Thyroid Glossary - YOUR THYROID And YOU
... or shins. This condition is associated with Graves' disease. Primary Amenorrhoea - The inability to menstruate, caused by a failure of sexual maturation and function. Prognosis - The probable outcome or course of a disease; the chance of recovery. Progression - Increase in the size of a tumor (such ...
... or shins. This condition is associated with Graves' disease. Primary Amenorrhoea - The inability to menstruate, caused by a failure of sexual maturation and function. Prognosis - The probable outcome or course of a disease; the chance of recovery. Progression - Increase in the size of a tumor (such ...
Nervous System Practice
... b) It is stored and released by the posterior pituitary gland. c) It keeps excessive amounts of water from being lost in the urine. d) All of the above. ...
... b) It is stored and released by the posterior pituitary gland. c) It keeps excessive amounts of water from being lost in the urine. d) All of the above. ...
Pharyngeal Apparatus
... upward from the isthmus in about 50% of people • The pyramidal lobe and the associated smooth muscle represent a persistent part of the distal end of the thyroglossal duct ...
... upward from the isthmus in about 50% of people • The pyramidal lobe and the associated smooth muscle represent a persistent part of the distal end of the thyroglossal duct ...
39_Autoimmune diseases_LA
... OF THYROID HORMONES The formation of autoantibodies driven by a CD4+Th2 response ...
... OF THYROID HORMONES The formation of autoantibodies driven by a CD4+Th2 response ...
Thyroid Profile
... (February, 2000), millions more may be undiagnosed for thyroid conditions. Hypothyroidism is estimated to affect up to 5% of the population with women at greatest risk, developing thyroid problems seven times more often than men, particularly during menopausal years; approximately 26% of women in or ...
... (February, 2000), millions more may be undiagnosed for thyroid conditions. Hypothyroidism is estimated to affect up to 5% of the population with women at greatest risk, developing thyroid problems seven times more often than men, particularly during menopausal years; approximately 26% of women in or ...
What is the Endocrine System?
... • thyroid gland secreted adequate hormones • pituitary gland senses the normal levels • adjusts thyrotropin release ...
... • thyroid gland secreted adequate hormones • pituitary gland senses the normal levels • adjusts thyrotropin release ...
MCB 135K Discussion
... Alt erat ion in insulin recept ors and t heir inte rna lizat ion in t arget t issues. Decreased num ber of glucose t ran spor t er units in t arget cells. Alt erat ions in act iviti es of cellular enzymes involved in po st -recept or cellular ...
... Alt erat ion in insulin recept ors and t heir inte rna lizat ion in t arget t issues. Decreased num ber of glucose t ran spor t er units in t arget cells. Alt erat ions in act iviti es of cellular enzymes involved in po st -recept or cellular ...
Pharyngeal Apparatus
... upward from the isthmus in about 50% of people • The pyramidal lobe and the associated smooth muscle represent a persistent part of the distal end of the thyroglossal duct ...
... upward from the isthmus in about 50% of people • The pyramidal lobe and the associated smooth muscle represent a persistent part of the distal end of the thyroglossal duct ...
MD0583 2-1 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 2 Diseases and
... Simmond's disease. Signs and symptoms include emaciation (extreme thinness), asthenia (severe weakness or loss of strength), lowered metabolic rate, low temperature, and low blood pressure. The cause of this deficiency in the production of hormones is usually trauma, tumor, or hemorrhage. (2) Treatm ...
... Simmond's disease. Signs and symptoms include emaciation (extreme thinness), asthenia (severe weakness or loss of strength), lowered metabolic rate, low temperature, and low blood pressure. The cause of this deficiency in the production of hormones is usually trauma, tumor, or hemorrhage. (2) Treatm ...
Endocrine Nuclear Medicine
... • Thyroid hormone or TSH secreting tumour eg some ovarian • Pituitary gland malfunction ...
... • Thyroid hormone or TSH secreting tumour eg some ovarian • Pituitary gland malfunction ...
Endocrinology - (Chemical signals in animals)
... Osmoreg.:Atrial natriuretic peptide • Induces Na+ and water excretion • Released from the heart when plasma volume is high • Peptide hormone • Acts on the kidney to increase Na+ & water excretion, mechanisms not well understood • Also act as antagonist to vasopressin and aldosterone ...
... Osmoreg.:Atrial natriuretic peptide • Induces Na+ and water excretion • Released from the heart when plasma volume is high • Peptide hormone • Acts on the kidney to increase Na+ & water excretion, mechanisms not well understood • Also act as antagonist to vasopressin and aldosterone ...
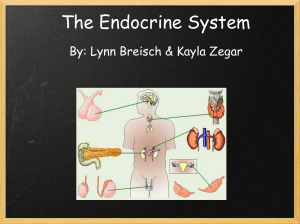
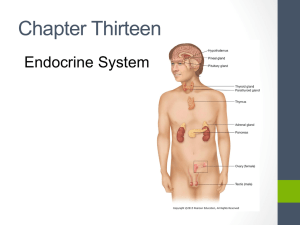
The Endocrine System
... • Made up of its glands and hormones • The glands are called ductless • The release hormones directly into the blood stream ...
... • Made up of its glands and hormones • The glands are called ductless • The release hormones directly into the blood stream ...
File
... • With diabetes mellitus, either your body doesn't make enough insulin, it can't use the insulin it does produce, or a combination of both. ...
... • With diabetes mellitus, either your body doesn't make enough insulin, it can't use the insulin it does produce, or a combination of both. ...
canine autoimmune mediated disease `awareness guidelines`
... Antibodies are produced that result in the invasion and destruction of thyroid tissue, causing a reduction in thyroid function. Symptoms include weight gain, lethargy, exercise intolerance, hair loss, mottled coat, dry flaky cool skin. Your Vet should conduct a complete blood serum thyroid panel (T3 ...
... Antibodies are produced that result in the invasion and destruction of thyroid tissue, causing a reduction in thyroid function. Symptoms include weight gain, lethargy, exercise intolerance, hair loss, mottled coat, dry flaky cool skin. Your Vet should conduct a complete blood serum thyroid panel (T3 ...
Endocrine System Lecture
... bb. Lack of sexual development cc. Mental development is normal (4) If diagnosed early, it can be treated with injections of somatotropic hormone for 5 or more years until long bone growth is complete D. Thyroid gland 1. Synthesizes hormones that regulate body’s metabolism and control the level of c ...
... bb. Lack of sexual development cc. Mental development is normal (4) If diagnosed early, it can be treated with injections of somatotropic hormone for 5 or more years until long bone growth is complete D. Thyroid gland 1. Synthesizes hormones that regulate body’s metabolism and control the level of c ...
The Master Gland/Pituitary Endocrine glands and hormones
... turgor** (normal elasticity in skin) ...
... turgor** (normal elasticity in skin) ...
Thyroid Metabolic Hormones
... hyperplastic glands secretion 5-15x TSH decreased to 0 thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI) bind with the same membrane receptors that bind TSH (lasting for as long as 12 hours) an autoimmune disease result from a adenoma – remainder inhibited ...
... hyperplastic glands secretion 5-15x TSH decreased to 0 thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI) bind with the same membrane receptors that bind TSH (lasting for as long as 12 hours) an autoimmune disease result from a adenoma – remainder inhibited ...
Endocrine Review
... • A 15 year old boy who still displays all the physical characteristics of boys 4-5 years younger than him and has not begun to show any developmental changes indicating he is entering manhood. • Hormone(s): • Gland where produced: ...
... • A 15 year old boy who still displays all the physical characteristics of boys 4-5 years younger than him and has not begun to show any developmental changes indicating he is entering manhood. • Hormone(s): • Gland where produced: ...
Autoimmune Endocrinopathies
... Graves disease • The hyperthyroidism is caused by caused by autoantibodies that bind to and stimulate the thyrotropin (TSH) receptor on the surface of thyroid follicular cells • The pathogenesis of ophthalmopathy and dermopathy is not known • HLA DR3 increases the risk of developing Graves diseas ...
... Graves disease • The hyperthyroidism is caused by caused by autoantibodies that bind to and stimulate the thyrotropin (TSH) receptor on the surface of thyroid follicular cells • The pathogenesis of ophthalmopathy and dermopathy is not known • HLA DR3 increases the risk of developing Graves diseas ...
BS963 (Autoimmunity) 2011
... cytotoxicity (CDC) and apoptosis have also been implicated. Anti-CD20–mediated B cell depletion prevents interaction with autoreactive T cells and reduces the amount of circulating autoantibodies, although with much slower kinetics. ...
... cytotoxicity (CDC) and apoptosis have also been implicated. Anti-CD20–mediated B cell depletion prevents interaction with autoreactive T cells and reduces the amount of circulating autoantibodies, although with much slower kinetics. ...
Cholinergics/anticholinergics and drugs affecting the endocrine
... Tx depends on cause. May need surgery or radioactive iodine therapy Antithyroid drugs include Propylthioruracil (PTU)and Tapazole (methimazole), and iodine preparations ...
... Tx depends on cause. May need surgery or radioactive iodine therapy Antithyroid drugs include Propylthioruracil (PTU)and Tapazole (methimazole), and iodine preparations ...
Pituitary Gland
... 1.Which cells are target cells for hormone A? Explain why. 2.Which cells are target cells for hormone B? Explain why. ...
... 1.Which cells are target cells for hormone A? Explain why. 2.Which cells are target cells for hormone B? Explain why. ...
Assessment and Management of Patients with Endocrine Disorders
... Each type of thyroiditis is characterized by inflammation, fibrosis, or lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid gland. Characterized by autoimmune damage to the thyroid. May cause thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism, or both ...
... Each type of thyroiditis is characterized by inflammation, fibrosis, or lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid gland. Characterized by autoimmune damage to the thyroid. May cause thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism, or both ...
Graves' disease

Graves' disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter and Flajani-Basedow-Graves disease, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in hyperthyroidism and an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, and weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye problems such as bulging, a condition known as Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25% to 80% of people develop eye problems.The exact cause is unclear; however, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A person is more likely to be affected if they have a family member with the disease. If one twin is affected there is a 30% chance the other twin will also have the disease. The onset of disease may be triggered by stress, infection, or giving birth. Those with other autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to be affected. Smoking increases the risk of disease and may make the eye problems worse. The disorder results from an antibody, called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI), that has a similar effect to thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). These antibodies cause the thyroid gland to produce excess thyroid hormone. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms with blood tests and radioiodine uptake used to confirm the disease. Typically blood tests show a raised T3 and T4, low TSH, increased radioiodine uptake in all areas of the thyroid, and TSI antibodies.There are three treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. Eye problems may require additional treatments.Graves' disease occurs in about 0.5% of people. It occurs about 7.5 times more often in women than men. Often it starts between the ages of forty and sixty. It is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in the United States (about 50% to 80% of cases). The condition is named after Robert Graves who described it in 1835. A number of prior descriptions also exist.