Solving Bayesian Networks by Weighted Model Counting
... all variables in one pass. A translation approach, therefore, would be at a serious disadvantage, if such a calculation required a separate translation and query for each variable. We therefore further extended our model-counting algorithm so that all marginals can be computed efficiently in one pas ...
... all variables in one pass. A translation approach, therefore, would be at a serious disadvantage, if such a calculation required a separate translation and query for each variable. We therefore further extended our model-counting algorithm so that all marginals can be computed efficiently in one pas ...
Neurocybernetics and Artificial Intelligence
... We can sum up this structure of Neurocybernetics levels in a way which indicates what are the appropriate tools for each level, keeping in mind that a notable change in level cannot be allowed in the theory without changing tools. But, if prudent, in the practical research into the brain and artific ...
... We can sum up this structure of Neurocybernetics levels in a way which indicates what are the appropriate tools for each level, keeping in mind that a notable change in level cannot be allowed in the theory without changing tools. But, if prudent, in the practical research into the brain and artific ...
Neural Network and Fuzzy Logic
... turned out to be very popular.[1, 2] Neural network have been successfully applied to problems in the field of pattern recognition, image processing, data compression forecasting and optimization to quote a few. Neurons considered as a threshold units that fire when their total input exceeds certain ...
... turned out to be very popular.[1, 2] Neural network have been successfully applied to problems in the field of pattern recognition, image processing, data compression forecasting and optimization to quote a few. Neurons considered as a threshold units that fire when their total input exceeds certain ...
Lecture 45 - KDD - Kansas State University
... Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU ...
... Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... the utility company to make its operation and unit commitment economical [2, 3]. Good prediction of electric load resolves the issues regarding to the reliability, security and efficiency of the power system [4]. Accuracy and time is more important parameters in the load forecasting. Under predictio ...
... the utility company to make its operation and unit commitment economical [2, 3]. Good prediction of electric load resolves the issues regarding to the reliability, security and efficiency of the power system [4]. Accuracy and time is more important parameters in the load forecasting. Under predictio ...
Learning to Remember Rare Events
... Figure 3: Extended Neural GPU with memory module. Memory query is read from the position one below the current output logit, and the embedded memory value is put at the same position of the output tape p. The network learns to use these values to produce the output in the next step. Sequence-to-sequ ...
... Figure 3: Extended Neural GPU with memory module. Memory query is read from the position one below the current output logit, and the embedded memory value is put at the same position of the output tape p. The network learns to use these values to produce the output in the next step. Sequence-to-sequ ...
Associative Learning and Long-Term Potentiation
... efficacy. It was generally assumed that the experimental induction of LTP would disturb the synaptic changes taking place during associative learning in selected neural sites. Indeed, our research group and others have shown that LTP saturation of hippocampal circuits disrupts spatial and associativ ...
... efficacy. It was generally assumed that the experimental induction of LTP would disturb the synaptic changes taking place during associative learning in selected neural sites. Indeed, our research group and others have shown that LTP saturation of hippocampal circuits disrupts spatial and associativ ...
Neural Network Structures
... mapping. • Neural networks have a powerful learning capability, that is, they can be trained to represent any given problem behavior. The weight parameters in the neural network represent the weighted connections between neurons. After training the neural network, the weighted connections capture/en ...
... mapping. • Neural networks have a powerful learning capability, that is, they can be trained to represent any given problem behavior. The weight parameters in the neural network represent the weighted connections between neurons. After training the neural network, the weighted connections capture/en ...
Open access
... job is to help the main controller to bring interesting images to the center of the retina. The image recognition agent or IRA is a trained ANN specialized in recognizing a particular kind of object (icon) and discriminates it from other objects or from the background noise. Its job is to help the m ...
... job is to help the main controller to bring interesting images to the center of the retina. The image recognition agent or IRA is a trained ANN specialized in recognizing a particular kind of object (icon) and discriminates it from other objects or from the background noise. Its job is to help the m ...
MS PowerPoint 97 format - KDD
... – Vertices (37): findings (e.g., esophageal intubation), intermediates, observables – K2: found BBN different in only 1 edge from gold standard (elicited from expert) ...
... – Vertices (37): findings (e.g., esophageal intubation), intermediates, observables – K2: found BBN different in only 1 edge from gold standard (elicited from expert) ...
Comparison of Neural Network and Statistical
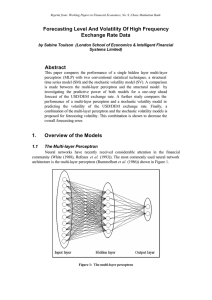
... The multi-layer perceptron was used to predict the one-step ahead level of the USD/DEM exchange rate in the following manner. At time t first differences of the previous 12 observations were encoded as an input vector to the network. The inputs were normalised to have zero mean and unit variance2 ac ...
... The multi-layer perceptron was used to predict the one-step ahead level of the USD/DEM exchange rate in the following manner. At time t first differences of the previous 12 observations were encoded as an input vector to the network. The inputs were normalised to have zero mean and unit variance2 ac ...
On supporting the process of learning design through planners
... of expert systems, but with the broad problem category of “designing learning activities”. The automated design of learning sequences is not a novel idea, but several authors have approached tools that aggregate contents into higher levels of instruction (Vassileva and Deters, 1998), use past activ ...
... of expert systems, but with the broad problem category of “designing learning activities”. The automated design of learning sequences is not a novel idea, but several authors have approached tools that aggregate contents into higher levels of instruction (Vassileva and Deters, 1998), use past activ ...
(1996). "A multi-threshold neural network for frequency estimation,"
... of the spikes. Thus, any theory of neural sound coding must explain how the temporal (time-period) ...
... of the spikes. Thus, any theory of neural sound coding must explain how the temporal (time-period) ...
PDF - Bentham Open
... Abstract: A theoretical model for deriving the origin of emotional functions from first principles is introduced. The model, called “Emotional Model Of the Theoretical Interpretations Of Neuroprocessing”, abbreviated as the “EMOTION”, derives how emotional context can be evolved from innate response ...
... Abstract: A theoretical model for deriving the origin of emotional functions from first principles is introduced. The model, called “Emotional Model Of the Theoretical Interpretations Of Neuroprocessing”, abbreviated as the “EMOTION”, derives how emotional context can be evolved from innate response ...
Utile Distinction Hidden Markov Models
... constructs a world model (HMM) that predicts observations based on actions, and can solve a number of POMDP problems. However, it fails to make distictions based on utility — it cannot discriminate between different parts of a world that look the same but are different in the assignment of rewards. ...
... constructs a world model (HMM) that predicts observations based on actions, and can solve a number of POMDP problems. However, it fails to make distictions based on utility — it cannot discriminate between different parts of a world that look the same but are different in the assignment of rewards. ...
Self-Organizing Map Considering False Neighboring Neuron
... Then, the Self-Organizing Map (SOM) has attracted attention for its clustering properties. SOM is an unsupervised neural network introduced by Kohonen in 1982 [1] and is a model simplifying self-organization process of the brain. SOM obtains statistical feature of input data and is applied to a wide ...
... Then, the Self-Organizing Map (SOM) has attracted attention for its clustering properties. SOM is an unsupervised neural network introduced by Kohonen in 1982 [1] and is a model simplifying self-organization process of the brain. SOM obtains statistical feature of input data and is applied to a wide ...
A CYBERNETIC VIEW OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE José Mira
... (AI as a science) and the objectives and methods of AI as engineering (KE). Then we summarize in section three the different historical stages of AI enhancing its cybernetic “flavour” (mechanisms underlying intelligent behavior). We thus arrive to the current state of AI characterized by some methodol ...
... (AI as a science) and the objectives and methods of AI as engineering (KE). Then we summarize in section three the different historical stages of AI enhancing its cybernetic “flavour” (mechanisms underlying intelligent behavior). We thus arrive to the current state of AI characterized by some methodol ...
Dynamic `frees: A Structured Variational Method Giving Efficient
... namic tree can then be written as P(Z, XHjXE) = P(Z, X)/ P(XE). Usually the evidential nodes are the leaf nodes of the network. Given some data, which we use to instantiate the leaf (evidential) nodes of the network, we want information about the posterior distribution of the tree structures and the ...
... namic tree can then be written as P(Z, XHjXE) = P(Z, X)/ P(XE). Usually the evidential nodes are the leaf nodes of the network. Given some data, which we use to instantiate the leaf (evidential) nodes of the network, we want information about the posterior distribution of the tree structures and the ...
associations
... of the output space is M. wij is the weight from neuron j to neuron i. aj is the activation of a neuron j. •The activation of each neuron is produced by using a suitable threshold function and a threshold. For example we can assume that the activations are binary (i.e. either 0 or 1) and to achieve ...
... of the output space is M. wij is the weight from neuron j to neuron i. aj is the activation of a neuron j. •The activation of each neuron is produced by using a suitable threshold function and a threshold. For example we can assume that the activations are binary (i.e. either 0 or 1) and to achieve ...
Computational Constraints that may have Favoured the Lamination
... receives Cff feedforward connections from a further array of N × N “thalamic” units, and Crc recurrent connections from other units in the patch. Both sets of connections are assigned to each receiving unit at random, with a Gaussian probability in register with the unit itself, and of width Sff and ...
... receives Cff feedforward connections from a further array of N × N “thalamic” units, and Crc recurrent connections from other units in the patch. Both sets of connections are assigned to each receiving unit at random, with a Gaussian probability in register with the unit itself, and of width Sff and ...
Expert system, fuzzy logic, and neural network applications in power
... were born as a result. Gradually, the advent of electronic logic and solid state IC’s ushered the modem era of Von Neumann type digital computation. Digital computers were defined as “intelligent” machines because of their capability to process human thought-like yes ( I t n o (0) logic. Of course, ...
... were born as a result. Gradually, the advent of electronic logic and solid state IC’s ushered the modem era of Von Neumann type digital computation. Digital computers were defined as “intelligent” machines because of their capability to process human thought-like yes ( I t n o (0) logic. Of course, ...
MACHINE LEARNING WHAT IS MACHINE LEARNING?
... The general effect of learning in a system is the improvement of the system’s capability to solve problems. It is hard to imagine a system capable of learning cannot improve its problem-solving performance. A system with learning capability should be able to do self-changing in order to perform bett ...
... The general effect of learning in a system is the improvement of the system’s capability to solve problems. It is hard to imagine a system capable of learning cannot improve its problem-solving performance. A system with learning capability should be able to do self-changing in order to perform bett ...
Catastrophic interference
Catastrophic Interference, also known as catastrophic forgetting, is the tendency of a artificial neural network to completely and abruptly forget previously learned information upon learning new information. Neural networks are an important part of the network approach and connectionist approach to cognitive science. These networks use computer simulations to try and model human behaviours, such as memory and learning. Catastrophic interference is an important issue to consider when creating connectionist models of memory. It was originally brought to the attention of the scientific community by research from McCloskey and Cohen (1989), and Ractcliff (1990). It is a radical manifestation of the ‘sensitivity-stability’ dilemma or the ‘stability-plasticity’ dilemma. Specifically, these problems refer to the issue of being able to make an artificial neural network that is sensitive to, but not disrupted by, new information. Lookup tables and connectionist networks lie on the opposite sides of the stability plasticity spectrum. The former remains completely stable in the presence of new information but lacks the ability to generalize, i.e. infer general principles, from new inputs. On the other hand, connectionst networks like the standard backpropagation network are very sensitive to new information and can generalize on new inputs. Backpropagation models can be considered good models of human memory insofar as they mirror the human ability to generalize but these networks often exhibit less stability than human memory. Notably, these backpropagation networks are susceptible to catastrophic interference. This is considered an issue when attempting to model human memory because, unlike these networks, humans typically do not show catastrophic forgetting. Thus, the issue of catastrophic interference must be eradicated from these backpropagation models in order to enhance the plausibility as models of human memory.