Small Networks
... • Do neurons act as input-output devices? • Do networks act as input-output devices? • Are networks (not individual neurons) really noisy? • Is maximum “information transfer” desirable for a neuron or network? – Not necessarily (McDonnell & Ward, 2011). ...
... • Do neurons act as input-output devices? • Do networks act as input-output devices? • Are networks (not individual neurons) really noisy? • Is maximum “information transfer” desirable for a neuron or network? – Not necessarily (McDonnell & Ward, 2011). ...
Agents with no central representation
... (which links nicely with our next three lectures) What are the really radical alternative to logic? We have already seen ANN's and behaviour based robotics. There are many others. One high level way of representing human performance is CPM-GOMS Other similar cognitive-orientated representations such ...
... (which links nicely with our next three lectures) What are the really radical alternative to logic? We have already seen ANN's and behaviour based robotics. There are many others. One high level way of representing human performance is CPM-GOMS Other similar cognitive-orientated representations such ...
Data Averaging and Data Snooping
... We are primarily interested in the distribution of results for practical problems, and the resulting implications for how results are presented. Therefore, we present the results of a number of experiments using problems that have been commonly used in the neural network literature. In each case, we ...
... We are primarily interested in the distribution of results for practical problems, and the resulting implications for how results are presented. Therefore, we present the results of a number of experiments using problems that have been commonly used in the neural network literature. In each case, we ...
Peering into the Future Through the Looking Glass of Artificial
... history,” wrote Stephen Hawking in an op-ed, which appeared in The Independent in 2014. • “Unfortunately, it might also be the last, unless we learn how to avoid the risks. In the near term, world militaries are considering autonomous-weapon systems that can choose and eliminate targets.” Professor ...
... history,” wrote Stephen Hawking in an op-ed, which appeared in The Independent in 2014. • “Unfortunately, it might also be the last, unless we learn how to avoid the risks. In the near term, world militaries are considering autonomous-weapon systems that can choose and eliminate targets.” Professor ...
Which Model to Use for the Liquid State Machine?
... In biological circuits a single neuron would not be able to process complex input information, and neural microcircuits constitute a computational base [1]. A new idea on microcircuit computing was suggested by Maass [2] and, since then, it has been called Liquid State Machine (LSM). In general, the ...
... In biological circuits a single neuron would not be able to process complex input information, and neural microcircuits constitute a computational base [1]. A new idea on microcircuit computing was suggested by Maass [2] and, since then, it has been called Liquid State Machine (LSM). In general, the ...
Differential Roles of the Frontal Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and
... different in terms of visuomotor sequence learning (Miyashita et al., 1997). Pre-SMA neurons were particularly interesting in that they discriminated between learned sequences and new sequences, as shown in Fig. 2. We asked the monkey to perform four learned hypersets and four new hypersets while we ...
... different in terms of visuomotor sequence learning (Miyashita et al., 1997). Pre-SMA neurons were particularly interesting in that they discriminated between learned sequences and new sequences, as shown in Fig. 2. We asked the monkey to perform four learned hypersets and four new hypersets while we ...
Neural Network Approach to Predict Quality of Data Warehouse
... This section briefly describes the architecture of the proposed neural network and the criteria on which the performance of the proposed neural network is evaluated. A. Architecture/Learning algorithm The general architecture of the present NN model shown in figure 2 is described in this section. Th ...
... This section briefly describes the architecture of the proposed neural network and the criteria on which the performance of the proposed neural network is evaluated. A. Architecture/Learning algorithm The general architecture of the present NN model shown in figure 2 is described in this section. Th ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... convex hull ratio, aspect ratio and eccentricity. These features were vital in identifying leaf shapes, number of lobes and margin types. Leaves of nine classes were used and a classifier was implemented and tested using 105 leaves of 38 different species. K-means clustering was used to classify 105 ...
... convex hull ratio, aspect ratio and eccentricity. These features were vital in identifying leaf shapes, number of lobes and margin types. Leaves of nine classes were used and a classifier was implemented and tested using 105 leaves of 38 different species. K-means clustering was used to classify 105 ...
1 Bayesian Networks
... This blocked given D by the node E, since this is not one of the given nodes (i.e., is not D) and has both arrows on the path going into it. (ii) C − B − A − D − E − F . This path is also blocked by E (and D as well). So, D does d-separate C and F. (ii) Do D and E d-separate C and F ? The path C − B ...
... This blocked given D by the node E, since this is not one of the given nodes (i.e., is not D) and has both arrows on the path going into it. (ii) C − B − A − D − E − F . This path is also blocked by E (and D as well). So, D does d-separate C and F. (ii) Do D and E d-separate C and F ? The path C − B ...
A Neural Model of Rule Generation in Inductive Reasoning
... look like, they can check for a match among the eight possible answers. Not all subjects will explicitly generate these exact rules, and their route to the answer may be more roundabout, but they do need to extract equivalent information if they are to correctly solve the problem. Despite the test’s ...
... look like, they can check for a match among the eight possible answers. Not all subjects will explicitly generate these exact rules, and their route to the answer may be more roundabout, but they do need to extract equivalent information if they are to correctly solve the problem. Despite the test’s ...
NetworkSecurityAITechniques
... static definitions of known patterns of attack or security events (worms, viruses, etc) that can compromise a network system. Most commercial implementations of Intrusion Detection apply the misuse, or signature-based model. Examples are anti-virus and antispam filtering software which use Artificia ...
... static definitions of known patterns of attack or security events (worms, viruses, etc) that can compromise a network system. Most commercial implementations of Intrusion Detection apply the misuse, or signature-based model. Examples are anti-virus and antispam filtering software which use Artificia ...
research statement
... 3. Improvement of Associative Self-Optimizing Neural Networks (ASONN) for classification: First generation of Self-Optimizing Neural Networks (SONN) did not use associative mechanisms at all, searching through the data for specific groups ...
... 3. Improvement of Associative Self-Optimizing Neural Networks (ASONN) for classification: First generation of Self-Optimizing Neural Networks (SONN) did not use associative mechanisms at all, searching through the data for specific groups ...
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
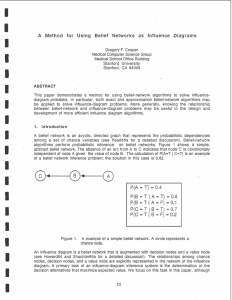
... solve influence-diagram problems. For example, the message-passing algorithm of Pearl for belief-network inference can be used to solve efficiently many influence diagrams that are singly connected [Pearl86a]. Those belief-network algorithms that are designed for performing probabilistic inference u ...
... solve influence-diagram problems. For example, the message-passing algorithm of Pearl for belief-network inference can be used to solve efficiently many influence diagrams that are singly connected [Pearl86a]. Those belief-network algorithms that are designed for performing probabilistic inference u ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... Now a day, many applications used by the civilians and army or police forces require effective face recognition. In this case face recognition is very useful to easily detect the human faces. This face recognition is a very challenging area in computer vision and pattern recognition due to various v ...
... Now a day, many applications used by the civilians and army or police forces require effective face recognition. In this case face recognition is very useful to easily detect the human faces. This face recognition is a very challenging area in computer vision and pattern recognition due to various v ...
Pattern Recognition by Labeled Graph Matching
... Hopfield, 1982; Kohonen, 1977; Palm, 1980; Steinbuch, 1961; Willshaw, Buneman, & Longuet-Higgins, 1969) has a number of properties which qualify it as an important neural paradigm. Among these is its ability to generalize over Hamming distance. One aspect of this is pattern completion. Translation i ...
... Hopfield, 1982; Kohonen, 1977; Palm, 1980; Steinbuch, 1961; Willshaw, Buneman, & Longuet-Higgins, 1969) has a number of properties which qualify it as an important neural paradigm. Among these is its ability to generalize over Hamming distance. One aspect of this is pattern completion. Translation i ...
Cognitive Architectures: Where do we go from here?
... reasoning. In fact simple vector-space techniques for knowledge representation are sufficient to play the 20question game [7]. Success in learning language depends on automatic creation and maintenance of largescale knowledge bases, bootstraping on the resources from the Internet. Question/answer sy ...
... reasoning. In fact simple vector-space techniques for knowledge representation are sufficient to play the 20question game [7]. Success in learning language depends on automatic creation and maintenance of largescale knowledge bases, bootstraping on the resources from the Internet. Question/answer sy ...
Introduction to Machine Learning 1
... regularities. This is the niche of machine learning. Such patterns may help us understand the process, or we can use those patterns to make predictions: Assuming that the future, at least the near future, will not be much different from the past when the sample data was collected, the future predict ...
... regularities. This is the niche of machine learning. Such patterns may help us understand the process, or we can use those patterns to make predictions: Assuming that the future, at least the near future, will not be much different from the past when the sample data was collected, the future predict ...
Event-Related Potentials
... auditory stimuli having physical acoustic properties that deviate from prior (standard) stimuli registered in auditory memory. Occurring between 80 and 200 ms after presentation of deviant auditory stimuli, thus overlapping the N1 and P2 components, the mismatch negativity is isolated by computing ...
... auditory stimuli having physical acoustic properties that deviate from prior (standard) stimuli registered in auditory memory. Occurring between 80 and 200 ms after presentation of deviant auditory stimuli, thus overlapping the N1 and P2 components, the mismatch negativity is isolated by computing ...
Quasi-isometric Representation of Three Dimensional
... Correspondence with the LSM theory • The neural network may be treated as a liquid • The readout function receives only the current state of the liquid and transforms it to an output signal • The system can perform several tasks simultaneously ...
... Correspondence with the LSM theory • The neural network may be treated as a liquid • The readout function receives only the current state of the liquid and transforms it to an output signal • The system can perform several tasks simultaneously ...
L8 slides
... • In short, the basal ganglia select one out of many possible actions to perform, and the cerebellum then makes sure the selected action is performed well. • Thus, parietal representations (i.e., the “where" pathway), drive motor action execution as coordinated by the cerebellum, and cerebellum is a ...
... • In short, the basal ganglia select one out of many possible actions to perform, and the cerebellum then makes sure the selected action is performed well. • Thus, parietal representations (i.e., the “where" pathway), drive motor action execution as coordinated by the cerebellum, and cerebellum is a ...
Catastrophic interference
Catastrophic Interference, also known as catastrophic forgetting, is the tendency of a artificial neural network to completely and abruptly forget previously learned information upon learning new information. Neural networks are an important part of the network approach and connectionist approach to cognitive science. These networks use computer simulations to try and model human behaviours, such as memory and learning. Catastrophic interference is an important issue to consider when creating connectionist models of memory. It was originally brought to the attention of the scientific community by research from McCloskey and Cohen (1989), and Ractcliff (1990). It is a radical manifestation of the ‘sensitivity-stability’ dilemma or the ‘stability-plasticity’ dilemma. Specifically, these problems refer to the issue of being able to make an artificial neural network that is sensitive to, but not disrupted by, new information. Lookup tables and connectionist networks lie on the opposite sides of the stability plasticity spectrum. The former remains completely stable in the presence of new information but lacks the ability to generalize, i.e. infer general principles, from new inputs. On the other hand, connectionst networks like the standard backpropagation network are very sensitive to new information and can generalize on new inputs. Backpropagation models can be considered good models of human memory insofar as they mirror the human ability to generalize but these networks often exhibit less stability than human memory. Notably, these backpropagation networks are susceptible to catastrophic interference. This is considered an issue when attempting to model human memory because, unlike these networks, humans typically do not show catastrophic forgetting. Thus, the issue of catastrophic interference must be eradicated from these backpropagation models in order to enhance the plausibility as models of human memory.