
1) What is the median eminence? a) The median eminence is the
... b) it acts at the anterior pituitary to inhibit the production and release of FSH 31) What does Dopamine do? a) inhibits the production and release of prolactin 32) What does PSH do? a) stimulates the production and release of prolactin 33) What RH releases two tropic hormones? a) GnRH releases both ...
... b) it acts at the anterior pituitary to inhibit the production and release of FSH 31) What does Dopamine do? a) inhibits the production and release of prolactin 32) What does PSH do? a) stimulates the production and release of prolactin 33) What RH releases two tropic hormones? a) GnRH releases both ...
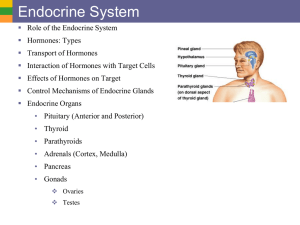
The Endocrine System
... glucose in the liver which is controlled by the concentration of glucose and amino acids in blood and somatostatin. 3. Other islet cells secrete somatostatin (also secreted by hypothalamus) that helps regulate the rate at which glucose and other nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream and may co ...
... glucose in the liver which is controlled by the concentration of glucose and amino acids in blood and somatostatin. 3. Other islet cells secrete somatostatin (also secreted by hypothalamus) that helps regulate the rate at which glucose and other nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream and may co ...
Lippincott`s Illustrated Reviews: Pharmacology
... This synthetic glucocorticoid suppresses cortisol release in individuals with pituitary-dependent Cushing syndrome, but it does not suppress glucocorticoid release from adrenal tumors. [Note: Chronic treatment with high doses of glucocorticoid is a frequent cause of iatrogenic Cushing syndrome.] 4. ...
... This synthetic glucocorticoid suppresses cortisol release in individuals with pituitary-dependent Cushing syndrome, but it does not suppress glucocorticoid release from adrenal tumors. [Note: Chronic treatment with high doses of glucocorticoid is a frequent cause of iatrogenic Cushing syndrome.] 4. ...
Chapter 51 The Endocrine System
... b. Hypothyroidism – under activity. Symptoms include lethargy, weight gain, and low heart rate and body temperature, cretinism (form of mental retardation), and goiter (a swelling of the thyroid gland because of lack of iodine). 3. Adrenal Gland – located above each kidney. The medulla and the corte ...
... b. Hypothyroidism – under activity. Symptoms include lethargy, weight gain, and low heart rate and body temperature, cretinism (form of mental retardation), and goiter (a swelling of the thyroid gland because of lack of iodine). 3. Adrenal Gland – located above each kidney. The medulla and the corte ...
03-Endocrine-Review
... 40. What are the manifestations of prolactin excess? 41. What is another name for antidiuretic hormone? What is its action in the body? 42. What are the names for too much and too little antidiuretic hormone? ...
... 40. What are the manifestations of prolactin excess? 41. What is another name for antidiuretic hormone? What is its action in the body? 42. What are the names for too much and too little antidiuretic hormone? ...
Chapter 5
... • Intersex (pseudohermaphrodite) biologically a person’s gender is ambiguous. • Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) - also called adrenogenital syndrome; normally-developed ovaries begin to function abnormally later in the course of prenatal development. ...
... • Intersex (pseudohermaphrodite) biologically a person’s gender is ambiguous. • Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) - also called adrenogenital syndrome; normally-developed ovaries begin to function abnormally later in the course of prenatal development. ...
a11 Endocrine System
... Sex hormones (steroids) • Produced in the inner layer of the adrenal cortex • Androgens (male) and some estrogen (female) -- both produced regardless of gender • Hypersecretion causes masculinization (regardless of gender) - most obvious effects in females • Hyposecretion causes Addison's disease ...
... Sex hormones (steroids) • Produced in the inner layer of the adrenal cortex • Androgens (male) and some estrogen (female) -- both produced regardless of gender • Hypersecretion causes masculinization (regardless of gender) - most obvious effects in females • Hyposecretion causes Addison's disease ...
Practical Strategies for Management of the Pseudo
... association with TSH levels that are low, normal or slightly elevated. Primary hypothyroidism is most often due to autoimmune lymphocytic thyroiditis, surgery or radiation therapy. Hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis physiology is highly complex, involving hypothalamic and pituitary regulation of t ...
... association with TSH levels that are low, normal or slightly elevated. Primary hypothyroidism is most often due to autoimmune lymphocytic thyroiditis, surgery or radiation therapy. Hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis physiology is highly complex, involving hypothalamic and pituitary regulation of t ...
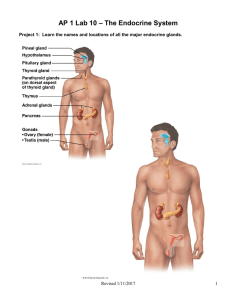
AP 1 Lab 10 – The Endocrine System
... Is called the "Master Gland" because it releases more Hs than any other and affects many other glands. _____________ Organ found adjacent to first part of the small intestine containing endocrine glands for control of blood sugar levels. _____________ This type of diabetes is caused by target tissue ...
... Is called the "Master Gland" because it releases more Hs than any other and affects many other glands. _____________ Organ found adjacent to first part of the small intestine containing endocrine glands for control of blood sugar levels. _____________ This type of diabetes is caused by target tissue ...
Anatomy of the Endocrine System
... Acromegaly is the Greek word for "extremities" and "enlargement." When the pituitary gland produces excess growth hormones, this results in excessive growth -- called acromegaly. The excessive growth occurs first in the hands and feet, as soft tissue begins to swell. Acromegaly affects mostly middle ...
... Acromegaly is the Greek word for "extremities" and "enlargement." When the pituitary gland produces excess growth hormones, this results in excessive growth -- called acromegaly. The excessive growth occurs first in the hands and feet, as soft tissue begins to swell. Acromegaly affects mostly middle ...
Endocrine PP - Laura Banks
... • Step 3: New hormones are released by the adrenal glands into the body AS WELL AS cutting off the hormone production in the pituitary glands • This allows the hypothalamus to start producing hormones again ...
... • Step 3: New hormones are released by the adrenal glands into the body AS WELL AS cutting off the hormone production in the pituitary glands • This allows the hypothalamus to start producing hormones again ...
Hormone - Denton ISD
... therefore their products are secreted into the blood stream for transport. ...
... therefore their products are secreted into the blood stream for transport. ...
Dec 21, 2010 Voice 114
... expressed as follicular development, oocyte maturation and ovulation. A range of peptide and steroid hormones regulate normal ovarian function, key members include the gonadotrophins (FSH & LH) and the ovarian steroids (oestradiol & progesterone). Other known factors, such as Inhibin B and AMH are a ...
... expressed as follicular development, oocyte maturation and ovulation. A range of peptide and steroid hormones regulate normal ovarian function, key members include the gonadotrophins (FSH & LH) and the ovarian steroids (oestradiol & progesterone). Other known factors, such as Inhibin B and AMH are a ...
Endocrine System Taken from kidshealth.org/.../body_basics
... The gonads are the main source of sex hormones. In males, they are located in the scrotum. Male gonads, or testes, secrete hormones called androgens, the most important of which is testosterone. These hormones regulate body changes associated with sexual development, including enlargement of the pen ...
... The gonads are the main source of sex hormones. In males, they are located in the scrotum. Male gonads, or testes, secrete hormones called androgens, the most important of which is testosterone. These hormones regulate body changes associated with sexual development, including enlargement of the pen ...
Endocrine System Facts Review
... What is most likely present in high amounts in an individual who has been fasting for 24 hours? A substance that is secreted directly into the bloodstream and that produces a specific effect on a particular tissue. A type of cell that contains receptors for a certain type of hormone. Endocrine contr ...
... What is most likely present in high amounts in an individual who has been fasting for 24 hours? A substance that is secreted directly into the bloodstream and that produces a specific effect on a particular tissue. A type of cell that contains receptors for a certain type of hormone. Endocrine contr ...
Orientation to the Human Body
... diabetic neuropathy – nerve damage from impoverished blood flow can lead to erectile dysfunction, incontinence, poor wound healing, and loss of sensation from area ...
... diabetic neuropathy – nerve damage from impoverished blood flow can lead to erectile dysfunction, incontinence, poor wound healing, and loss of sensation from area ...
chapter # 29 > human anatomy - the endocrine system
... 2. WHAT IS THE SCIENTIFIC NAME OF THE LITTLE MASTER GLAND IN US JUST BELOW OUR BRAIN ? 3. THE _____________________ GLANDS PRODUCE THE HORMONES CORTISOL , TO HELP US WAKE UP , AND ADRENALINE TO HELP US MANAGE STRESS 4. THE ______________________ GLAND HELPS US PROCESS _____________ AND BURN ________ ...
... 2. WHAT IS THE SCIENTIFIC NAME OF THE LITTLE MASTER GLAND IN US JUST BELOW OUR BRAIN ? 3. THE _____________________ GLANDS PRODUCE THE HORMONES CORTISOL , TO HELP US WAKE UP , AND ADRENALINE TO HELP US MANAGE STRESS 4. THE ______________________ GLAND HELPS US PROCESS _____________ AND BURN ________ ...
4-Amenorrhea [Dr.Mandeel]. - King Saud University Medical Student
... Each year of athelitic training before menarche delayed menarche 5 M ...
... Each year of athelitic training before menarche delayed menarche 5 M ...





















![4-Amenorrhea [Dr.Mandeel]. - King Saud University Medical Student](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008318431_1-2f431d9b56a0e06930dc30cd21126053-300x300.png)