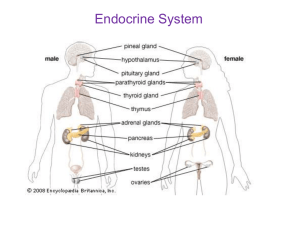
Lab 2
... • Acinar cells produce an enzyme-rich juice used for digestion (exocrine product) • Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) produce hormones (endocrine products) • The islets contain two major cell types: – Alpha () cells that produce glucagon – Beta () cells that produce insulin ...
... • Acinar cells produce an enzyme-rich juice used for digestion (exocrine product) • Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) produce hormones (endocrine products) • The islets contain two major cell types: – Alpha () cells that produce glucagon – Beta () cells that produce insulin ...
Chapter 11 The Endocrine System - Linn
... decrease in the number of lymphocytes and plasma cells and therefore a decrease in the amount of antibodies formed • Secretion of glucocorticoid quickly increases when the body is thrown into a condition of stress; high blood concentration of glucocorticoids, in turn, brings about many other stress ...
... decrease in the number of lymphocytes and plasma cells and therefore a decrease in the amount of antibodies formed • Secretion of glucocorticoid quickly increases when the body is thrown into a condition of stress; high blood concentration of glucocorticoids, in turn, brings about many other stress ...
An Introduction to the Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonadal Axis
... the proliferation phase to prepare for ovulation, the secretory phase after ovulation, and menstruation when conception does not occur. HPG axis activation in both males and females during puberty also causes individuals to gain secondary sex characteristics. HPG axis activation and deactivation als ...
... the proliferation phase to prepare for ovulation, the secretory phase after ovulation, and menstruation when conception does not occur. HPG axis activation in both males and females during puberty also causes individuals to gain secondary sex characteristics. HPG axis activation and deactivation als ...
Document
... – Positive Feedback, Levels will continue to escalate • Keeping up with the Jones’. ...
... – Positive Feedback, Levels will continue to escalate • Keeping up with the Jones’. ...
Medical Terminology: Language for Healthcare Nina Thierer Lisa Breitbard
... •Usually caused by a tumor •Symptoms may include the ...
... •Usually caused by a tumor •Symptoms may include the ...
Incomplete A-Z list of lurpon / leuprolide `Off
... effects in animal and man; effect on embryos (”accelerated development”); endometrial preparation for transfer of frozen-thawed pre-embryos in patients with anovulatory or irregular cycles; effects on follicular fluid hormone composition at oocyte retrieval for IVF; effect on hair growth and hormone ...
... effects in animal and man; effect on embryos (”accelerated development”); endometrial preparation for transfer of frozen-thawed pre-embryos in patients with anovulatory or irregular cycles; effects on follicular fluid hormone composition at oocyte retrieval for IVF; effect on hair growth and hormone ...
Slide 1
... – Glucagon: increases blood glucose (hyperglycemic) – Insulin: decreases blood glucose, only hormone that is hypoglycemic, absolutely necessary is only way that glucose can get to cells to be used – How insulin works ...
... – Glucagon: increases blood glucose (hyperglycemic) – Insulin: decreases blood glucose, only hormone that is hypoglycemic, absolutely necessary is only way that glucose can get to cells to be used – How insulin works ...
The Endocrine System
... •Symptoms may include hirsuitism(hairy female), and virilism(masculine features) ...
... •Symptoms may include hirsuitism(hairy female), and virilism(masculine features) ...
GRS8EndocrineMetabolicDisorders
... • In older adults in US, usually due to Graves disease • Triples the risk of developing AF within 10 years, and present in 13%–30% of older people with AF • Causes secondary osteoporosis and should be suspected in patients with low bone mineral density • Apathetic thyrotoxicosis Characterized by d ...
... • In older adults in US, usually due to Graves disease • Triples the risk of developing AF within 10 years, and present in 13%–30% of older people with AF • Causes secondary osteoporosis and should be suspected in patients with low bone mineral density • Apathetic thyrotoxicosis Characterized by d ...
Ectopic_Hormone_Syndromes
... y/o F presents with 20 lb weight loss over last 2 months, new onset hyperglycemia, HTN, and hypokalemia Pt is markedly hyperpigmented and cachectic ...
... y/o F presents with 20 lb weight loss over last 2 months, new onset hyperglycemia, HTN, and hypokalemia Pt is markedly hyperpigmented and cachectic ...
HORMONES
... human growth hormone—HGH This is produced by the pituitary gland and converted by the liver into a protein called somatomedin-C or IGF-1 (insulinlike growth factor-one). It is IGF-1 that is responsible for most of growth hormone functions in the body. Growth hormone contributes to ongoing tissue rep ...
... human growth hormone—HGH This is produced by the pituitary gland and converted by the liver into a protein called somatomedin-C or IGF-1 (insulinlike growth factor-one). It is IGF-1 that is responsible for most of growth hormone functions in the body. Growth hormone contributes to ongoing tissue rep ...
The Endocrine System
... • The binding of the hormone activates enzymes on the inner surface of the cell membrane • These enzymes release secondary messengers such as calcium ions, nucleotides, and fatty acids. • Another very common type of secondary messenger is cAMP which is produced from ATP • Secondary messengers activa ...
... • The binding of the hormone activates enzymes on the inner surface of the cell membrane • These enzymes release secondary messengers such as calcium ions, nucleotides, and fatty acids. • Another very common type of secondary messenger is cAMP which is produced from ATP • Secondary messengers activa ...
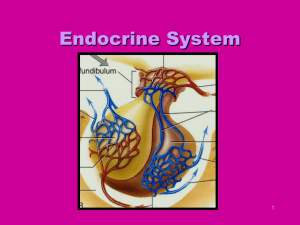
Endocrine System
... The hypothalamus controls the endocrine system. The hypothalamus is located in the brain. The hypothalamus detects when the body needs a particular hormone. The hypothalamus then stimulates the pituitary gland to bring about the production of the necessary hormone. When the hormone levels in the bod ...
... The hypothalamus controls the endocrine system. The hypothalamus is located in the brain. The hypothalamus detects when the body needs a particular hormone. The hypothalamus then stimulates the pituitary gland to bring about the production of the necessary hormone. When the hormone levels in the bod ...
Shawn Smith`s notes 12-01
... o For child birth Causes milk ejection from lactating women Tropic Hormones Control release of other hormones o (ex: Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) triggers release of thyroid hormone from thyroid gland) Allow for multiple steps o Aids in regulation (tine tuning) Anterior Pituitary TSH (t ...
... o For child birth Causes milk ejection from lactating women Tropic Hormones Control release of other hormones o (ex: Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) triggers release of thyroid hormone from thyroid gland) Allow for multiple steps o Aids in regulation (tine tuning) Anterior Pituitary TSH (t ...
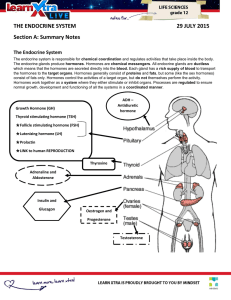
Get Notes - Mindset Learn
... Undersecretion: lack of secondary sexual characteristics and lack of healthy sperm production. Low libido in males ...
... Undersecretion: lack of secondary sexual characteristics and lack of healthy sperm production. Low libido in males ...
8Aldosterone 8Na + secretion 8 H 2 O reabsorption9 urine volume
... • Addison’s disease - hyposecretion of glucocorticoids due to lack of response to ACTH; symptoms include weight loss, weakness, hypoglycemia, skin bronzing due to increased activity of melanocytes ...
... • Addison’s disease - hyposecretion of glucocorticoids due to lack of response to ACTH; symptoms include weight loss, weakness, hypoglycemia, skin bronzing due to increased activity of melanocytes ...
Osmoregulation and excretion (kidney function): Two basic ideas: 1
... - If salt concentration rises, then more water is needed in the body. So ADH is released. ADH increases the permeability of the collecting duct and so more water is reabsorbed. - If the salt concentration drops, then the opposite happens. ADH is not released, and collecting duct remains impermeable ...
... - If salt concentration rises, then more water is needed in the body. So ADH is released. ADH increases the permeability of the collecting duct and so more water is reabsorbed. - If the salt concentration drops, then the opposite happens. ADH is not released, and collecting duct remains impermeable ...
Lecture 25 - The Endocrine System
... homeostatic functions including water balance People with adrenal insufficiency: these stresses can cause hypotension, shock and death: must give glucocorticoids, eg for surgery or if have infection, etc.18 ...
... homeostatic functions including water balance People with adrenal insufficiency: these stresses can cause hypotension, shock and death: must give glucocorticoids, eg for surgery or if have infection, etc.18 ...
What is the median eminence? The median eminence is the nucleus
... 52. How does androstenedione have a testosterone effect in women without having the overall masculinizing effect of testosterone? a. Once androstenedione enters into its target tissue it is converted to testosterone. This way, the testosterone acts only on the specific tissue it is meant for and doe ...
... 52. How does androstenedione have a testosterone effect in women without having the overall masculinizing effect of testosterone? a. Once androstenedione enters into its target tissue it is converted to testosterone. This way, the testosterone acts only on the specific tissue it is meant for and doe ...
Packet18 - SFP Online!
... They bond to specific receptor molecules (proteins) found on the cell membrane—this causes a change inside the target cell Some hormones pass right through the cell membrane Only small amounts of hormones are usually needed to produce the required effect (D) FEEDBACK MECHANISMS ...
... They bond to specific receptor molecules (proteins) found on the cell membrane—this causes a change inside the target cell Some hormones pass right through the cell membrane Only small amounts of hormones are usually needed to produce the required effect (D) FEEDBACK MECHANISMS ...