Chapter One: An Introduction to Nonlinear Optics, Second Order
... Since the initial observation in 1961 of second harmonic generation from a quartz crystal pumped by a ruby laser1, second order non-linear optical effects have been of great interest. Frequency mixing capabilities are routinely used in laboratory settings to convert laser wavelengths to different re ...
... Since the initial observation in 1961 of second harmonic generation from a quartz crystal pumped by a ruby laser1, second order non-linear optical effects have been of great interest. Frequency mixing capabilities are routinely used in laboratory settings to convert laser wavelengths to different re ...
Optical simulation to enhance PV module encapsulation
... (part of irradiance entering the silicon solar cell at an incidence angle of 80 deg) as a function of the refractive indices of the upper two layers. Also indicated is the point of best optical matching (“Max”) and an example of a real PV module (“Real”). Figure 8 shows the optical transmission for ...
... (part of irradiance entering the silicon solar cell at an incidence angle of 80 deg) as a function of the refractive indices of the upper two layers. Also indicated is the point of best optical matching (“Max”) and an example of a real PV module (“Real”). Figure 8 shows the optical transmission for ...
Optical Fiber Communication
... chromatic dispersion. Furthermore, semiconductor lasers can be modulated directly at high frequencies because of short recombination time. ...
... chromatic dispersion. Furthermore, semiconductor lasers can be modulated directly at high frequencies because of short recombination time. ...
Fiber Bragg Gratings
... decrease equally for any index change experienced by the Bloch wave. Floquet’s theorem requires that neither wave-vector’s real component may change in the stop band, thus only the imaginary part may change. Further properties given by Bloch wave analysis such as higher-order dispersion will not be ...
... decrease equally for any index change experienced by the Bloch wave. Floquet’s theorem requires that neither wave-vector’s real component may change in the stop band, thus only the imaginary part may change. Further properties given by Bloch wave analysis such as higher-order dispersion will not be ...
Optical power - WordPress.com
... rates between core and cladding. Geometric imperfection along the axis. constant radius bend – excessive pressure and tension during handling and installation ...
... rates between core and cladding. Geometric imperfection along the axis. constant radius bend – excessive pressure and tension during handling and installation ...
Brightfield Contrasting Techniques
... • Polarizers specifically transmit one polarization angle of light ...
... • Polarizers specifically transmit one polarization angle of light ...
Review sheet - Carleton College
... Purpose: This lab will introduce you to some of the important optical properties of uniaxial minerals. Optically uniaxial minerals are those that belong to the tetragonal and hexagonal crystal systems. These minerals appear anisotropic in all orientations but one: that being the section cut perpendi ...
... Purpose: This lab will introduce you to some of the important optical properties of uniaxial minerals. Optically uniaxial minerals are those that belong to the tetragonal and hexagonal crystal systems. These minerals appear anisotropic in all orientations but one: that being the section cut perpendi ...
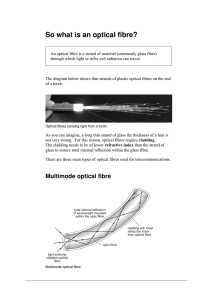
optical fibres
... Only one light wave can fit inside the inner core at one time. An impulse of light travels through the high refractive index material centre. Because there is no interference with other waves and the light contained inside the core cannot spread out due to the size of the core, the quality of the in ...
... Only one light wave can fit inside the inner core at one time. An impulse of light travels through the high refractive index material centre. Because there is no interference with other waves and the light contained inside the core cannot spread out due to the size of the core, the quality of the in ...
Universal Description of Spherical Aberration Free Lenses
... It was known to René Descartes as early as 1637 that aspherical surfaces are required to convert plane waves into spherical waves and vice versa. In the short wavelength limit of geometric optics, the right conic surface can bring all parallel incident light rays to a single common focus point. Mos ...
... It was known to René Descartes as early as 1637 that aspherical surfaces are required to convert plane waves into spherical waves and vice versa. In the short wavelength limit of geometric optics, the right conic surface can bring all parallel incident light rays to a single common focus point. Mos ...
- vjs.ac.vn
... For simplicity, we assume that the radius (a) of the particle is much smaller than the wavelength of the laser (i.e., a ), in this case we can treat the dielectric particle as a point dipole. We also assume that the refractive index of the dielectric particle is n1 and n1 n2 . This is the ne ...
... For simplicity, we assume that the radius (a) of the particle is much smaller than the wavelength of the laser (i.e., a ), in this case we can treat the dielectric particle as a point dipole. We also assume that the refractive index of the dielectric particle is n1 and n1 n2 . This is the ne ...
SRON presentation - University of Groningen
... But: “Pure” (geometrical) optical systems would require components much larger than λ. In sub- /mm range diffraction is important, and quasi-optics handles this in a theorectical way. ...
... But: “Pure” (geometrical) optical systems would require components much larger than λ. In sub- /mm range diffraction is important, and quasi-optics handles this in a theorectical way. ...
Poincare Modes of Light
... Poincaré beams are a general form of vector beams. Their transverse profile carries a state of polarization that varies from point to point. These polarization-state patterns constitute partial, full or multiple mappings of the Poincaré sphere onto the transverse plane of the mode. A general state ...
... Poincaré beams are a general form of vector beams. Their transverse profile carries a state of polarization that varies from point to point. These polarization-state patterns constitute partial, full or multiple mappings of the Poincaré sphere onto the transverse plane of the mode. A general state ...
Lecture_1
... • Coordination # increases with Issue: How many anions can you arrange around a cation? ...
... • Coordination # increases with Issue: How many anions can you arrange around a cation? ...
1 L2: Reflection and Refraction c3.L2 REFLECTION AND
... Colours of objects can be explained by supposing that their surfaces reflect different proportions of the various frequency (or wavelength) components of the incident light. Different mixes of these components produce the different visual sensations that we call colour. It is worth noting in passing ...
... Colours of objects can be explained by supposing that their surfaces reflect different proportions of the various frequency (or wavelength) components of the incident light. Different mixes of these components produce the different visual sensations that we call colour. It is worth noting in passing ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).