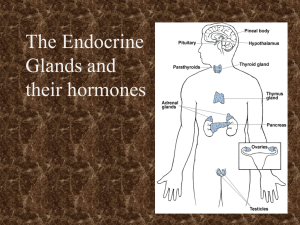
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production ...
... Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 4.) What is the difference between endocrine glands and organs with endocrine cells? a. 5.) When specialized neurons typically found in the brain secrete molecules that diffuse from nerve cell endings into the bloodstream, this process is a part of what signaling pathway? a. neuroendocrine 6.) Give ...
... 4.) What is the difference between endocrine glands and organs with endocrine cells? a. 5.) When specialized neurons typically found in the brain secrete molecules that diffuse from nerve cell endings into the bloodstream, this process is a part of what signaling pathway? a. neuroendocrine 6.) Give ...
Endocrine Problems after Childhood Cancer: Hypopituitarism
... The symptoms depend on the specific hormones that are lacking. One or more of the following hormones may be affected: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) deficiency: The adrenal glands (located on top of the kidneys) are stimulated by ACTH to produce cortisol. If the pituitary gland doesn’t make enou ...
... The symptoms depend on the specific hormones that are lacking. One or more of the following hormones may be affected: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) deficiency: The adrenal glands (located on top of the kidneys) are stimulated by ACTH to produce cortisol. If the pituitary gland doesn’t make enou ...
The Endocrine System
... leads to an increase in blood pressure, which shuts off ADH secretion and water reabsorption. This cycle of maintaining body fluids at a constant level is called osmoregulation. • The hypothalamus links the nervous system to the endocrine system by regulating hormone secretion by the pituitary gland ...
... leads to an increase in blood pressure, which shuts off ADH secretion and water reabsorption. This cycle of maintaining body fluids at a constant level is called osmoregulation. • The hypothalamus links the nervous system to the endocrine system by regulating hormone secretion by the pituitary gland ...
Chapter 10: Hormonal Control Systems
... Which organs are responsible for most of the metabolism or excretion of hormones? Give two examples of hormones that are secreted in inactive forms, and are converted to the active form in the target tissue. Since all hormones are delivered to all regions of the body, why doesn’t each cell respond t ...
... Which organs are responsible for most of the metabolism or excretion of hormones? Give two examples of hormones that are secreted in inactive forms, and are converted to the active form in the target tissue. Since all hormones are delivered to all regions of the body, why doesn’t each cell respond t ...
Bacterial infection that usually affects mucous membranes
... Female reproductive Tubes that run from structure that the testes to the ...
... Female reproductive Tubes that run from structure that the testes to the ...
Cardiovascular: Heart
... may stimulate thyroid without negative feedback control • Exophthalmos –symptom present in many hyperthyroid patients ...
... may stimulate thyroid without negative feedback control • Exophthalmos –symptom present in many hyperthyroid patients ...
Endocrine System
... • Paracrines (Local hormones): a cell of tissue that stimulates other cells around them with secretion • Hormones: chemical messenger that travels through blood and stimulates target cells ...
... • Paracrines (Local hormones): a cell of tissue that stimulates other cells around them with secretion • Hormones: chemical messenger that travels through blood and stimulates target cells ...
Histology of the Endocrine Glands [PPT]
... – Hormones synthesized as part of larger proteins (neurophysins) in neuron cell bodies of hypothalamus. – Transported in axons to pars nervosa (hormone cleaved from ...
... – Hormones synthesized as part of larger proteins (neurophysins) in neuron cell bodies of hypothalamus. – Transported in axons to pars nervosa (hormone cleaved from ...
Unit Four - Regulation Unit 4- REGULATORY
... respond correctly to insulin. In other words, glucose cannot enter the body cells to be used in energy production. It is the most common form of diabetes. Risk factors include genetics, race, age, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, history of gestational diabetes, low activity level, poor ...
... respond correctly to insulin. In other words, glucose cannot enter the body cells to be used in energy production. It is the most common form of diabetes. Risk factors include genetics, race, age, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, history of gestational diabetes, low activity level, poor ...
8.2 Major Endocrine Organs
... Both part of endocrine and lymphatic system Lies under sternum and anterior to heart Large during childhood, shrinks with age Thymosin • development of immune system – T lymphocytes (white blood cells) aka T Cells ...
... Both part of endocrine and lymphatic system Lies under sternum and anterior to heart Large during childhood, shrinks with age Thymosin • development of immune system – T lymphocytes (white blood cells) aka T Cells ...
垂体分泌的激素
... 2.Endocrine glands secrete hormones. 3.Hormones are carried to distant target cells through the bloodstream. 4.Hormones only act on cells (target cells) that possess receptors sensitive to the hormone – highly specific action. ...
... 2.Endocrine glands secrete hormones. 3.Hormones are carried to distant target cells through the bloodstream. 4.Hormones only act on cells (target cells) that possess receptors sensitive to the hormone – highly specific action. ...
The Endocrine System - Valhalla High School
... regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbs and lipids. Diseases of the thyroid lead to either hyperthyroidism(too much thyroxine), or hypothyroidism(not enough thyroxine). How do you these conditions would affect a ...
... regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbs and lipids. Diseases of the thyroid lead to either hyperthyroidism(too much thyroxine), or hypothyroidism(not enough thyroxine). How do you these conditions would affect a ...
The Endocrine System - Valhalla High School
... regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbs and lipids. Diseases of the thyroid lead to either hyperthyroidism(too much thyroxine), or hypothyroidism(not enough thyroxine). How do you these conditions would affect a ...
... regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbs and lipids. Diseases of the thyroid lead to either hyperthyroidism(too much thyroxine), or hypothyroidism(not enough thyroxine). How do you these conditions would affect a ...
hormones 3
... • Two major types – Type I diabetes (insulin dependent) – Type II diabetes (maturity onset diabetes) ...
... • Two major types – Type I diabetes (insulin dependent) – Type II diabetes (maturity onset diabetes) ...
the endocrine system - The Liberty Common School
... Core Knowledge Unit: V. The Human Body B. The Endocrine System · The human body has two types of glands: duct glands (such as salivary glands), and ductless glands, also known as endocrine glands. K · Endocrine glands secrete (give off) chemicals called hormones. Different hormones control different ...
... Core Knowledge Unit: V. The Human Body B. The Endocrine System · The human body has two types of glands: duct glands (such as salivary glands), and ductless glands, also known as endocrine glands. K · Endocrine glands secrete (give off) chemicals called hormones. Different hormones control different ...
Endocrine Review Package
... (in this booklet): hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries and testes. ...
... (in this booklet): hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries and testes. ...
The Endocrine System
... usually need insulin injections (why not glucagon injections?) usually inherited ...
... usually need insulin injections (why not glucagon injections?) usually inherited ...
Hormones of the Body
... Function of Posterior Pituitary Lobe Hormones ADH: • Regulates sodium levels. As sodium increases ADH is secreted • as an “antidiuretic,” ADH decreases urine formation by having kidneys conserve water • also can contract smooth muscle cells, as found in blood vessels-- this causes an increase in bl ...
... Function of Posterior Pituitary Lobe Hormones ADH: • Regulates sodium levels. As sodium increases ADH is secreted • as an “antidiuretic,” ADH decreases urine formation by having kidneys conserve water • also can contract smooth muscle cells, as found in blood vessels-- this causes an increase in bl ...
Name
... Thyroid gland - colloid-filled follicles, follicle cells, parafollicular cells. Parathyroid gland - chief cells. Adrenal gland - cortex and medulla.. Pancreas - islets of Langerhans and acinar cells. ...
... Thyroid gland - colloid-filled follicles, follicle cells, parafollicular cells. Parathyroid gland - chief cells. Adrenal gland - cortex and medulla.. Pancreas - islets of Langerhans and acinar cells. ...
Endocrine System - East Porter County School Corporation
... Derives its name from the fact that various glands release hormones directly into the blood, which in turn transports the hormones to target ...
... Derives its name from the fact that various glands release hormones directly into the blood, which in turn transports the hormones to target ...
Endocrine System Lecture
... 4. Disorders of the Parathyroid Glands a. Hyperparathyroidism (1) Over-activity of the parathyroid gland resulting in an overproduction of parathormone (2) Results in hypercalcemia, which leads to formation of renal calculi, lethargy; gastrointestinal disturbances, and calcium deposits on walls of b ...
... 4. Disorders of the Parathyroid Glands a. Hyperparathyroidism (1) Over-activity of the parathyroid gland resulting in an overproduction of parathormone (2) Results in hypercalcemia, which leads to formation of renal calculi, lethargy; gastrointestinal disturbances, and calcium deposits on walls of b ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.








![Histology of the Endocrine Glands [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000594794_1-37eba56f108bb48e0be040863df8f2e5-300x300.png)