Chapter 9 The Endocrine System
... ANS and Adrenal Medulla Adrenal medulla (like posterior pituitary) develops from neural tissue When stimulated sympathetic NS neurons, its cells release 2 similar hormones Hormones called catecholamines Epinephrine (adrenaline) & norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Sympathetic division called “fight or ...
... ANS and Adrenal Medulla Adrenal medulla (like posterior pituitary) develops from neural tissue When stimulated sympathetic NS neurons, its cells release 2 similar hormones Hormones called catecholamines Epinephrine (adrenaline) & norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Sympathetic division called “fight or ...
1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... c. ACTH: Stimulates the release of steroid hormones (glucocorticoids like cortisol) from the adrenal glands. d. Thyroxine: acts to increase metabolism by improving energy utilization, oxygen consumption, growth and development e. Epinephrine (adrenaline): helps us with our emergency and stress respo ...
... c. ACTH: Stimulates the release of steroid hormones (glucocorticoids like cortisol) from the adrenal glands. d. Thyroxine: acts to increase metabolism by improving energy utilization, oxygen consumption, growth and development e. Epinephrine (adrenaline): helps us with our emergency and stress respo ...
Document
... “The adrenal glands produce hormones that adjust metabolic activities at specific sites, affecting either the pattern of nutrient utilization, mineral ion balance, or the rate of energy consumption by active tissues.” ...
... “The adrenal glands produce hormones that adjust metabolic activities at specific sites, affecting either the pattern of nutrient utilization, mineral ion balance, or the rate of energy consumption by active tissues.” ...
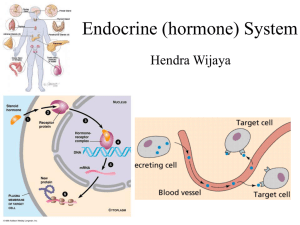
The Endocrine System
... B. Hormone – Testosterone C. Primary function as an organ to produce sperm D. Testosterone controls male characteristics – growth of body hair, widening of shoulders, muscle development, enlargement of larynx (Adam’s Apple) and deepening of voice ...
... B. Hormone – Testosterone C. Primary function as an organ to produce sperm D. Testosterone controls male characteristics – growth of body hair, widening of shoulders, muscle development, enlargement of larynx (Adam’s Apple) and deepening of voice ...
The Endocrine System
... 5. Often called “master gland”, but its secretions are actually controlled by the hypothalamus ...
... 5. Often called “master gland”, but its secretions are actually controlled by the hypothalamus ...
Endocrine System
... Steroid hormone molecules are made by endocrine cells from cholesterol, an important lipid All have a characteristic chemical group at the core of each molecule Lipid-soluble, thus they can easily pass through the phospholipid plasma membrane of target cells. Examples: cortisol, aldosterone, estroge ...
... Steroid hormone molecules are made by endocrine cells from cholesterol, an important lipid All have a characteristic chemical group at the core of each molecule Lipid-soluble, thus they can easily pass through the phospholipid plasma membrane of target cells. Examples: cortisol, aldosterone, estroge ...
Endocrine System
... Endocrinology, the study of the endocrine glands, is an important branch of modern medicine. Endocrinologists are medical doctors who specialize in researching and treating disorders and diseases of the endocrine system. ...
... Endocrinology, the study of the endocrine glands, is an important branch of modern medicine. Endocrinologists are medical doctors who specialize in researching and treating disorders and diseases of the endocrine system. ...
ENDOCRINE pathology
... (1) large, pleomorphicgiant cells, including occasional osteoclast-like multinucleate giant cells (2) spindle cells with a sarcomatous ...
... (1) large, pleomorphicgiant cells, including occasional osteoclast-like multinucleate giant cells (2) spindle cells with a sarcomatous ...
Continuing Education Independent Study Series
... chromaffin cells are directly innervated by cells of the autonomic nervous system. This allows the autonomic nervous system to control the release of the horm~nesproduced in the medulla and ensures a quick response to any stimulus. The hormones produced by the medulla are epinephrine and norepinephr ...
... chromaffin cells are directly innervated by cells of the autonomic nervous system. This allows the autonomic nervous system to control the release of the horm~nesproduced in the medulla and ensures a quick response to any stimulus. The hormones produced by the medulla are epinephrine and norepinephr ...
File
... Hormone: a chemical substance produced by the body that affects growth and development, sexual function, mood, metabolism and many other processes Metabolism: the sum of all chemical and physical processes occurring within living cells ...
... Hormone: a chemical substance produced by the body that affects growth and development, sexual function, mood, metabolism and many other processes Metabolism: the sum of all chemical and physical processes occurring within living cells ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... gland, which is the “master gland” The pituitary gland secretes a large number of hormones which carry messages through the blood stream These hormone messages carry information to the organs that regulate storing of nutrients, growth and reproduction. ...
... gland, which is the “master gland” The pituitary gland secretes a large number of hormones which carry messages through the blood stream These hormone messages carry information to the organs that regulate storing of nutrients, growth and reproduction. ...
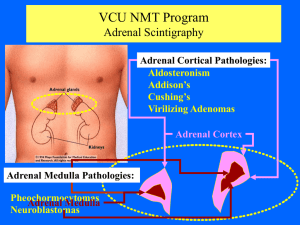
CSTCC NMT Program Adrenal Scintigraphy
... VCU NMT Program Adrenal Scintigraphy Specific points which you should remember: •mIBG should only be used for Adrenal Medulla pathologies. •Before administering mIBG the patient should be treated with Lugol’s solution which blocks thyroid uptake of free I131. •Lugol’s administration should continue ...
... VCU NMT Program Adrenal Scintigraphy Specific points which you should remember: •mIBG should only be used for Adrenal Medulla pathologies. •Before administering mIBG the patient should be treated with Lugol’s solution which blocks thyroid uptake of free I131. •Lugol’s administration should continue ...
Thyroid hormones
... • Insulin promotes a decrease in blood glucose • Glucagon promotes an increase in blood glucose ...
... • Insulin promotes a decrease in blood glucose • Glucagon promotes an increase in blood glucose ...
Chapter 17 The endocrine system overview hypothalamus * pituitary
... IGF-1 is a primary mediator of the effects of growth hormone(GH). Growth hormone is made in the anterior pituitary gland, is released into the blood stream, and then stimulates the liver to produce IGF-1. IGF-1 then stimulates systemic body growth, and has growth-promoting effects on almost every c ...
... IGF-1 is a primary mediator of the effects of growth hormone(GH). Growth hormone is made in the anterior pituitary gland, is released into the blood stream, and then stimulates the liver to produce IGF-1. IGF-1 then stimulates systemic body growth, and has growth-promoting effects on almost every c ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... The anterior pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone » The thyroid then produces hormones ...
... The anterior pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone » The thyroid then produces hormones ...
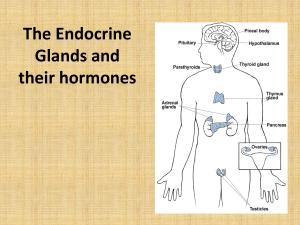
Endocrine Glands
... Hormones and their Target Organ • Hormones: are chemical signals released into the body/blood to initiate a response in their target cell. – Adrenaline/noradrenaline are released from the neurons of the adrenal gland to trigger “fight or flight” ...
... Hormones and their Target Organ • Hormones: are chemical signals released into the body/blood to initiate a response in their target cell. – Adrenaline/noradrenaline are released from the neurons of the adrenal gland to trigger “fight or flight” ...
PDF - True-2-me
... The pituitary is composed of two lobes: the posterior lobe and the anterior lobe (called adenohypophysis) containing the five hormone-secreting cell types. The pituitary posterior lobe stores two hormones produced by the hypothalamus: antidiuretic hormone (ADH) important for water reabsorption and o ...
... The pituitary is composed of two lobes: the posterior lobe and the anterior lobe (called adenohypophysis) containing the five hormone-secreting cell types. The pituitary posterior lobe stores two hormones produced by the hypothalamus: antidiuretic hormone (ADH) important for water reabsorption and o ...
enodcrine newer - ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... Exocrine glands 1. secrete products into ducts which empty into body cavities or body surface a) ...
... Exocrine glands 1. secrete products into ducts which empty into body cavities or body surface a) ...
File
... and allows the body to resist longterm with fat and protein breakdown; also involved in pain reduction ...
... and allows the body to resist longterm with fat and protein breakdown; also involved in pain reduction ...
Lecture 1. Introduction
... maintenance of pregnancy initiation of labor milk secretion and ejection ...
... maintenance of pregnancy initiation of labor milk secretion and ejection ...
8-9 (Cotlin)
... a. Parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin in the blood and have the effect of lowering the calcium concentration in the blood. IX. Thyroid Gland [S9] a. skipped X. Synthesis of Thyroid Hormone [S10] a. 2 things dependent on producing T3 and T4---collectively thyroid hormone. i. 1. Stimulation by th ...
... a. Parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin in the blood and have the effect of lowering the calcium concentration in the blood. IX. Thyroid Gland [S9] a. skipped X. Synthesis of Thyroid Hormone [S10] a. 2 things dependent on producing T3 and T4---collectively thyroid hormone. i. 1. Stimulation by th ...
Chapter 1 Goals
... 1. Cortisol – influence the metabolism of sugar, fats, & proteins within all body cells & have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. 2. Aldosterone – regulate blood volume, blood pressure & electrolyte concentration 3. (Androgens & estrogens) Sex hormones – secreted in small amounts & influence secon ...
... 1. Cortisol – influence the metabolism of sugar, fats, & proteins within all body cells & have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. 2. Aldosterone – regulate blood volume, blood pressure & electrolyte concentration 3. (Androgens & estrogens) Sex hormones – secreted in small amounts & influence secon ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.