Synthesis of highly focused fields with circular
... requirements of a specific problem [10]. Interestingly, several authors described inverse methods to find the pupil function from a predetermined field distribution in the focal area [11, 12]. Light shaping can be accomplished by using an optical setup able to generate beams with arbitrary polariza ...
... requirements of a specific problem [10]. Interestingly, several authors described inverse methods to find the pupil function from a predetermined field distribution in the focal area [11, 12]. Light shaping can be accomplished by using an optical setup able to generate beams with arbitrary polariza ...
Experimental implementation of the gyrator transform - E
... a function of the transformation angle ␣. In Fig. 2 the operation curves 1共␣兲 for the generalized lens L1 (a) and L2 (b) are shown. Note that 2共␣兲 is derived from the relation 2 = −共1 + / 2兲. In addition, when the angle between the cylindrical lenses is / 2 a generalized lens reduces to a sp ...
... a function of the transformation angle ␣. In Fig. 2 the operation curves 1共␣兲 for the generalized lens L1 (a) and L2 (b) are shown. Note that 2共␣兲 is derived from the relation 2 = −共1 + / 2兲. In addition, when the angle between the cylindrical lenses is / 2 a generalized lens reduces to a sp ...
optically active substances.
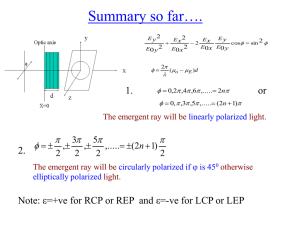
... Quest: What about superposition of two circularly polarized light (RCP and LCP) beams with same amplitude and wavelength. Any plane polarized light wave can be obtained as a superposition of a left circularly polarized and a right circularly polarized light wave, whose amplitude is identical. This ...
... Quest: What about superposition of two circularly polarized light (RCP and LCP) beams with same amplitude and wavelength. Any plane polarized light wave can be obtained as a superposition of a left circularly polarized and a right circularly polarized light wave, whose amplitude is identical. This ...
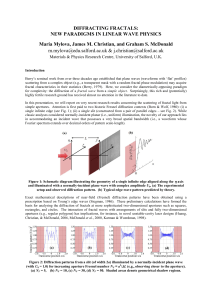
Diffracting fractals: new paradigms in linear wave physics
... of the dimension D at a single slit when D = 1.99. (a) NF = 5, (b) NF = 10, (c) NF = 30, (d) NF = 50. Other parameters: = 1.2, /a = 1.0, L/k = 1, and = 0.1. Shaded areas denote geometrical shadow regions, and the same random phases are used in each pane. Red line: pattern from plane wave illumi ...
... of the dimension D at a single slit when D = 1.99. (a) NF = 5, (b) NF = 10, (c) NF = 30, (d) NF = 50. Other parameters: = 1.2, /a = 1.0, L/k = 1, and = 0.1. Shaded areas denote geometrical shadow regions, and the same random phases are used in each pane. Red line: pattern from plane wave illumi ...
Inverse scattering for frequency-scanned full-field
... this case phase shifting is not performed, and the imaginary component of D共r ; k兲 is not obtainable. If the imaginary part of D共r ; k兲 is assumed to be zero, then due to the Hermitian symmetry of the Fourier transform of real functions D̃共−q , k兲 = D̃共q , k兲*. The function ˜共Q兲 then also has Hermi ...
... this case phase shifting is not performed, and the imaginary component of D共r ; k兲 is not obtainable. If the imaginary part of D共r ; k兲 is assumed to be zero, then due to the Hermitian symmetry of the Fourier transform of real functions D̃共−q , k兲 = D̃共q , k兲*. The function ˜共Q兲 then also has Hermi ...
amplitude transfer function
... the edges of the field (narrower MTF ⇔broader PSF) • This, in addition, means that real–life optical systems are not shift invariant either! • ⇒ the concept of MTF is approximate, near the region where the system is approximately shift invariant (recall: transfer functions can be defined only for sh ...
... the edges of the field (narrower MTF ⇔broader PSF) • This, in addition, means that real–life optical systems are not shift invariant either! • ⇒ the concept of MTF is approximate, near the region where the system is approximately shift invariant (recall: transfer functions can be defined only for sh ...
The present work gives recommendations for rational - Dimka
... The analysis of different vendors’ microobjective series of a given class [9] gave the following default values of their basic optical characteristics: the back focal length f 3,7 mm; relative aperture – 1:2,4; field angle in object space – 2 =60○. Such characteristics justify the starting sch ...
... The analysis of different vendors’ microobjective series of a given class [9] gave the following default values of their basic optical characteristics: the back focal length f 3,7 mm; relative aperture – 1:2,4; field angle in object space – 2 =60○. Such characteristics justify the starting sch ...
Analytical Expression for the Standing Wave Intensity in Photoresist
... reflecting substrate (P2g= -1). The factor exp(-m) accounts for absorption by the film. Of course, an exact expression for the intensity may be obtained by squaring the magnitude of E2 in Eq. (1). III. MultipleFilms It is very common to have more than one film coated on a substrate. The problem then ...
... reflecting substrate (P2g= -1). The factor exp(-m) accounts for absorption by the film. Of course, an exact expression for the intensity may be obtained by squaring the magnitude of E2 in Eq. (1). III. MultipleFilms It is very common to have more than one film coated on a substrate. The problem then ...
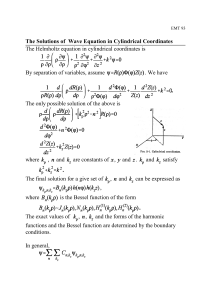
The Solutions of Wave Equation in Cylindrical Coordinates The
... Assume an x-polarized ztraveling plane wave incident on a PEC sphere with radius a. Then, ...
... Assume an x-polarized ztraveling plane wave incident on a PEC sphere with radius a. Then, ...
Analysis of photonic crystals for light emitting
... P. Harms, R. Mittra, W. Ko, "Implementation of the periodic boundary condition in the Finite-Difference Time-Domain algorithm for FSS Structures," IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 42, no. 9, 1994. ...
... P. Harms, R. Mittra, W. Ko, "Implementation of the periodic boundary condition in the Finite-Difference Time-Domain algorithm for FSS Structures," IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 42, no. 9, 1994. ...
Experiment 4: Refraction and Interference with Microwaves
... 1.1 Electromagnetic Radiation The term electromagnetic radiation encompasses a wide variety of radiative phenomena that seem at first to be quite different from one another. For example, radio waves, visible light, and the “gamma rays” which emanate from radioactive substances all fall into this cat ...
... 1.1 Electromagnetic Radiation The term electromagnetic radiation encompasses a wide variety of radiative phenomena that seem at first to be quite different from one another. For example, radio waves, visible light, and the “gamma rays” which emanate from radioactive substances all fall into this cat ...
Optical laser beam scanner lens relay system
... neither the X or the Y scanners are optimally placed and the beam ‘moves’ in the objective back focal plane. We have never found such arrangements to be optimal when attempting to construct high quality microscopes, particularly when two-photon excitation is used. A superior method exploits the fac ...
... neither the X or the Y scanners are optimally placed and the beam ‘moves’ in the objective back focal plane. We have never found such arrangements to be optimal when attempting to construct high quality microscopes, particularly when two-photon excitation is used. A superior method exploits the fac ...
CHAPTER 11. SUPERPOSITION OF LIGHT WAVE When two waves
... This is the equation for standing or stationary wave, as opposed to traveling wave. Its profile does not move through space. At any fixed point, the amplitude is a constant equal to 2 E0 I sin kx and varies harmonically as cos t. At certain points, namely, x=0, /2, , 3/2,…, the disturbance will ...
... This is the equation for standing or stationary wave, as opposed to traveling wave. Its profile does not move through space. At any fixed point, the amplitude is a constant equal to 2 E0 I sin kx and varies harmonically as cos t. At certain points, namely, x=0, /2, , 3/2,…, the disturbance will ...