Thyroid Hormone Treatment FAQ - American Thyroid Association
... Desiccated (dried and powdered) animal thyroid (Armour®), now mainly obtained from pigs, was the most common form of thyroid therapy before the individual active thyroid hormones were discovered. While desiccated thyroid contains both T4 and T3, the balance of T4 and T3 in animals is not the same as ...
... Desiccated (dried and powdered) animal thyroid (Armour®), now mainly obtained from pigs, was the most common form of thyroid therapy before the individual active thyroid hormones were discovered. While desiccated thyroid contains both T4 and T3, the balance of T4 and T3 in animals is not the same as ...
Name Endocrine system Write the letter of the correct match next to
... maintain a steady level of glucose in the blood and keep the body supplied with fuel to produce and maintain stores of energy ...
... maintain a steady level of glucose in the blood and keep the body supplied with fuel to produce and maintain stores of energy ...
IODINE - TRACE ELEMENT
... even in the presence of iodine excess. However, dysfunction of these mechanisms can result in either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism in the setting of sudden iodine excess. Iodine-induced hyperthyroidism has frequently been observed in patients with euthyroid iodinedeficient goitre. It has also be ...
... even in the presence of iodine excess. However, dysfunction of these mechanisms can result in either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism in the setting of sudden iodine excess. Iodine-induced hyperthyroidism has frequently been observed in patients with euthyroid iodinedeficient goitre. It has also be ...
Hashitoxicosis – Three Cases and a Review of the Literature
... normal size and hypoechoic areas occur in a diffuse pattern. In the hyperthyroid phase of Hashimoto thyroiditis – hashitoxicosis – it is necessary to distinguish this picture from Graves’ disease. The differential diagnosis in ultrasound between hashitoxicosis and Graves’ disease is based on the gra ...
... normal size and hypoechoic areas occur in a diffuse pattern. In the hyperthyroid phase of Hashimoto thyroiditis – hashitoxicosis – it is necessary to distinguish this picture from Graves’ disease. The differential diagnosis in ultrasound between hashitoxicosis and Graves’ disease is based on the gra ...
Thyroid Disorders
... In secondary hypothyroidism, further testing with pituitary provocative testing and imaging to rule out microadenoma. In general, evidence of decreased levels of more than one pituitary hormone is indicative of a panhypopituitary problem. ...
... In secondary hypothyroidism, further testing with pituitary provocative testing and imaging to rule out microadenoma. In general, evidence of decreased levels of more than one pituitary hormone is indicative of a panhypopituitary problem. ...
The roles of the different hormones in your body
... conversion of T4 to T3 is important for the body to utilize it. This step of T4 to T3 conversion requires an enzyme and certain nutrients, specifically iodine. If thyroid hormone production is lowered, it means the metabolic rate is reduced and the patient will experience lower energy or fatigue and ...
... conversion of T4 to T3 is important for the body to utilize it. This step of T4 to T3 conversion requires an enzyme and certain nutrients, specifically iodine. If thyroid hormone production is lowered, it means the metabolic rate is reduced and the patient will experience lower energy or fatigue and ...
physiology5
... hormones under the stimulation of the fetal hypothalamus and pituitary gland. This entire axis is required for subsequence normal intrauterine development of the central nervous system and the skeleton. To simplify thyroid hormones are essential for normal development of the central nervous system a ...
... hormones under the stimulation of the fetal hypothalamus and pituitary gland. This entire axis is required for subsequence normal intrauterine development of the central nervous system and the skeleton. To simplify thyroid hormones are essential for normal development of the central nervous system a ...
The Endocrine System
... Hypothyroidism (cretinism in infants) – stunted growth, mental retardation, sluggishness, weight gain in adults Hyperthyroidism (Grave’s disease) - restlessness, weight loss, anxiety; can cause Goiter (enlarged thyroid) Parathyroid Gland ...
... Hypothyroidism (cretinism in infants) – stunted growth, mental retardation, sluggishness, weight gain in adults Hyperthyroidism (Grave’s disease) - restlessness, weight loss, anxiety; can cause Goiter (enlarged thyroid) Parathyroid Gland ...
File
... 9) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) causes all of the following EXCEPT: a) activation of thyroid follicular cells b) increased iodide trapping in thyroid follicles c) increased thyroglobulin synthesis d) increased release of T3/ T4 e) all of above are correct 10) The pancreatic cells that secrete i ...
... 9) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) causes all of the following EXCEPT: a) activation of thyroid follicular cells b) increased iodide trapping in thyroid follicles c) increased thyroglobulin synthesis d) increased release of T3/ T4 e) all of above are correct 10) The pancreatic cells that secrete i ...
Endocrine Study Guide - health sciences at chs
... mellitus / Cushing’s syndrome). 28. Hypothyroidism can be due to a deficiency of iodine. Treatment is to use iodized salt (this is not common in the US since we use iodized salt). Another form of this disease is an autoimmune disease that destroys the thyroid gland from producing thyroxin. Without t ...
... mellitus / Cushing’s syndrome). 28. Hypothyroidism can be due to a deficiency of iodine. Treatment is to use iodized salt (this is not common in the US since we use iodized salt). Another form of this disease is an autoimmune disease that destroys the thyroid gland from producing thyroxin. Without t ...
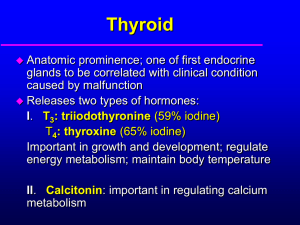
The Thyroid Gland
... Hyperthyroidism – ‘thyrotoxicosis’ restless, anxiety eye problems goitre tachycardia and rapid pulse lose weight despite normal appetite intolerance of heat hot hands ...
... Hyperthyroidism – ‘thyrotoxicosis’ restless, anxiety eye problems goitre tachycardia and rapid pulse lose weight despite normal appetite intolerance of heat hot hands ...
The Thyroid and Low Thyroid Function
... attacked by bacteria, viruses etc, the immune system goes into hyper-drive to fight the infection. In some people the immune system becomes dysfunctional and the body starts to fight itself and attacks its own tissues. This is known as an autoimmune disorder. Graves Disease and Hashimoto’s Disease a ...
... attacked by bacteria, viruses etc, the immune system goes into hyper-drive to fight the infection. In some people the immune system becomes dysfunctional and the body starts to fight itself and attacks its own tissues. This is known as an autoimmune disorder. Graves Disease and Hashimoto’s Disease a ...
Pathology of the thyroid, and parathyroid gland(s)
... Skin: warm, wet, heat intolerance Loss of weight, diomyopatia Heart: tachycardy, cardiomegaly, arrhytmia (atrial fibrillation), CHF- TDC (congestive heart failure, thyreotoxic dilatative cardiomyopaty) ...
... Skin: warm, wet, heat intolerance Loss of weight, diomyopatia Heart: tachycardy, cardiomegaly, arrhytmia (atrial fibrillation), CHF- TDC (congestive heart failure, thyreotoxic dilatative cardiomyopaty) ...
Hormonal Control of Growth in Animals
... the thyroid gland & produces thyroxine (another hormone!) Thyroxine regulates metabolic processes in the body. drop in metabolic rate Lack of TSH lack of thyroxine ...
... the thyroid gland & produces thyroxine (another hormone!) Thyroxine regulates metabolic processes in the body. drop in metabolic rate Lack of TSH lack of thyroxine ...
The Endocrine system - Aurora City Schools
... Produces hormones that regulate metabolism Located in the front of the throat, shaped like a butterfly Produces Thyroxine, which regulates the way cells release energy from nutrients ...
... Produces hormones that regulate metabolism Located in the front of the throat, shaped like a butterfly Produces Thyroxine, which regulates the way cells release energy from nutrients ...
Methods - Shantou University
... Ipodate and Iopanoic Acid -Inhibit conversion T4 3 T in liver, kidney, pituitary and brain -Used in adjunct therapy ...
... Ipodate and Iopanoic Acid -Inhibit conversion T4 3 T in liver, kidney, pituitary and brain -Used in adjunct therapy ...
Thyroid Medications
... o Diminished appetite (but weight gain due to decreased metabolism) Cretinism: hypothyroidism present from birth, resulting in dwarfism and mental retardation o Most common cause is failure of development of thyroid gland o Thyroid hormone actions on brain development are most significant in the wee ...
... o Diminished appetite (but weight gain due to decreased metabolism) Cretinism: hypothyroidism present from birth, resulting in dwarfism and mental retardation o Most common cause is failure of development of thyroid gland o Thyroid hormone actions on brain development are most significant in the wee ...
Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism and
... intolerance, generalized aches and pains, weakness, tiredness and sleepiness. Some people appear confused, forgetful or even demented. When very severe hypothyroidism can cause anemia, low body temperature, heart failure, and life threatening myxedema coma. Treatment Hypothyroidism is an easily trea ...
... intolerance, generalized aches and pains, weakness, tiredness and sleepiness. Some people appear confused, forgetful or even demented. When very severe hypothyroidism can cause anemia, low body temperature, heart failure, and life threatening myxedema coma. Treatment Hypothyroidism is an easily trea ...
Radioiodine removal effect of parotid gland massage
... • From February 2012 to July 2012 • PG massages and salivary gland scans were performed who underwent I-123 whole body scan. • Inclusion criteria ▫ Total thyroidectomy due to thyroid cancer ▫ Followed by 3.7-5.6 GBq of radioiodine ablation ...
... • From February 2012 to July 2012 • PG massages and salivary gland scans were performed who underwent I-123 whole body scan. • Inclusion criteria ▫ Total thyroidectomy due to thyroid cancer ▫ Followed by 3.7-5.6 GBq of radioiodine ablation ...
Hypothyroidism
... • TPO more sensitive and specific • Ultrasound not a part of routine screening ...
... • TPO more sensitive and specific • Ultrasound not a part of routine screening ...
Iodine deficiency disorders
... Neonatal hypothyroidism Endemic mental retardation Increased susceptibility of the thyroid gland to nuclear radiation Child and Goiter adolescent (Subclinical) hypothyroidism Impaired mental function Retarded physical development Increased susceptibility of the thyroid gland to nuclear radiation ...
... Neonatal hypothyroidism Endemic mental retardation Increased susceptibility of the thyroid gland to nuclear radiation Child and Goiter adolescent (Subclinical) hypothyroidism Impaired mental function Retarded physical development Increased susceptibility of the thyroid gland to nuclear radiation ...
Text Version
... Initially: Increased thyroid hormone release leads to hyperthyroidism, but RAIU is low and synthesis is low Next: Hormone depletion leads to a period of hypothyroidism Finally: Most will recover and become euthyroid in 2-6 months RX: -blockers, NSAID, ASA, steroids ...
... Initially: Increased thyroid hormone release leads to hyperthyroidism, but RAIU is low and synthesis is low Next: Hormone depletion leads to a period of hypothyroidism Finally: Most will recover and become euthyroid in 2-6 months RX: -blockers, NSAID, ASA, steroids ...
1 High level of Ca 2+ in blood stimulates thyroid gland parafollicular
... increase loss of phosphate (HPO4) -2 in urine promote formation of calcitriol (vitamin D3) by kidney which increases absorption of Ca+2, HPO4 and Mg+2 by intestinal tract ...
... increase loss of phosphate (HPO4) -2 in urine promote formation of calcitriol (vitamin D3) by kidney which increases absorption of Ca+2, HPO4 and Mg+2 by intestinal tract ...
Ch 36 Endocrine System
... Thyroxine Deficiency (Hypothryroidism) Thyroxine secretion is below normal. Causes cretinism in childhood — poor growth and poor brain development. Causes myxoedema in adults — fatigue, low energy, reduced resistance to disease. goitre. A severe lack of iodine in the diet can cause hypothyroidism. C ...
... Thyroxine Deficiency (Hypothryroidism) Thyroxine secretion is below normal. Causes cretinism in childhood — poor growth and poor brain development. Causes myxoedema in adults — fatigue, low energy, reduced resistance to disease. goitre. A severe lack of iodine in the diet can cause hypothyroidism. C ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.