadotropins because they exert their actions on the gonads (reproductive organs.) ...
Document
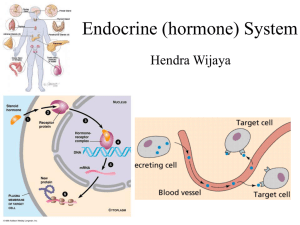
... circulate in the extracellular fluid and bind to specific receptors on or in target cells. They then modify cellular activities by altering membrane permeability, activating or inactivating key enzymes, or changing genetic activity.” ...
... circulate in the extracellular fluid and bind to specific receptors on or in target cells. They then modify cellular activities by altering membrane permeability, activating or inactivating key enzymes, or changing genetic activity.” ...
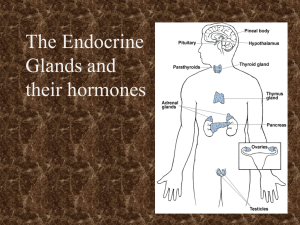
The Endocrine System
... Produces adrenaline that helps control your heart beat and breathing rate. testes: Produces male reproductive hormones like testosterone. ...
... Produces adrenaline that helps control your heart beat and breathing rate. testes: Produces male reproductive hormones like testosterone. ...
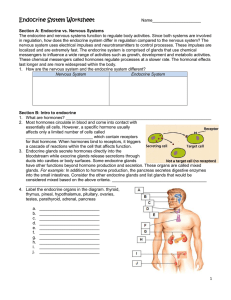
Endocrine System Worksheet
... Section B: Intro to endocrine 1. What are hormones? _______________________________________________________________ 2. Most hormones circulate in blood and come into contact with essentially all cells. However, a specific hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells called ________________ ...
... Section B: Intro to endocrine 1. What are hormones? _______________________________________________________________ 2. Most hormones circulate in blood and come into contact with essentially all cells. However, a specific hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells called ________________ ...
The Endocrine System
... Hormones – chemical substances secreted by cells into the extracellular fluids o Regulate the metabolic function of other cells o Have lag times ranging from seconds to hours o Tend to have prolonged effects Hormones circulate to all tissues but only activate cells referred to as target cells o ...
... Hormones – chemical substances secreted by cells into the extracellular fluids o Regulate the metabolic function of other cells o Have lag times ranging from seconds to hours o Tend to have prolonged effects Hormones circulate to all tissues but only activate cells referred to as target cells o ...
Chapter 11: The Endocrine System (pp
... The endocrine system, like the nervous system, controls body activities to maintain a relatively constant internal environment. The methods used by these two systems are different. This chapter describes the location of the endocrine glands and the hormones they secrete. It Explains the nature of ho ...
... The endocrine system, like the nervous system, controls body activities to maintain a relatively constant internal environment. The methods used by these two systems are different. This chapter describes the location of the endocrine glands and the hormones they secrete. It Explains the nature of ho ...
Endocrine System 2
... • LH regulates testosterone in men and estrogen in women. • FSH promotes sperm production in men and stimulates the ovaries to release eggs (ovulate) in women. ...
... • LH regulates testosterone in men and estrogen in women. • FSH promotes sperm production in men and stimulates the ovaries to release eggs (ovulate) in women. ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: INTRODUCTION
... the small intestine through a duct. As a ductless gland, the pancreas produces two hormones. One of these is called insulin. Insulin is produced in clusters of cells scattered throughout the pancreas. These groups of cells are called the islets of Langerhans. Insulin controls the amount of sugar (gl ...
... the small intestine through a duct. As a ductless gland, the pancreas produces two hormones. One of these is called insulin. Insulin is produced in clusters of cells scattered throughout the pancreas. These groups of cells are called the islets of Langerhans. Insulin controls the amount of sugar (gl ...
The Endocrine System
... Primary function is to control other glands. Produces many hormones. Secretion is controlled by the hypothalamus in the base of the brain. ...
... Primary function is to control other glands. Produces many hormones. Secretion is controlled by the hypothalamus in the base of the brain. ...
Endocrine System Endocrine Glands
... Note on the figure above that the blood supply to the anterior pituitary passes through the hypothalamus first where it picks up regulating hormones that control the release of hormones from the anterior pituitary. ...
... Note on the figure above that the blood supply to the anterior pituitary passes through the hypothalamus first where it picks up regulating hormones that control the release of hormones from the anterior pituitary. ...
Lab Endocrine Disorders
... The endocrine system consists of a group of glands and organs that regulate and control various body functions by producing and secreting hormones. The glands of the endocrine system do not have ducts but rather release their hormones directly into the bloodstream. The endocrine system is the slow m ...
... The endocrine system consists of a group of glands and organs that regulate and control various body functions by producing and secreting hormones. The glands of the endocrine system do not have ducts but rather release their hormones directly into the bloodstream. The endocrine system is the slow m ...
Endocrine Review Sheet
... 1. Why are calcitonin and PTH said to be antagonistic hormones? Explain the feedback mechanisms involved in maintaining the appropriate level of calcium in the blood and interstitial fluid. Please be sure to include what hormones are involved, where they are produced, what stimulates the production ...
... 1. Why are calcitonin and PTH said to be antagonistic hormones? Explain the feedback mechanisms involved in maintaining the appropriate level of calcium in the blood and interstitial fluid. Please be sure to include what hormones are involved, where they are produced, what stimulates the production ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.