SPATIALLY RESOLVED SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND
... in Figure S: A) phase matching temperature ~rresponding to the (assumed) real ,index profile (as measured by focused be~m method), B) phase matching " temperature as 'seen' by optical multichannei analyzer method. The calculation shows that large deviations occur between the two methods when large i ...
... in Figure S: A) phase matching temperature ~rresponding to the (assumed) real ,index profile (as measured by focused be~m method), B) phase matching " temperature as 'seen' by optical multichannei analyzer method. The calculation shows that large deviations occur between the two methods when large i ...
The Polarization of Light
... be limiting cases.) For light to be ”unpolarized” requires a random phase variation between the x and y components of the field, and some time averaging. All light is always fully polarized at any instant in time. Unpolarized light is only possible if there are multiple frequencies present. Our HeNe ...
... be limiting cases.) For light to be ”unpolarized” requires a random phase variation between the x and y components of the field, and some time averaging. All light is always fully polarized at any instant in time. Unpolarized light is only possible if there are multiple frequencies present. Our HeNe ...
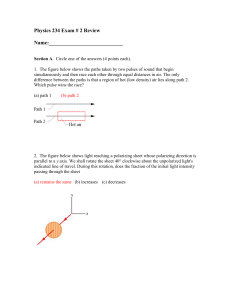
Polarized light and polarizers
... In practice, some light is lost in the polarizer and the actual transmission of unpolarized light will be somewhat lower than this, around 38% for Polaroid-type polarizers. ...
... In practice, some light is lost in the polarizer and the actual transmission of unpolarized light will be somewhat lower than this, around 38% for Polaroid-type polarizers. ...
Slide
... refractive index n is given by n = 0 /n, where 0 is the wavelength in air The optical path difference (OPD) for normal incidence is (AB+BC) times the refractive index of the film. (AB+BC) is approximately equal to twice the thickness, so OPD = n(2t) Reflections are in-phase and therefore add cons ...
... refractive index n is given by n = 0 /n, where 0 is the wavelength in air The optical path difference (OPD) for normal incidence is (AB+BC) times the refractive index of the film. (AB+BC) is approximately equal to twice the thickness, so OPD = n(2t) Reflections are in-phase and therefore add cons ...
Minerals and Their Physical Properties
... The speed of light in a vacuum is always faster than in any other medium so all RI values are >1 ...
... The speed of light in a vacuum is always faster than in any other medium so all RI values are >1 ...
II. Optical properties of glass
... glasses form the basic elements of virtually all optical systems ...
... glasses form the basic elements of virtually all optical systems ...
Anisotropic Minerals
... The equation holds whether light travels from air to water, or water to air. In general, the light is refracted towards the normal to the boundary on entering the material with a higher refractive index and is refracted away from the normal on entering the material with lower refractive index. ...
... The equation holds whether light travels from air to water, or water to air. In general, the light is refracted towards the normal to the boundary on entering the material with a higher refractive index and is refracted away from the normal on entering the material with lower refractive index. ...
Light - Kelso High School
... •Refraction of light including identification of the normal, angle of incidence and angle of refraction. •Description of refraction in terms of change of wave speed. ...
... •Refraction of light including identification of the normal, angle of incidence and angle of refraction. •Description of refraction in terms of change of wave speed. ...
PPT
... ends up bending upwards. We seem to see water on the road, but in fact we are looking at the sky! ...
... ends up bending upwards. We seem to see water on the road, but in fact we are looking at the sky! ...
Optical techniques for molecular manipulation
... • polarization-sensitive absorption (dichroism) • polarization-sensitive dispersion (birefringence, optical activity) • reflection at interfaces • scattering ...
... • polarization-sensitive absorption (dichroism) • polarization-sensitive dispersion (birefringence, optical activity) • reflection at interfaces • scattering ...
Chapter 4
... If the phase matching condition could be fulfilled by some means then instead of the coherence length of Lc=50 m the full length of a crystal of e.g. 2 cm could be used. This would lead to an increase of second harmonic power of a factor 1.6x105. This condition can be met in a special class of crys ...
... If the phase matching condition could be fulfilled by some means then instead of the coherence length of Lc=50 m the full length of a crystal of e.g. 2 cm could be used. This would lead to an increase of second harmonic power of a factor 1.6x105. This condition can be met in a special class of crys ...
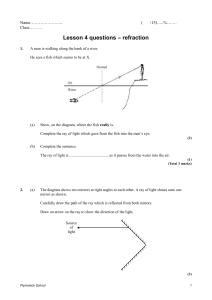
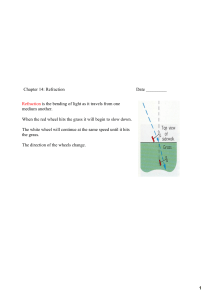
1 Chapter 14: Refraction
... As light enters a different medium, (water in this case) the wave front slows down, but the wave fronts in the air continue to travel at the speed of light in air. The slower wave fronts in water travel a smaller distance than the wave fronts in air so the entire wave front changes direction. The w ...
... As light enters a different medium, (water in this case) the wave front slows down, but the wave fronts in the air continue to travel at the speed of light in air. The slower wave fronts in water travel a smaller distance than the wave fronts in air so the entire wave front changes direction. The w ...
Chapter1 Fundamental law of geometrical optics 第一章 几何光学的
... Ⅰ. Condition:① light in a optically dense medium approach the boundary of a lens dense medium. ② incident angle is larger than critical angle. Ⅱ. Bundles of tiny rods or fibers of clear glass or plastic in orderly array, used to transmit light images. ...
... Ⅰ. Condition:① light in a optically dense medium approach the boundary of a lens dense medium. ② incident angle is larger than critical angle. Ⅱ. Bundles of tiny rods or fibers of clear glass or plastic in orderly array, used to transmit light images. ...
Integrated Optics: Guiding and manipulating light for device
... curiosity. The light behaves as wave and also as particle called photon. It has four primary parameters namely intensity, frequency or wavelength, polarisation and phase. It travels in a straight line unless the space-time itself is curved or the path is altered by means of external optical componen ...
... curiosity. The light behaves as wave and also as particle called photon. It has four primary parameters namely intensity, frequency or wavelength, polarisation and phase. It travels in a straight line unless the space-time itself is curved or the path is altered by means of external optical componen ...
Unit 7 Lab Review - Harrison High School
... speed of sound? 2. In this lab what factor did we have to use to find the theoretical value for the speed of sound? ...
... speed of sound? 2. In this lab what factor did we have to use to find the theoretical value for the speed of sound? ...
Atomic and Molecular Physics for Physicists Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
... Lets use the polarization as a tagging device: The experiment is the famous double slit experiment and the question is: “is complementarity more fundamental than the uncertainty principle…?” You don’t have to measure the photons (or kick them)… its enough that you make such “which path knowledge” ...
... Lets use the polarization as a tagging device: The experiment is the famous double slit experiment and the question is: “is complementarity more fundamental than the uncertainty principle…?” You don’t have to measure the photons (or kick them)… its enough that you make such “which path knowledge” ...
Link to PowerPoint Presentation
... ٭There is a special case of Snell’s Law ٭When going from high density to low density, there is a point after which all of the light is reflected ٭This point is the Critical Angle ...
... ٭There is a special case of Snell’s Law ٭When going from high density to low density, there is a point after which all of the light is reflected ٭This point is the Critical Angle ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).