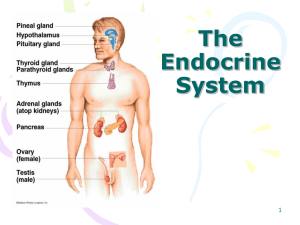
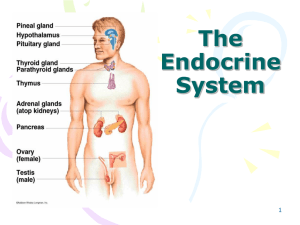
Hormones and The Endocrine System
... 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Comparing the endocrine and nervous systems – The nervous system reacts faster. – The responses of the endocrine system last longer. ...
... 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Comparing the endocrine and nervous systems – The nervous system reacts faster. – The responses of the endocrine system last longer. ...
The Endocrine System
... feels more alert, observing their environment with more interest. When there is too much TH, they get muscles tremors and increased blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia). • With not enough TH, they lose interest, become sluggish, they get low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia). ...
... feels more alert, observing their environment with more interest. When there is too much TH, they get muscles tremors and increased blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia). • With not enough TH, they lose interest, become sluggish, they get low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia). ...
Endocrine System PPT
... feels more alert, observing their environment with more interest. When there is too much TH, they get muscles tremors and increased blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia). • With not enough TH, they lose interest, become sluggish, they get low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia). ...
... feels more alert, observing their environment with more interest. When there is too much TH, they get muscles tremors and increased blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia). • With not enough TH, they lose interest, become sluggish, they get low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia). ...
Hormones and The Endocrine System
... 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Comparing the endocrine and nervous systems – The nervous system reacts faster. – The responses of the endocrine system last longer. ...
... 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Comparing the endocrine and nervous systems – The nervous system reacts faster. – The responses of the endocrine system last longer. ...
ENDOCRINE - Wikispaces
... • Occurs when actions of several hormones are complementary (added) & their combined effects is more than their individual effect. e.g. • Synergistic action of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and testosterone in sperm production (spermatogenesis). • This is due to influence on each other receptor ...
... • Occurs when actions of several hormones are complementary (added) & their combined effects is more than their individual effect. e.g. • Synergistic action of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and testosterone in sperm production (spermatogenesis). • This is due to influence on each other receptor ...
Chapter 23
... i. numerous principal cells which secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) or parathormone - this hormone increases blood calcium and magnesium levels, decreases blood phosphate levels, and promotes the formation of calcitriol, which is the active form of vitamin D ii. less numerous oxyphil cells whose fun ...
... i. numerous principal cells which secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) or parathormone - this hormone increases blood calcium and magnesium levels, decreases blood phosphate levels, and promotes the formation of calcitriol, which is the active form of vitamin D ii. less numerous oxyphil cells whose fun ...
Chapter 45. - RMC Science Home
... organs via circulatory system Contact many cells but only affect those with specific receptors Longer lasting affect (in comparison to neurotransmitters) growth hormones ...
... organs via circulatory system Contact many cells but only affect those with specific receptors Longer lasting affect (in comparison to neurotransmitters) growth hormones ...
2014 - EndoBridge
... Introduction: Subclinical Cushing Syndrome has been firstly defined in patients with adrenal incidentaloma who lack clinical symptoms of hypercortisolism. Patients with incidental pituitary adenoma or adrenocortical carcinoma may also have this syndrome. We present a case of subclinical Cushing synd ...
... Introduction: Subclinical Cushing Syndrome has been firstly defined in patients with adrenal incidentaloma who lack clinical symptoms of hypercortisolism. Patients with incidental pituitary adenoma or adrenocortical carcinoma may also have this syndrome. We present a case of subclinical Cushing synd ...
Endocrine system Questions (in class)
... 1. Suppose a girl ate too many sweets for breakfast and forgot to bring her lunch to school. How will the hormones insulin and glucagon from her pancreas help her body with an increase and then decrease of glucose? 2. Name two different events that may happen if a person’s nervous system and endocri ...
... 1. Suppose a girl ate too many sweets for breakfast and forgot to bring her lunch to school. How will the hormones insulin and glucagon from her pancreas help her body with an increase and then decrease of glucose? 2. Name two different events that may happen if a person’s nervous system and endocri ...
Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... • Promotes secretion of sex hormones • In women, promotes egg release • Gonadotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates secretion ...
... • Promotes secretion of sex hormones • In women, promotes egg release • Gonadotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates secretion ...
139 Endocrine System
... development of secondary sex characteristics in both males and females (Figure 2). GnRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to release two gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH). Gonadotropins are peptide hormones that target the gonads. In males, these hormones ...
... development of secondary sex characteristics in both males and females (Figure 2). GnRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to release two gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH). Gonadotropins are peptide hormones that target the gonads. In males, these hormones ...
Power Point - Science Olympiad
... Images are upside down and backwards when they reach the retina ...
... Images are upside down and backwards when they reach the retina ...
Hypopituitarism
... Hypopituitarism may be congenital. This means that the pituitary or hypothalamus did not form normally before birth. In other cases it may be acquired. This occurs if there was damage to the pituitary or hypothalamus during or after birth. Hypopituitarism can be caused by a tumor in the pituitary ar ...
... Hypopituitarism may be congenital. This means that the pituitary or hypothalamus did not form normally before birth. In other cases it may be acquired. This occurs if there was damage to the pituitary or hypothalamus during or after birth. Hypopituitarism can be caused by a tumor in the pituitary ar ...
Lect 08 Endocrine 1 - intro (KKD)
... conc. off hormones h controlled t ll d b by rate t of: f – secretion – metabolism and excretion – binding to plasma proteins • secretory output of endocrine cells controlled by – neurall input i – other hormones ...
... conc. off hormones h controlled t ll d b by rate t of: f – secretion – metabolism and excretion – binding to plasma proteins • secretory output of endocrine cells controlled by – neurall input i – other hormones ...
Endocrine Drugs - My Illinois State
... Stage 3: In cases of ambiguity or in patients with persistently poor augmentation of plasma cortisol, other problems should be considered, such as coexistent pituitary or adrenal disease, or an associated endocrinopathy (hypothyroidism). ...
... Stage 3: In cases of ambiguity or in patients with persistently poor augmentation of plasma cortisol, other problems should be considered, such as coexistent pituitary or adrenal disease, or an associated endocrinopathy (hypothyroidism). ...
Physiopathological determinants of human infertility
... reveal disorders that cause morbidity in the normally fertile population, which might or might not contribute to the infertility. Endocrine dysfunction is a signi®cant cause of infertility due to amenorrhoea and dysfunctional uterine bleeding, and hirsutism is a familiar problem in the normal popula ...
... reveal disorders that cause morbidity in the normally fertile population, which might or might not contribute to the infertility. Endocrine dysfunction is a signi®cant cause of infertility due to amenorrhoea and dysfunctional uterine bleeding, and hirsutism is a familiar problem in the normal popula ...
Endocrine System
... testosterone) are the primary gonadocorticoids. • Hormones may be involved in outset of puberty • Androgens for females are thought to influence sex drive and may be converted to estrogens after menopause • Hypersecretion of gonadocorticoids produces masculinization. At a young age females produce f ...
... testosterone) are the primary gonadocorticoids. • Hormones may be involved in outset of puberty • Androgens for females are thought to influence sex drive and may be converted to estrogens after menopause • Hypersecretion of gonadocorticoids produces masculinization. At a young age females produce f ...
University of Groningen Maternal androgens in egg yolks Eising
... onset of incubation onwards may counteract the uneven distribution of maternal hormones in the yolk. Furthermore, in chicken embryos, endogenous production of steroids occurs as early as day 5 of development (Woods and Erton, 1978; Woods et al., 1975). The sex differences in yolk hormone content foun ...
... onset of incubation onwards may counteract the uneven distribution of maternal hormones in the yolk. Furthermore, in chicken embryos, endogenous production of steroids occurs as early as day 5 of development (Woods and Erton, 1978; Woods et al., 1975). The sex differences in yolk hormone content foun ...
View Newsletter - Bristlecone Behavioral Health
... the ‘orchestra of organs’ to the conductor’s cue. Are the muscles, liver and brain sensitive to insulin’s message or have they down-regulated their receptors becoming functionally deaf to insulin? The loss of sensitivity to insulin, known as insulin resistance, pre-diabetes or metabolic syndrome, ca ...
... the ‘orchestra of organs’ to the conductor’s cue. Are the muscles, liver and brain sensitive to insulin’s message or have they down-regulated their receptors becoming functionally deaf to insulin? The loss of sensitivity to insulin, known as insulin resistance, pre-diabetes or metabolic syndrome, ca ...
Cytomegalovirus and BK-Virus co-infection of a clinically non
... common finding in clinical practice, being encountered in 0.5-2% of abdominal computed tomography scans (Barzon et al., 2003). The pathogenetic mechanisms at the basis of the development of adrenal masses are still largely unknown. Several viruses, including polyomaviruses and herpes viruses, can ca ...
... common finding in clinical practice, being encountered in 0.5-2% of abdominal computed tomography scans (Barzon et al., 2003). The pathogenetic mechanisms at the basis of the development of adrenal masses are still largely unknown. Several viruses, including polyomaviruses and herpes viruses, can ca ...
Applied Endocrinology
... • Follicular pool is established in utero • Placental estrogen levels increase with gestation • Estrogen regulates fetal ovarian follicle development ...
... • Follicular pool is established in utero • Placental estrogen levels increase with gestation • Estrogen regulates fetal ovarian follicle development ...
Endocrinology-general physiolofy of hormone, hormonal feed
... Peripheral glands Hormones of peripheral glands Tissue ...
... Peripheral glands Hormones of peripheral glands Tissue ...
8. Endocrine System 8.1 Basic Concepts The endocrine system is
... food supply and to genetic endowment, a number of hormones are involved, GH, sex hormones, thyroxine and insulin. There are two periods of accelerated growth. The first occurs in the first two years of life and the second at the time of puberty. The period of accelerated growth at puberty is associa ...
... food supply and to genetic endowment, a number of hormones are involved, GH, sex hormones, thyroxine and insulin. There are two periods of accelerated growth. The first occurs in the first two years of life and the second at the time of puberty. The period of accelerated growth at puberty is associa ...