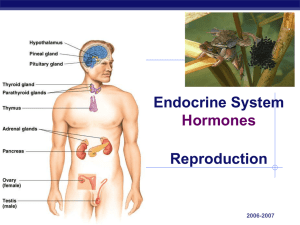
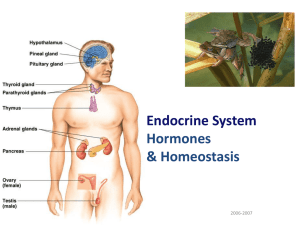
The Endocrine System
... parathyroid hormone (PTH) by parathyroid glands* Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... parathyroid hormone (PTH) by parathyroid glands* Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Document
... PRESSURE • SYNTHESIZED IN SUPRAOPTIC NUCLEI OF HYPOTHALAMUS • CARRIED IN HYPOTHALAMOHYPOPYSEAL TRACT • STORED IN AXON TERMINALS IN PITUITARY ...
... PRESSURE • SYNTHESIZED IN SUPRAOPTIC NUCLEI OF HYPOTHALAMUS • CARRIED IN HYPOTHALAMOHYPOPYSEAL TRACT • STORED IN AXON TERMINALS IN PITUITARY ...
Hyperthyroidism - The Endocrine Center
... -Weight loss -Irregular periods How is hyperthyroidism diagnosed? Your doctor will first do a blood test. Further tests will depend on these results on your individual case, and may include nuclear thyroid scan or ultrasound. What causes hyperthyroidism? Hyperthyroidism can be caused by 3 main cause ...
... -Weight loss -Irregular periods How is hyperthyroidism diagnosed? Your doctor will first do a blood test. Further tests will depend on these results on your individual case, and may include nuclear thyroid scan or ultrasound. What causes hyperthyroidism? Hyperthyroidism can be caused by 3 main cause ...
Growth Hormone New
... Treatment of growth hormone deficiency in children (including pituitary dwarfism as well as growth hormone deficiency following cranial irradiation), where: Patient must be evaluated by a pediatric endocrinologist The patient’s baseline height must be < the third percentile (i.e. >2 standard dev ...
... Treatment of growth hormone deficiency in children (including pituitary dwarfism as well as growth hormone deficiency following cranial irradiation), where: Patient must be evaluated by a pediatric endocrinologist The patient’s baseline height must be < the third percentile (i.e. >2 standard dev ...
hypothyroidism in childhood
... The thyroid gland lies in the neck at the front of the windpipe and produces a hormone called thyroxine. Thyroxine is a chemical secreted into the blood that controls the function of other organs. Thyroxine has major effects on all the organ systems of the body by controlling the rate at which they ...
... The thyroid gland lies in the neck at the front of the windpipe and produces a hormone called thyroxine. Thyroxine is a chemical secreted into the blood that controls the function of other organs. Thyroxine has major effects on all the organ systems of the body by controlling the rate at which they ...
introduction to the biochemistry of hormones and their recptors
... Arachadonic acid is the most abundant precursor for these hormones. Stores of arachadonic acid are present in membrane lipids and released through the action of various lipases. A great variety of cells produce prostaglandins , including those of the liver, kidneys, heart, lungs, thymus gland, pancr ...
... Arachadonic acid is the most abundant precursor for these hormones. Stores of arachadonic acid are present in membrane lipids and released through the action of various lipases. A great variety of cells produce prostaglandins , including those of the liver, kidneys, heart, lungs, thymus gland, pancr ...
Hipofizer hastal*klar
... If abnormal growth patterns are seen, and GHD is strongly suspected, further provocative testing of GH secretion is typically performed under the supervision of a pediatric endocrinologist. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia is the most reliable provocative test for GHD and has the added advantage of acc ...
... If abnormal growth patterns are seen, and GHD is strongly suspected, further provocative testing of GH secretion is typically performed under the supervision of a pediatric endocrinologist. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia is the most reliable provocative test for GHD and has the added advantage of acc ...
Endocrine System - Bellefonte Area School District
... development of Type II diabetes. With aging, the target cell response time becomes slower, especially in people who might be at risk for this disorder. • The signs and symptoms of endocrine system diseases affect many body systems. In elderly persons, they are frequently subtle and may be harder to ...
... development of Type II diabetes. With aging, the target cell response time becomes slower, especially in people who might be at risk for this disorder. • The signs and symptoms of endocrine system diseases affect many body systems. In elderly persons, they are frequently subtle and may be harder to ...
2,3,4-Anterior Pituitary 12017-02-05 00:361.9 MB
... anterior pituitary by the hypothalamichypophysial-portal system. CRH stimulates the synthesis of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH). ACTH stimulates the synthesis of adrenal steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids (cortisol) released into the systemic circulation exert negative feedback inhibition of CRF ...
... anterior pituitary by the hypothalamichypophysial-portal system. CRH stimulates the synthesis of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH). ACTH stimulates the synthesis of adrenal steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids (cortisol) released into the systemic circulation exert negative feedback inhibition of CRF ...
Assessment of the Endocrine System
... When the hormone concentration rises, further production of that hormone is inhibited When the hormone concentration falls, the rate of production of that hormone increases ...
... When the hormone concentration rises, further production of that hormone is inhibited When the hormone concentration falls, the rate of production of that hormone increases ...
Hormones - HCC Learning Web
... – Secreted by zona fasciculata and zona reticulata in response to ACTH – Regulate metabolism of glucose and other fuels – Cortisol and corticosterone stimulate fat and protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis (glucose from amino acids and fatty acids) and release of fatty acids and glucose into blood ...
... – Secreted by zona fasciculata and zona reticulata in response to ACTH – Regulate metabolism of glucose and other fuels – Cortisol and corticosterone stimulate fat and protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis (glucose from amino acids and fatty acids) and release of fatty acids and glucose into blood ...
Regents Biology
... Fertilization is the fusion of a sperm and an egg to form a zygote, the single cell from which all cells of the human body are derived. When an egg is fertilized, the remarkable process of human development begins. 1.If two eggs are released during ovulation, each can be fertilized by a sperm. What ...
... Fertilization is the fusion of a sperm and an egg to form a zygote, the single cell from which all cells of the human body are derived. When an egg is fertilized, the remarkable process of human development begins. 1.If two eggs are released during ovulation, each can be fertilized by a sperm. What ...
Hypothyroidism
... Hypothyroidism is more likely to develop in women and in those individuals where a close family member has an autoimmune disease. ...
... Hypothyroidism is more likely to develop in women and in those individuals where a close family member has an autoimmune disease. ...
Hormonal Control
... In addition to other homeostatic mechanisms of the body, one of the two major regulatory systems of the body is the endocrine system (the other being the nervous system). This system comprises the endocrine glands that release their secretions, called hormones, into the blood stream which transports ...
... In addition to other homeostatic mechanisms of the body, one of the two major regulatory systems of the body is the endocrine system (the other being the nervous system). This system comprises the endocrine glands that release their secretions, called hormones, into the blood stream which transports ...
The Endocrine System
... – Permissiveness: one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present – Synergism: more than one hormone produces same effects on target cell, causing amplification – Antagonism: one or more hormones oppose(s) action of another hormone ...
... – Permissiveness: one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present – Synergism: more than one hormone produces same effects on target cell, causing amplification – Antagonism: one or more hormones oppose(s) action of another hormone ...
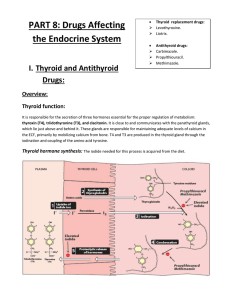
PART 8: Drugs Affecting the Endocrine System Thyroid and
... During pregnancy, treatment for hypothyroidism should continue Fetal growth may be retarded if maternal hypothyroidism is untreated during pregnancy Adjust dosage every 4 weeks to keep TSH at the lower end of the normal range Teach patient to take thyroxin once daily in the morning to decrea ...
... During pregnancy, treatment for hypothyroidism should continue Fetal growth may be retarded if maternal hypothyroidism is untreated during pregnancy Adjust dosage every 4 weeks to keep TSH at the lower end of the normal range Teach patient to take thyroxin once daily in the morning to decrea ...
Human Physiology/The endocrine system
... Antagonistic Hormones Maintaining homeostasis often requires conditions to be limited to a narrow range. When conditions exceed the upper limit of homeostasis, specific action, usually the production of a hormone is triggered. When conditions return to normal, hormone production is discontinued. If ...
... Antagonistic Hormones Maintaining homeostasis often requires conditions to be limited to a narrow range. When conditions exceed the upper limit of homeostasis, specific action, usually the production of a hormone is triggered. When conditions return to normal, hormone production is discontinued. If ...
Anabolic steroid induced hypogonadism treated with human
... use of human chorionic gonadotropin should be considered in prolonged hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism due to anabolic steroid abuse. Keywords: anabolic steroids; drug abuse; hypogonadism; human chorionic gonadotropin ...
... use of human chorionic gonadotropin should be considered in prolonged hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism due to anabolic steroid abuse. Keywords: anabolic steroids; drug abuse; hypogonadism; human chorionic gonadotropin ...
Thyroid hormones
... • Negative feedback is most common: for example, LH from pituitary stimulates the testis to produce testosterone which in turn feeds back and inhibits LH secretion. The hormone (or one of its products) has a negative feedback effect to prevent oversecretion of the hormone or overactivity at the targ ...
... • Negative feedback is most common: for example, LH from pituitary stimulates the testis to produce testosterone which in turn feeds back and inhibits LH secretion. The hormone (or one of its products) has a negative feedback effect to prevent oversecretion of the hormone or overactivity at the targ ...
Hormones general characteristics, classification
... Hormonoids (tissue hormones) – compounds that are produced not in glands but in different tissues and regulate metabolic processes on the local level, but some of them (serotonin, acetylcholine) enters blood and regulate processes on the organism level. ...
... Hormonoids (tissue hormones) – compounds that are produced not in glands but in different tissues and regulate metabolic processes on the local level, but some of them (serotonin, acetylcholine) enters blood and regulate processes on the organism level. ...
SELECTED CASES
... Introduction: Cushing’ syndrome (CS) is extremely rare in pregnancy with fewer than 150 cases in the world literature as individual cases and small case series. The clinical diagnosis of CS may be missed because of the overlapping features of weight gain, hypertension, fatigue, hyperglycemia, and em ...
... Introduction: Cushing’ syndrome (CS) is extremely rare in pregnancy with fewer than 150 cases in the world literature as individual cases and small case series. The clinical diagnosis of CS may be missed because of the overlapping features of weight gain, hypertension, fatigue, hyperglycemia, and em ...
Lect E1 - Endocrine intro 1
... why puberty initiates both growth and its cessation effects of abnormal GH before and after puberty common synthesis of adrenal & gonadal steriods hypothalamo-pituitary axis function major role of pineal gland in endocrine regulation normal range of plasma free calcium conc hormonal regulation of ca ...
... why puberty initiates both growth and its cessation effects of abnormal GH before and after puberty common synthesis of adrenal & gonadal steriods hypothalamo-pituitary axis function major role of pineal gland in endocrine regulation normal range of plasma free calcium conc hormonal regulation of ca ...
Document
... too little or no insulin, resulting in high blood glucose levels. Symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, thirst, and frequent urination. ...
... too little or no insulin, resulting in high blood glucose levels. Symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, thirst, and frequent urination. ...