Document
... glands are not anatomically connected and are scattered throughout the body (Figure 1–1). Communication among the different organs is ensured through the release of hormones or neurotransmitters. Hormones—Hormones are chemical products, released in very small amounts from the cell, that exert a biolo ...
... glands are not anatomically connected and are scattered throughout the body (Figure 1–1). Communication among the different organs is ensured through the release of hormones or neurotransmitters. Hormones—Hormones are chemical products, released in very small amounts from the cell, that exert a biolo ...
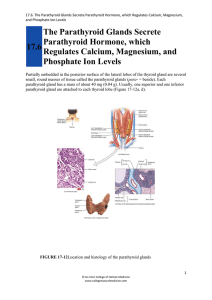
17.6 The Parathyroid Glands Secrete Parathyroid Hormone, which
... c). The more numerous cells, called chief cells, produce parathyroid hormone (PTH). The function of the other kind of cell, called an oxyphil cell, is not known. ...
... c). The more numerous cells, called chief cells, produce parathyroid hormone (PTH). The function of the other kind of cell, called an oxyphil cell, is not known. ...
neuroimmunoendocrinology of the cervical auto no mic
... neural input to the pineal gland, an organ heavily depending on SCO projections to synthesize the hormone melatonin. In a number of experiments we, as well as other researchers, found that pinealectomy (Px) and superior cervical ganglionectomy (SCGx), a procedure supposed to act exclusively via supp ...
... neural input to the pineal gland, an organ heavily depending on SCO projections to synthesize the hormone melatonin. In a number of experiments we, as well as other researchers, found that pinealectomy (Px) and superior cervical ganglionectomy (SCGx), a procedure supposed to act exclusively via supp ...
Thyroid Gland
... Each follicle is surrounded by basement membrane, between follicular cells there are parafollicular cells containing calcitonin secreting C cells ...
... Each follicle is surrounded by basement membrane, between follicular cells there are parafollicular cells containing calcitonin secreting C cells ...
$doc.title
... Posterior pituitary hormones are synthesized in supraoptic nucleus and paraventricular nucleus, which have 2 cell types (magnocellular, which terminate in pars nervosa and parvocellular, which end in median eminance and influence anterior pituitary secretion) ...
... Posterior pituitary hormones are synthesized in supraoptic nucleus and paraventricular nucleus, which have 2 cell types (magnocellular, which terminate in pars nervosa and parvocellular, which end in median eminance and influence anterior pituitary secretion) ...
Growth Hormone In Musculoskeletal Pain States
... discovered in 1999. Ghrelin is a 28 amino acid peptide produced by endocrine cells within the stomach that increases appetite and stimulates GH secretion. Ghrelin secreting cells have also been reported in the intestine, pancreas, hypothalamus, and testis. There is an inverse relationship between bo ...
... discovered in 1999. Ghrelin is a 28 amino acid peptide produced by endocrine cells within the stomach that increases appetite and stimulates GH secretion. Ghrelin secreting cells have also been reported in the intestine, pancreas, hypothalamus, and testis. There is an inverse relationship between bo ...
(tsh) test in master health checkups
... releasing the hormones T4 and T3, the biologically active agents central to metabolic regulation. Both T3 and T4 are used to treat thyroid hormone deficiency hypothyroidism. They are both absorbed well by the gut, so can be given orally3,4,5. Disorders:Thyroid disorders include hyperthyroidism and H ...
... releasing the hormones T4 and T3, the biologically active agents central to metabolic regulation. Both T3 and T4 are used to treat thyroid hormone deficiency hypothyroidism. They are both absorbed well by the gut, so can be given orally3,4,5. Disorders:Thyroid disorders include hyperthyroidism and H ...
Full version (PDF file)
... demonstrated that dorsal agranular insular cortex and dorsal prelimbic cortex project primarily to the dorsal NAc core, while the ventral NAc core is mainly innervated by pathways originating in the ventral prelimbic cortex, ventral agranular insular cortex and olfactory tubercle (Groenewegen et al. ...
... demonstrated that dorsal agranular insular cortex and dorsal prelimbic cortex project primarily to the dorsal NAc core, while the ventral NAc core is mainly innervated by pathways originating in the ventral prelimbic cortex, ventral agranular insular cortex and olfactory tubercle (Groenewegen et al. ...
Thyroid Physiology and Thyroid Function Tests
... is considered to be a pre-hormone for T3. *T4 and T3 are bound to thyroid binding globulin (TBG), thyroxine-binding prealbumin, and albumin. Around 70% of T4 is bound to TBG, 20% to TBPA, and 10% to albumin. All bound T3 is bound to TBG. Only 0.04% of T4 and 0.4% of T3 is unbound. The free hormone i ...
... is considered to be a pre-hormone for T3. *T4 and T3 are bound to thyroid binding globulin (TBG), thyroxine-binding prealbumin, and albumin. Around 70% of T4 is bound to TBG, 20% to TBPA, and 10% to albumin. All bound T3 is bound to TBG. Only 0.04% of T4 and 0.4% of T3 is unbound. The free hormone i ...
Hypothyroidism in Dogs
... "If the thyroid is overactive (hyperthyroidism), the body's metabolism is elevated. If it is underactive (hypothyroidism), the metabolism slows down." The thyroid gland regulates the body's metabolic rate. If the thyroid is overactive (hyperthyroidism), the body's metabolism is elevated. If it is un ...
... "If the thyroid is overactive (hyperthyroidism), the body's metabolism is elevated. If it is underactive (hypothyroidism), the metabolism slows down." The thyroid gland regulates the body's metabolic rate. If the thyroid is overactive (hyperthyroidism), the body's metabolism is elevated. If it is un ...
Follitropin subunit beta, Follicle- stimulating hormone beta subunit
... critical for spermatogenesis. In both males and females, FSH stimulates the maturation of germ cells. In females, FSH initiates follicular growth, specifically affecting granulosa cells. With the concomitant rise in inhibin B FSH levels then decline in the late follicular phase. This seems to be cri ...
... critical for spermatogenesis. In both males and females, FSH stimulates the maturation of germ cells. In females, FSH initiates follicular growth, specifically affecting granulosa cells. With the concomitant rise in inhibin B FSH levels then decline in the late follicular phase. This seems to be cri ...
PowerPoint
... Thyroid helps set the rate of metabolism - the rate at which the body uses energy. Hashimoto’s prevents the gland from producing enough thyroid hormones for the body to work correctly. It is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Have statistically increased risk of developing other ...
... Thyroid helps set the rate of metabolism - the rate at which the body uses energy. Hashimoto’s prevents the gland from producing enough thyroid hormones for the body to work correctly. It is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Have statistically increased risk of developing other ...
iodide-iodine-metabolism - DC Vitamin C Iinfusions
... level in blood. A fall in T4 level stimulates the pituitary to increase its TSH secretion which in turn stimulates the thyroid gland to release T4 in circulation to maintain normal level of the hormone in blood (4). ...
... level in blood. A fall in T4 level stimulates the pituitary to increase its TSH secretion which in turn stimulates the thyroid gland to release T4 in circulation to maintain normal level of the hormone in blood (4). ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... cell. T3 and T4 are transported by various proteins (LAT2, MCT8, OATP14) into the target cell where they can interact with the thyroid hormone receptor (TR) to alter transcription and protein synthesis. Alternatively, T 3 and T4 can interact with a domain on the extracellular portion of the integrin ...
... cell. T3 and T4 are transported by various proteins (LAT2, MCT8, OATP14) into the target cell where they can interact with the thyroid hormone receptor (TR) to alter transcription and protein synthesis. Alternatively, T 3 and T4 can interact with a domain on the extracellular portion of the integrin ...
a.central precocious puberty
... the aetiology is often unknown ,it’s a gonadotropin-dependent. Although up to 25% are due to central nervous system malformation or brain tumours. B.peripheral precocious puberty: Its always pathological & can be caused by estrogen secretion such as exogenous ingestion like pills or a hormone-produc ...
... the aetiology is often unknown ,it’s a gonadotropin-dependent. Although up to 25% are due to central nervous system malformation or brain tumours. B.peripheral precocious puberty: Its always pathological & can be caused by estrogen secretion such as exogenous ingestion like pills or a hormone-produc ...
Product Data Douglas Laboratories®
... The thyroid is an endocrine gland, a ductless organ that secretes chemicals directly into the bloodstream, which regulates the functioning of virtually all cells in your body. Your thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the front base of your neck. When your thyroid produces thy ...
... The thyroid is an endocrine gland, a ductless organ that secretes chemicals directly into the bloodstream, which regulates the functioning of virtually all cells in your body. Your thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the front base of your neck. When your thyroid produces thy ...
Thyroid Hormone Treatment FAQ - American Thyroid Association
... How is the dose of thyroxine chosen? The initial T4 dose is carefully selected based on your weight, age, and other medical conditions. The dose is then adjusted based on your thyroid hormone levels and your symptoms. The current branded forms of T4 are Synthroid® Levoxyl® Levothyroid®, Tirosint® an ...
... How is the dose of thyroxine chosen? The initial T4 dose is carefully selected based on your weight, age, and other medical conditions. The dose is then adjusted based on your thyroid hormone levels and your symptoms. The current branded forms of T4 are Synthroid® Levoxyl® Levothyroid®, Tirosint® an ...
Cardiovascular Hormones
... Elevations in circulating natriuretic peptides have been reported in a variety of pathophysiologic states. CNP is remarkably elevated in septic shock, but not in hypertension or congestive heart failure (CHF). This again points to the more likely paracrine actions of CNP within the endothelial cell ...
... Elevations in circulating natriuretic peptides have been reported in a variety of pathophysiologic states. CNP is remarkably elevated in septic shock, but not in hypertension or congestive heart failure (CHF). This again points to the more likely paracrine actions of CNP within the endothelial cell ...
MR Height of the Pituitary Gland as a Function of Age and Sex
... this period. The greater pituitary height in young subjects, both male and female, may reflect physiological neuroendocrine differences between younger and older subjects. The decline in pituitary height with age may also reflect the endocrinology of aging and a physiological pituitary atrophy. It h ...
... this period. The greater pituitary height in young subjects, both male and female, may reflect physiological neuroendocrine differences between younger and older subjects. The decline in pituitary height with age may also reflect the endocrinology of aging and a physiological pituitary atrophy. It h ...
Definition of Neuronal Circuitry Controlling the Activity of Phrenic
... the MRF were also infected by transynaptic passage of PRV from the ferret rectus abdominis (RA) muscle, along with neurons in portions of the ventrolateral reticular formation known to contain the ventral respiratory group, the nucleus retroambiguus, and the raphe nuclei (Billig et al., 1999). The o ...
... the MRF were also infected by transynaptic passage of PRV from the ferret rectus abdominis (RA) muscle, along with neurons in portions of the ventrolateral reticular formation known to contain the ventral respiratory group, the nucleus retroambiguus, and the raphe nuclei (Billig et al., 1999). The o ...
Basic endocrinology Pituitary Gland Endocrine disorders Endocrine
... – Tertiary – lack of hypothalamic stimulation ...
... – Tertiary – lack of hypothalamic stimulation ...
PDF. - Veterinary Sciences Tomorrow
... redundant in dogs and the function of exon 1 may be to circumvent exon 2 in order to direct production of isoform M2-LHX3. These results highlight the significance of isoform M2-LHX3 and the canine situation opens the possibility that also in other species the LHX3a isoform is redundant. The most im ...
... redundant in dogs and the function of exon 1 may be to circumvent exon 2 in order to direct production of isoform M2-LHX3. These results highlight the significance of isoform M2-LHX3 and the canine situation opens the possibility that also in other species the LHX3a isoform is redundant. The most im ...
Endocrinology
... Site of Neural – Hormonal interaction Sets temporal release of hormones Responsible for stress reaction of hormones ...
... Site of Neural – Hormonal interaction Sets temporal release of hormones Responsible for stress reaction of hormones ...
Hormonal responses to a 160-km race across frozen
... and the training of these athletes was not a significant source of physical stress inducing raised resting cortisol levels. It has been proposed that these stress hormones may be responsible for the feedback disruption, as strong negative relationships have been observed between testosterone and cor ...
... and the training of these athletes was not a significant source of physical stress inducing raised resting cortisol levels. It has been proposed that these stress hormones may be responsible for the feedback disruption, as strong negative relationships have been observed between testosterone and cor ...
The human medial geniculate body
... the study of the great sensory systems in particular, is one of progressive subdivision, both anatomical and physiological. Structures and functions once believed to be uniform and isomorphic are reluctantly but nonetheless inevitably subdi037X-5955/84/$03.00 ...
... the study of the great sensory systems in particular, is one of progressive subdivision, both anatomical and physiological. Structures and functions once believed to be uniform and isomorphic are reluctantly but nonetheless inevitably subdi037X-5955/84/$03.00 ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.