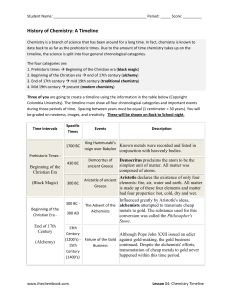
Gas Laws Practice Test.Ans.Key
... into a 4.00-liter container. The mixture has an equilibrium temperature of 75.0 C. What is the partial pressure (in atm.) of the nitrogen gas in the vessel? No reaction takes place between these two gases. ...
... into a 4.00-liter container. The mixture has an equilibrium temperature of 75.0 C. What is the partial pressure (in atm.) of the nitrogen gas in the vessel? No reaction takes place between these two gases. ...
Surface Plasmon Resonance
... - collective oscillations of the “free electron gas” density, often at optical frequencies. Surface Plasmons: - plasmons confined to surface (interface) and interact with light resulting in polaritons. - propagating electron density waves occurring at the interface between metal and dielectric. Surf ...
... - collective oscillations of the “free electron gas” density, often at optical frequencies. Surface Plasmons: - plasmons confined to surface (interface) and interact with light resulting in polaritons. - propagating electron density waves occurring at the interface between metal and dielectric. Surf ...
Wave Equation - web page for staff
... Two identical thin lenses with f = 15 cm and D = 5 cm are located in plane z = 0 and z = L. A Gaussian beam of diameter 0.5 cm to e-2 relavtive power density for λ = 0.63 μm is incident on the first lens. The value of L is constained such that the e-2 relative power density locus is contained within ...
... Two identical thin lenses with f = 15 cm and D = 5 cm are located in plane z = 0 and z = L. A Gaussian beam of diameter 0.5 cm to e-2 relavtive power density for λ = 0.63 μm is incident on the first lens. The value of L is constained such that the e-2 relative power density locus is contained within ...
Review Worksheet
... b) Ideal gases consist of small particles (molecules or atoms) that are far apart in comparison to their own size. The molecules of a gas are very __________ compared to the distances between them. c) These particles are considered to be dimensionless points which occupy zero volume. The volume of r ...
... b) Ideal gases consist of small particles (molecules or atoms) that are far apart in comparison to their own size. The molecules of a gas are very __________ compared to the distances between them. c) These particles are considered to be dimensionless points which occupy zero volume. The volume of r ...
CHEMICAL BONDING
... Also, there may be unbonded pairs of electrons. These create a very large concentration of negative charge and these repel other areas of negative charge. ...
... Also, there may be unbonded pairs of electrons. These create a very large concentration of negative charge and these repel other areas of negative charge. ...
The Photoelectric Effect
... Monochromatic light (in this case produced by a broadband mercury lamp passing through a wavelengthselective interference filter) is incident on the cathode K of the photocell. This is typically made from potassium. This causes electrons to be liberated from the cathode, which then flow to ground vi ...
... Monochromatic light (in this case produced by a broadband mercury lamp passing through a wavelengthselective interference filter) is incident on the cathode K of the photocell. This is typically made from potassium. This causes electrons to be liberated from the cathode, which then flow to ground vi ...
1 - PLK Vicwood KT Chong Sixth Form College
... So for any frequency of radiation, we would expect electrons to be ejected if sufficient time is allowed for them to gather enough energy to escape but observation (3) gives a different result. (II) Einstein assumed that electromagnetic radiations are emitted and absorbed in whole numbers of quanta, ...
... So for any frequency of radiation, we would expect electrons to be ejected if sufficient time is allowed for them to gather enough energy to escape but observation (3) gives a different result. (II) Einstein assumed that electromagnetic radiations are emitted and absorbed in whole numbers of quanta, ...
electrons - Purdue Physics
... A particle (wave) of mass m is in a one-dimensional box of width ℓ. The box puts boundary conditions on the wave. The wave function must be zero at the walls of the box and on the outside. In order for the probability to vanish at the walls, we must have an integral number of half wavelengths in the ...
... A particle (wave) of mass m is in a one-dimensional box of width ℓ. The box puts boundary conditions on the wave. The wave function must be zero at the walls of the box and on the outside. In order for the probability to vanish at the walls, we must have an integral number of half wavelengths in the ...
CHEM1405 2012-J-2 June 2012 • What is the ground state electron
... The number of nuclei, N, decays with time, t, according to ln(N0/Nt) = λt where λ is the activity coefficient. This is related to the half life, t1/2 by λ = ln2/t1/2. For 131I, t1/2 = 8 days = 8/365 years: λ = ln2 / (8/365) years-1 = 32 years-1 When t = 25 years, ln(N0/Nt) = λt = (32 years-1)(25 yea ...
... The number of nuclei, N, decays with time, t, according to ln(N0/Nt) = λt where λ is the activity coefficient. This is related to the half life, t1/2 by λ = ln2/t1/2. For 131I, t1/2 = 8 days = 8/365 years: λ = ln2 / (8/365) years-1 = 32 years-1 When t = 25 years, ln(N0/Nt) = λt = (32 years-1)(25 yea ...
Chemistry - Beachwood City Schools
... orbital diagrams Hund’s rule Pauli exclusion principle ionization energy atomic radius electron configuration & the Periodic Table Chemistry ...
... orbital diagrams Hund’s rule Pauli exclusion principle ionization energy atomic radius electron configuration & the Periodic Table Chemistry ...
FTIR Spectrometer - Pat Arnott Web Site
... result in a free hole as well. If this happens close enough to the electric field, or if free electron and free hole happen to wander into its range of influence, the field will send the electron to the N side and the hole to the P side. This causes further disruption of electrical neutrality, and i ...
... result in a free hole as well. If this happens close enough to the electric field, or if free electron and free hole happen to wander into its range of influence, the field will send the electron to the N side and the hole to the P side. This causes further disruption of electrical neutrality, and i ...
FTIR Spectrometer
... result in a free hole as well. If this happens close enough to the electric field, or if free electron and free hole happen to wander into its range of influence, the field will send the electron to the N side and the hole to the P side. This causes further disruption of electrical neutrality, and i ...
... result in a free hole as well. If this happens close enough to the electric field, or if free electron and free hole happen to wander into its range of influence, the field will send the electron to the N side and the hole to the P side. This causes further disruption of electrical neutrality, and i ...
7.1.3 Optimizing Light Confinement and Gain in Laser Diodes
... As soon as enough carriers are injected to cause sufficient inversion, some modes of the resonator with the "right" wavelengths will become amplified and appear as small peaks on the spectral distribution of the light. Well above threshold, the frequency with the highest coefficient "wins" and the L ...
... As soon as enough carriers are injected to cause sufficient inversion, some modes of the resonator with the "right" wavelengths will become amplified and appear as small peaks on the spectral distribution of the light. Well above threshold, the frequency with the highest coefficient "wins" and the L ...
The Photoelectric Effect
... where W is the amount of work that must be done to separate an electron from the metal. For the least strongly bound electrons (the ones easiest to tear away from the metal) this amount of work is known as the "work function" and is labelled Wo. These electrons will leave with the greatest kinetic e ...
... where W is the amount of work that must be done to separate an electron from the metal. For the least strongly bound electrons (the ones easiest to tear away from the metal) this amount of work is known as the "work function" and is labelled Wo. These electrons will leave with the greatest kinetic e ...
Environmental Physics for Freshman Geography Students Professor
... where q1 and q2 are the amounts of electric charge (measured in special units called “coulombs”, C), r is the distance between the charges (measured in m), and K is Coulomb’s electrostatic constant (= 8.99 x 10 9 kg m3 s-2 C-2). The introduction of electric charges into the simple world of mechanics ...
... where q1 and q2 are the amounts of electric charge (measured in special units called “coulombs”, C), r is the distance between the charges (measured in m), and K is Coulomb’s electrostatic constant (= 8.99 x 10 9 kg m3 s-2 C-2). The introduction of electric charges into the simple world of mechanics ...
Answers - Shelton State
... Melting point and freezing point are the same temperature. What is vapor pressure? The pressure of vapor in equilibrium with its liquid state. The pressure of a vapor evaporating from the liquid state. What is boiling? The especially rapid evaporation that occurs when the vapor pressure of a liquid ...
... Melting point and freezing point are the same temperature. What is vapor pressure? The pressure of vapor in equilibrium with its liquid state. The pressure of a vapor evaporating from the liquid state. What is boiling? The especially rapid evaporation that occurs when the vapor pressure of a liquid ...
File
... More complex reactions cannot be explained using simple redox theory. Chemists have developed a method of “electron bookkeeping” to describe the redox of molecules and complex ions. The oxidation state of an atom in an entity is defined as the apparent net electric charge that it would have if elec ...
... More complex reactions cannot be explained using simple redox theory. Chemists have developed a method of “electron bookkeeping” to describe the redox of molecules and complex ions. The oxidation state of an atom in an entity is defined as the apparent net electric charge that it would have if elec ...
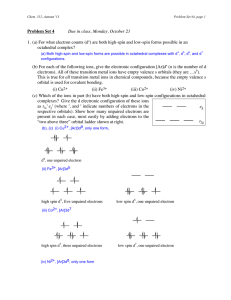
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... because a photon can be absorbed by promotion of one electron from the t2g set of orbitals to the t2g eg set. In a diagram like the one at right, add ground state excited state electrons to represent the ground state and the lowest energy excited state. When you put the electrons in, you should foll ...
... because a photon can be absorbed by promotion of one electron from the t2g set of orbitals to the t2g eg set. In a diagram like the one at right, add ground state excited state electrons to represent the ground state and the lowest energy excited state. When you put the electrons in, you should foll ...
Hooman Mohseni - Center for Detectors
... Traditional semiconductor photon detectors are based on layered heterostructures without a significant geometrical variation along lateral directions. In contrast, we have developed a detector that exploits the additional degrees of freedom offered by a three-dimensional geometry, and utilized a det ...
... Traditional semiconductor photon detectors are based on layered heterostructures without a significant geometrical variation along lateral directions. In contrast, we have developed a detector that exploits the additional degrees of freedom offered by a three-dimensional geometry, and utilized a det ...
7 - Mona Shores Blogs
... 7. At constant temperature, the behavior of a sample of a real gas more closely approximates that of an ideal gas as its volume is increased because the a. collisions with the walls of the container become less frequent b. average molecular speed decreases c. molecules have expanded d. average dista ...
... 7. At constant temperature, the behavior of a sample of a real gas more closely approximates that of an ideal gas as its volume is increased because the a. collisions with the walls of the container become less frequent b. average molecular speed decreases c. molecules have expanded d. average dista ...
QUATERLY 3 REVIEW CHAPTER 12- Stoichiometry Define the law
... 10. Volume and number of gas particles at constant pressure and temperature are ___________________ proportional. 11. If two containers are at the same temperature and pressure and their volumes are equal, they must contain the same ________________________________. Which scientist said this? ______ ...
... 10. Volume and number of gas particles at constant pressure and temperature are ___________________ proportional. 11. If two containers are at the same temperature and pressure and their volumes are equal, they must contain the same ________________________________. Which scientist said this? ______ ...
Gaseous detection device
The gaseous detection device-GDD is a method and apparatus for the detection of signals in the gaseous environment of an environmental scanning electron microscope (ESEM) and all scanned beam type of instruments that allow a minimum gas pressure for the detector to operate.