Hormones
... • The endocrine system comprises a group of ductless glands that secrete chemical messenger substances, called hormones, into the bloodstream. • Hormones are responsible for the longterm regulation of many bodily functions. • The endocrine system includes the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus ...
... • The endocrine system comprises a group of ductless glands that secrete chemical messenger substances, called hormones, into the bloodstream. • Hormones are responsible for the longterm regulation of many bodily functions. • The endocrine system includes the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus ...
Document
... • Each lobule is drained by a lactiferous duct, which usually opens independently on the nipple. • Deep to the areola, each duct has a dilated portion, the lactiferous sinus, in which a small droplet of milk accumulates or remains in the nursing mother. As the infant begins to suckle, compression of ...
... • Each lobule is drained by a lactiferous duct, which usually opens independently on the nipple. • Deep to the areola, each duct has a dilated portion, the lactiferous sinus, in which a small droplet of milk accumulates or remains in the nursing mother. As the infant begins to suckle, compression of ...
I. Overview of the Endocrine System
... Risk factors: overweight or obese, heredity, certain ethnic groups ...
... Risk factors: overweight or obese, heredity, certain ethnic groups ...
CLASS-X BIOLOGY EPISODE
... 5). Luteinising Hormone(LH):- In females LH stimulates ovulation formation of corpus leuteum and its hormones. In male it is called Insterstitial cell stimulating hormone which is responsible for testosterone secretion. The secretion of the above hormones starts from Puberty. These hormones are cal ...
... 5). Luteinising Hormone(LH):- In females LH stimulates ovulation formation of corpus leuteum and its hormones. In male it is called Insterstitial cell stimulating hormone which is responsible for testosterone secretion. The secretion of the above hormones starts from Puberty. These hormones are cal ...
Sialography - El Camino College
... 4. After procedure _______ to clear contrast 5. _____min after procedure take radiograph ...
... 4. After procedure _______ to clear contrast 5. _____min after procedure take radiograph ...
endocrine glands
... particular area (the target organ), where they have their effect. E.g. insulin Hormones are mainly made of PROTEIN. Some hormones are steroid based (made of lipid) e.g. male hormones Even though hormones are carried to all parts of the body in the blood stream they only affect specific areas called ...
... particular area (the target organ), where they have their effect. E.g. insulin Hormones are mainly made of PROTEIN. Some hormones are steroid based (made of lipid) e.g. male hormones Even though hormones are carried to all parts of the body in the blood stream they only affect specific areas called ...
Endocrine System Anatomy
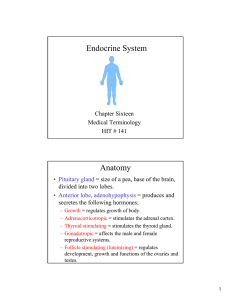
... Gonadotropic = affects the male and female reproductive systems. – Follicle stimulating (luteinizing) = regulates development, growth and functions of the ovaries and testes. ...
... Gonadotropic = affects the male and female reproductive systems. – Follicle stimulating (luteinizing) = regulates development, growth and functions of the ovaries and testes. ...
Structure and Functions of Important Endocrine Glands
... • They are e xocrine glands are glands that secrete their products (enzymes excluding hormones and other chemical messengers like Neurotransmitter communicates to adjacent cells, Neuropeptide - a protein sequence which acts as a hormone or neurotransmitter, Pheromone - a chemical factor that trigge ...
... • They are e xocrine glands are glands that secrete their products (enzymes excluding hormones and other chemical messengers like Neurotransmitter communicates to adjacent cells, Neuropeptide - a protein sequence which acts as a hormone or neurotransmitter, Pheromone - a chemical factor that trigge ...
Pituitary Gland Hormones
... Target: Adrenal Cortex (outer layer of gland) Action: stim. release of corticosteroid hormones (Cortisol is the main one) to help the body resist stress Stimulus for release: CRH (corticotropic releasing hormone) from hypothalamus Inhibit: Neg. feedback, an inc. of Cortisol in bl. causes hypothal. t ...
... Target: Adrenal Cortex (outer layer of gland) Action: stim. release of corticosteroid hormones (Cortisol is the main one) to help the body resist stress Stimulus for release: CRH (corticotropic releasing hormone) from hypothalamus Inhibit: Neg. feedback, an inc. of Cortisol in bl. causes hypothal. t ...
Endocrine System Introduction
... ENDOCRINE = released into the blood stream or interstitial space. EXOCRINE = released onto epithelial surface. Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system. Uses chemical messengers called hormones. Controls a variety of necessary biological functions such as: *Re ...
... ENDOCRINE = released into the blood stream or interstitial space. EXOCRINE = released onto epithelial surface. Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system. Uses chemical messengers called hormones. Controls a variety of necessary biological functions such as: *Re ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 27
... Autocrine hormones interact with receptors on the surface of the same cell that was responsible for their secretion, and as such can be seen as the ultimate in locally acting hormones. Paracrine hormones usually act over only very short distances, travelling to their site of action by diffusion thro ...
... Autocrine hormones interact with receptors on the surface of the same cell that was responsible for their secretion, and as such can be seen as the ultimate in locally acting hormones. Paracrine hormones usually act over only very short distances, travelling to their site of action by diffusion thro ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... b. signal transduction, and c. response. 3. An amino-acid-derived hormone a. binds to plasma-membrane receptors on target cells and b. initiates a signal transduction pathway. 4. A steroid hormone can a. diffuse through plasma membranes, b. bind to a receptor protein in the cytoplasm or nucleus, and ...
... b. signal transduction, and c. response. 3. An amino-acid-derived hormone a. binds to plasma-membrane receptors on target cells and b. initiates a signal transduction pathway. 4. A steroid hormone can a. diffuse through plasma membranes, b. bind to a receptor protein in the cytoplasm or nucleus, and ...
Endocrine System Answer Key Across
... factor ( regulates cell growth & development), angiotensin/angiotensinogen (vasoconstriction), hepcidin (absorption & release of iron), & thrombopoetin (production of platelets) 13. DIABETESMELLITUS—Chronic condition associated with abnormal levels of glucose due to decrease insulin production by th ...
... factor ( regulates cell growth & development), angiotensin/angiotensinogen (vasoconstriction), hepcidin (absorption & release of iron), & thrombopoetin (production of platelets) 13. DIABETESMELLITUS—Chronic condition associated with abnormal levels of glucose due to decrease insulin production by th ...
Chapter 11 The Endocrine System - Linn
... reverse the direction of a change in a physiological system • Positive feedback—(uncommon) mechanisms that amplify physiological changes ...
... reverse the direction of a change in a physiological system • Positive feedback—(uncommon) mechanisms that amplify physiological changes ...
Unit 3_Lesson 74_Endocrine - DPH6Science
... The _______________________________glands regulate your response to stress. Right, they release the hormone adrenaline in dangerous or exciting situations. It gives you a quick burst of strength and speed. The adrenal glands are also involved with your body’s regulation of salt, and its sexual devel ...
... The _______________________________glands regulate your response to stress. Right, they release the hormone adrenaline in dangerous or exciting situations. It gives you a quick burst of strength and speed. The adrenal glands are also involved with your body’s regulation of salt, and its sexual devel ...
Sialography - El Camino College
... Term applied to radiographic exam of salivary glands – Only one gland done at a time – CT and MRI have largely replaced this exam for Salivary stone or lesion is suspected ...
... Term applied to radiographic exam of salivary glands – Only one gland done at a time – CT and MRI have largely replaced this exam for Salivary stone or lesion is suspected ...
Chapter 11 • The Endocrine System • What you absolutely need to
... Help maintain normal blood glucose concentration by increasing gluconeogenesis—the formation of “new” glucose from amino acids produced by the breakdown of proteins, mainly those in muscle tissue cells; also the conversion to glucose of fatty acids produced by the breakdown of fats stored in adipose ...
... Help maintain normal blood glucose concentration by increasing gluconeogenesis—the formation of “new” glucose from amino acids produced by the breakdown of proteins, mainly those in muscle tissue cells; also the conversion to glucose of fatty acids produced by the breakdown of fats stored in adipose ...
Copy of Ms. Myers` Endocrine Power Point
... islets secrete insulin, which lowers the blood glucose level, and glucagon, which has the opposite effect, together regulating the glucose level in the blood. ...
... islets secrete insulin, which lowers the blood glucose level, and glucagon, which has the opposite effect, together regulating the glucose level in the blood. ...
correct - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... a. cause the uterus to contract b. induce labor c. stimulate the release of milk from the mother's mammary glands when her baby is nursing. d. all of the above 12 : Hypothalamic releasing and releaseinhibiting hormones are transported from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary by way of _______ ...
... a. cause the uterus to contract b. induce labor c. stimulate the release of milk from the mother's mammary glands when her baby is nursing. d. all of the above 12 : Hypothalamic releasing and releaseinhibiting hormones are transported from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary by way of _______ ...
Chapter 16: Endocrine System
... Anterior Lobe secretes tropic hormones that regulate other endocrine glands: • Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH or thyrotropin) – regulates thyroid • Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) – regulates gonads • Luteinzing hormone (LH) – regulates gonads • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH or corticotroph ...
... Anterior Lobe secretes tropic hormones that regulate other endocrine glands: • Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH or thyrotropin) – regulates thyroid • Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) – regulates gonads • Luteinzing hormone (LH) – regulates gonads • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH or corticotroph ...
Endocrine System
... caused by a tumor, infection, genetic factors, or injury – Small body size, short extremeties, lack of sexual development, mental development is usually normal – If diagnosed early, can be treated with injections of somatotropin (GH) hormone for 5 years or more until long bone growth is complete ...
... caused by a tumor, infection, genetic factors, or injury – Small body size, short extremeties, lack of sexual development, mental development is usually normal – If diagnosed early, can be treated with injections of somatotropin (GH) hormone for 5 years or more until long bone growth is complete ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.