LBS-100 System
... LBS-100 Attenuator The LBS-100 system that is not as compact as the LBS-300 above but has larger aperture, and has versions for longer wavelengths. The system contains the mounting frame, 1 wedge beam splitter and several attenuators. The exit end of the LBS-100 is standard C mount thread so all our ...
... LBS-100 Attenuator The LBS-100 system that is not as compact as the LBS-300 above but has larger aperture, and has versions for longer wavelengths. The system contains the mounting frame, 1 wedge beam splitter and several attenuators. The exit end of the LBS-100 is standard C mount thread so all our ...
Applying the Concepts of Matter Waves The Heisenberg Uncertainty
... The function ψ is the “wavefunction”, the amplitude of the matter wave. The operator for kinetic energy has second derivatives in it, so the wave equation is a second-order differential equation. Because the equation allows for the incorporation of the “true” potential energy of the system, atoms wi ...
... The function ψ is the “wavefunction”, the amplitude of the matter wave. The operator for kinetic energy has second derivatives in it, so the wave equation is a second-order differential equation. Because the equation allows for the incorporation of the “true” potential energy of the system, atoms wi ...
幻灯片 1
... or fade under illumination. The two-photon method eliminates that problem because the beam is only intense enough to get excitation at the focal point so no other molecules fluoresce. This also eliminates the need for the pinhole because light only comes from the one point. Scanning gives you images ...
... or fade under illumination. The two-photon method eliminates that problem because the beam is only intense enough to get excitation at the focal point so no other molecules fluoresce. This also eliminates the need for the pinhole because light only comes from the one point. Scanning gives you images ...
electron spin and the pauli principle
... assignments of electrons to orbitals: 1) At ground state the electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals available. 2) No orbitals can have more than two electrons. The total number of electrons at any sublevel is shown by a superscript number. Using these rules we can find the electron configuration ...
... assignments of electrons to orbitals: 1) At ground state the electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals available. 2) No orbitals can have more than two electrons. The total number of electrons at any sublevel is shown by a superscript number. Using these rules we can find the electron configuration ...
Photoelectric Effect Lab
... electron, T, is related to the energy of the light absorbed, E, and its initial potential energy in well, U, by the formula TEU ...
... electron, T, is related to the energy of the light absorbed, E, and its initial potential energy in well, U, by the formula TEU ...
ppt file - University of Utah Physics
... fluorescence yield to better than 10%. • Investigate effects of electron energy. • Study effects of atmospheric impurities. • Observe showering of electron pulses in air equivalent substance (Al2O3) with energy equivalents around 1018 eV. ...
... fluorescence yield to better than 10%. • Investigate effects of electron energy. • Study effects of atmospheric impurities. • Observe showering of electron pulses in air equivalent substance (Al2O3) with energy equivalents around 1018 eV. ...
Photoelectric Effect
... The kinetic energy can be measured indirectly by using what is known as the stopping voltage. As the electrons escape, they find themselves moving through an electric field that wants to stop them before they complete their journey to the other electrode. If the field is too great, they turn around ...
... The kinetic energy can be measured indirectly by using what is known as the stopping voltage. As the electrons escape, they find themselves moving through an electric field that wants to stop them before they complete their journey to the other electrode. If the field is too great, they turn around ...
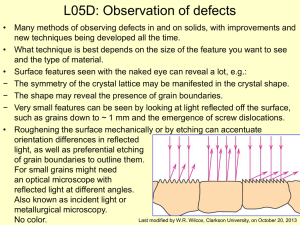
L05D - Clarkson University
... field is on the order of the resolution. As you go up in magnification the depth that is in focus becomes smaller and smaller so only view planar surfaces. • Modern electronics enables imaging of non-planar surfaces. • In SEM a finely focused electron beam is raster scanned across the surface in syn ...
... field is on the order of the resolution. As you go up in magnification the depth that is in focus becomes smaller and smaller so only view planar surfaces. • Modern electronics enables imaging of non-planar surfaces. • In SEM a finely focused electron beam is raster scanned across the surface in syn ...
Sodium: A Charge-Transfer Insulator at High Pressures
... excitonic peaks. This is a sign of highly correlated excitonic states. Anisotropy and inhomogeneity.—By comparing the optical spectra obtained with light polarized either along the hexagonal c axis or in the perpendicular ab plane [Fig. 2(a)], we find that the spectra with the two light polarization ...
... excitonic peaks. This is a sign of highly correlated excitonic states. Anisotropy and inhomogeneity.—By comparing the optical spectra obtained with light polarized either along the hexagonal c axis or in the perpendicular ab plane [Fig. 2(a)], we find that the spectra with the two light polarization ...
Data Analysis
... to be represented by one independent variable x (increasing from left to right) and one dependent variable y (increasing from bottom to top). The word "normally" is required in the above sentence because three-dimensional plots, representing, for example, points with coordinates x, y, and z, can be ...
... to be represented by one independent variable x (increasing from left to right) and one dependent variable y (increasing from bottom to top). The word "normally" is required in the above sentence because three-dimensional plots, representing, for example, points with coordinates x, y, and z, can be ...
Transmission Electron Microscopy
... a. Bright)Field)Imaging)) The conventional TEM imaging mode, often referred as bright field imaging (BF), is based on the sample illumination by a collimated and broad electron beam. Figure 5 presents a simplified electron ray path diagram for the most common TEM configurations, BF and electron diff ...
... a. Bright)Field)Imaging)) The conventional TEM imaging mode, often referred as bright field imaging (BF), is based on the sample illumination by a collimated and broad electron beam. Figure 5 presents a simplified electron ray path diagram for the most common TEM configurations, BF and electron diff ...
Design and Characterization of a Novel Hybrid-field Ion
... mesh and contains a single electrode centered at 0o. The mesh in the nearfield region of the diffusive jet is “unstructured” to satisfy cell size requirements while a “structured” mesh is used throughout the remaining volume with a total number of ~7.5 M cells. Figures 1 (b) and (c) show axial (X) a ...
... mesh and contains a single electrode centered at 0o. The mesh in the nearfield region of the diffusive jet is “unstructured” to satisfy cell size requirements while a “structured” mesh is used throughout the remaining volume with a total number of ~7.5 M cells. Figures 1 (b) and (c) show axial (X) a ...
Measuring and Calculating
... atoms are held together by the sharing of a pair of electrons, which involves an overlap of the electron clouds and thus forms a strong bond and forms individual molecules. Occurs between nonmetal atoms. Nonpolar covalent bond – very low electronegativity difference, results in a nearly equal sh ...
... atoms are held together by the sharing of a pair of electrons, which involves an overlap of the electron clouds and thus forms a strong bond and forms individual molecules. Occurs between nonmetal atoms. Nonpolar covalent bond – very low electronegativity difference, results in a nearly equal sh ...
Semester II Review
... – Determine the Limiting reactant if 3.50 g of hydrogen reacts with 42.0 g of nitrogen. – What is the theoretical yield of the above problem? 39.4 g NH3 – What is the % yield if the reaction produced 15.3 g of ammonia. 38.8 % – Calculate the amount of grams of excess reactant leftover at the end of ...
... – Determine the Limiting reactant if 3.50 g of hydrogen reacts with 42.0 g of nitrogen. – What is the theoretical yield of the above problem? 39.4 g NH3 – What is the % yield if the reaction produced 15.3 g of ammonia. 38.8 % – Calculate the amount of grams of excess reactant leftover at the end of ...
Practice Multiple Choice Questions for the Chemistry Final Exam
... b) fall to a lower energy level. level. c) absorb energy and jump to d) absorb energy and fall to a a higher energy level. lower energy level. 28. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a) energy must be released. b) energy must be absorbed. c) radiation must ...
... b) fall to a lower energy level. level. c) absorb energy and jump to d) absorb energy and fall to a a higher energy level. lower energy level. 28. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a) energy must be released. b) energy must be absorbed. c) radiation must ...
Dear Chemistry Student, I am excited that you have chosen to
... 40. If I have 5.6 liters of gas in a piston at a pressure of 1.5 atm and compress the gas until its volume is 4.8 L, what will the new pressure inside the piston be? 41. A toy balloon has an internal pressure of 1.05 atm and a volume of 5.0 L. If the temperature where the balloon is released is 20°C ...
... 40. If I have 5.6 liters of gas in a piston at a pressure of 1.5 atm and compress the gas until its volume is 4.8 L, what will the new pressure inside the piston be? 41. A toy balloon has an internal pressure of 1.05 atm and a volume of 5.0 L. If the temperature where the balloon is released is 20°C ...
Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in H SO ? A)
... 67) The diagram below represents the electroplating of a metal fork with Ag(s). ...
... 67) The diagram below represents the electroplating of a metal fork with Ag(s). ...
File
... be lost or gained by an atom. Max Planck explained relationship between a quantum of energy and the frequency of radiation: E=hv E=energy in joules v= frequency is s-1 h= Planck’s constant 6.626 X 10-34 J s ...
... be lost or gained by an atom. Max Planck explained relationship between a quantum of energy and the frequency of radiation: E=hv E=energy in joules v= frequency is s-1 h= Planck’s constant 6.626 X 10-34 J s ...
Measurements/Unit Cancellation/Significant Figures 1. When
... Periodic trend: how a certain aspect of periodicity changes as you move down and across the periodic table Ionization energy: the amount of energy needed to remove an outer electron from its orbit periodic trend: increases to the right, decreases going down Electron affinity: energy change that occu ...
... Periodic trend: how a certain aspect of periodicity changes as you move down and across the periodic table Ionization energy: the amount of energy needed to remove an outer electron from its orbit periodic trend: increases to the right, decreases going down Electron affinity: energy change that occu ...
chapter5
... He proposed a planetary model of the atom with the electrons orbiting around the nucleus in a specific circular paths. Each electron has an energy level. Each energy level of the electron can be thought of as rungs on a ladder. The energy levels closest to the nucleus are like rungs of a ladder clos ...
... He proposed a planetary model of the atom with the electrons orbiting around the nucleus in a specific circular paths. Each electron has an energy level. Each energy level of the electron can be thought of as rungs on a ladder. The energy levels closest to the nucleus are like rungs of a ladder clos ...
File
... the temperature is raised to 273DC and the pressure remains constant, the new volume of the gas will be 1) 5.0 L 3) 1.25 L ___ 25) 2) 10. L 4) 2.5 L As the space between molecules in a gas sample decreases, the tendency for the behavior of this gas to deviate from the ideal gas laws 1) decreases 2) ...
... the temperature is raised to 273DC and the pressure remains constant, the new volume of the gas will be 1) 5.0 L 3) 1.25 L ___ 25) 2) 10. L 4) 2.5 L As the space between molecules in a gas sample decreases, the tendency for the behavior of this gas to deviate from the ideal gas laws 1) decreases 2) ...
Electron Beam Lithography
... The history of the electron microscopes starts already in 1930’s and has many interesting features. As the details of the history and the development can be easily found from internet sources let’s skip it here. An electron microscope is a device in which the light used in traditional optical micros ...
... The history of the electron microscopes starts already in 1930’s and has many interesting features. As the details of the history and the development can be easily found from internet sources let’s skip it here. An electron microscope is a device in which the light used in traditional optical micros ...
Chip Scale Light Deflector Enables Solid
... based on three-dimensional (3-D) soliton solutions (or soliton bullets) have been suggested as a means of overcoming this problem.1 However, 3-D soliton bullets are by nature highly unstable and thus tend to disintegrate during propagation. In addition, they require high power levels that are on man ...
... based on three-dimensional (3-D) soliton solutions (or soliton bullets) have been suggested as a means of overcoming this problem.1 However, 3-D soliton bullets are by nature highly unstable and thus tend to disintegrate during propagation. In addition, they require high power levels that are on man ...
Gaseous detection device
The gaseous detection device-GDD is a method and apparatus for the detection of signals in the gaseous environment of an environmental scanning electron microscope (ESEM) and all scanned beam type of instruments that allow a minimum gas pressure for the detector to operate.