Ultrafast holographic Stokesmeter for polarization imaging in real time Mark Kleinschmit
... SFS 苷 MFS Si , where MFS11 苷 MFS22 苷 tjj 2 1 t⬜ 2 , MFS12 苷 MFS21 苷 t⬜ 2 2 tjj 2 , and MFS33 苷 MFS44 苷 2tjj t⬜ . MFS is the Mueller matrix for the transmission from the front surface and tk and t⬜ are the Fresnel transmission coeff icients corresponding to the components of linearly polarized light ...
... SFS 苷 MFS Si , where MFS11 苷 MFS22 苷 tjj 2 1 t⬜ 2 , MFS12 苷 MFS21 苷 t⬜ 2 2 tjj 2 , and MFS33 苷 MFS44 苷 2tjj t⬜ . MFS is the Mueller matrix for the transmission from the front surface and tk and t⬜ are the Fresnel transmission coeff icients corresponding to the components of linearly polarized light ...
R.J.Kasumova, Second harmonic generation in
... with the unique properties. Most of us are acquainted with the lenses from the materials with positive refraction in cameras, magnifying glasses, microscopes and telescopes. They have focus distance and place, where depiction is formed, depends on combination of focal distance and the distance bet ...
... with the unique properties. Most of us are acquainted with the lenses from the materials with positive refraction in cameras, magnifying glasses, microscopes and telescopes. They have focus distance and place, where depiction is formed, depends on combination of focal distance and the distance bet ...
Geometric Optics - IndiaStudyChannel.com
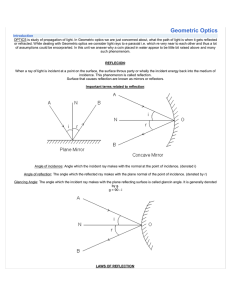
... OPTICS is study of propagation of light. In Geometric optics we are just concerned about, what the path of light is when it gets reflected or refracted. While dealing with Geometric optics we consider light rays to e paraxial i.e. which re very near to each other and thus a lot of assumptions could ...
... OPTICS is study of propagation of light. In Geometric optics we are just concerned about, what the path of light is when it gets reflected or refracted. While dealing with Geometric optics we consider light rays to e paraxial i.e. which re very near to each other and thus a lot of assumptions could ...
Basics of Non-Linear Fiber Optics
... The non-linear Schrodinger equation (NSE) has special importance in the propagation of light in the optical fibers in presence of non-linearity. Although the equation has been derived from the classical Maxwell’s equations, the name has been assigned to the equation due to the fact that in presence ...
... The non-linear Schrodinger equation (NSE) has special importance in the propagation of light in the optical fibers in presence of non-linearity. Although the equation has been derived from the classical Maxwell’s equations, the name has been assigned to the equation due to the fact that in presence ...
may11-95 as a Word 6.0 doc - Lyle School of Engineering
... Note #1: each question is worth 3 points except #23, which is worth 1 point. Note #2: ...
... Note #1: each question is worth 3 points except #23, which is worth 1 point. Note #2: ...
Download PDF
... a multiple-scattering medium. In LCI, only the class of waves that have traveled an optical distance that corresponds to the length of the reference arm is able to produce fringes and is, therefore, detected. In the optical path-length domain, the interferometer acts as a bandpass filter with a band ...
... a multiple-scattering medium. In LCI, only the class of waves that have traveled an optical distance that corresponds to the length of the reference arm is able to produce fringes and is, therefore, detected. In the optical path-length domain, the interferometer acts as a bandpass filter with a band ...
Lens Aberrations
... It is therefore possible to define any polarization orientation with a constant vector in the x-y plane for the case of linear polarization. For linear polarization, the state of polarization is often referred to as a P - state. This is the symbol for a script P. ...
... It is therefore possible to define any polarization orientation with a constant vector in the x-y plane for the case of linear polarization. For linear polarization, the state of polarization is often referred to as a P - state. This is the symbol for a script P. ...
propagation of light in an optical fiber
... core, or decrease in wavelength) more values of m satisfy the condition and therefore have sustained propagation inside the fiber. The above phase condition can be satisfied only by discrete rays entering the structure i.e. rays at finite number of angles are accepted by the optical fiber. The ensem ...
... core, or decrease in wavelength) more values of m satisfy the condition and therefore have sustained propagation inside the fiber. The above phase condition can be satisfied only by discrete rays entering the structure i.e. rays at finite number of angles are accepted by the optical fiber. The ensem ...
introduction - Academic Science,International Journal of Computer
... quantum well is computed as a function of wavelength for the incident normal and p-polarized electromagnetic waves respectively centered at 1.55 µm. In Fig 2a, transmittance of 11 layers GaN/Al0.35Ga0.65N PMQW is plotted for normal incidence at 1.55 µm, and results are compared with conventional pho ...
... quantum well is computed as a function of wavelength for the incident normal and p-polarized electromagnetic waves respectively centered at 1.55 µm. In Fig 2a, transmittance of 11 layers GaN/Al0.35Ga0.65N PMQW is plotted for normal incidence at 1.55 µm, and results are compared with conventional pho ...
Total Reflection and Negative Refraction of
... to 180˚ , the condition of k x′′ = k x0 required for refraction of the incident DESWs is no longer satisfied. The total reflection for the 45˚ incidence angle shown in Figs. 3(a) and 3(b) is one among those available angles. We also report on an intriguing negative refraction behavior of DESWs. Nega ...
... to 180˚ , the condition of k x′′ = k x0 required for refraction of the incident DESWs is no longer satisfied. The total reflection for the 45˚ incidence angle shown in Figs. 3(a) and 3(b) is one among those available angles. We also report on an intriguing negative refraction behavior of DESWs. Nega ...
4 Lab 1: Scattering and Reflection of Polarized Light
... reflected from a surface can be polarized. Apparently, as the sun was setting, Malus was looking at the light reflected from the windows of the Luxembourg palace through a calcite crystal. Because calcite produces two images corresponding to its two mutually perpendicular polarization directions, on ...
... reflected from a surface can be polarized. Apparently, as the sun was setting, Malus was looking at the light reflected from the windows of the Luxembourg palace through a calcite crystal. Because calcite produces two images corresponding to its two mutually perpendicular polarization directions, on ...
Low-Loss TiO2 Planar Waveguides for Nanophotonic
... School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, 9 Oxford Street, Cambridge, MA, 02138 ...
... School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, 9 Oxford Street, Cambridge, MA, 02138 ...
Observation of total omnidirectional reflection from a one
... In this communication, we report that total omnidirectional reflection does not require a 2D or 3D photonic crystal [15]. We demonstrate theoretically and experimentally that under certain conditions a 1D photonic crystal can exhibit total reflection for all incident angles. A one-dimensional photon ...
... In this communication, we report that total omnidirectional reflection does not require a 2D or 3D photonic crystal [15]. We demonstrate theoretically and experimentally that under certain conditions a 1D photonic crystal can exhibit total reflection for all incident angles. A one-dimensional photon ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).