Liquid crystals
... gradually rotates the plane of polarization of light by 90o . Hence a linearly polarized light incident on the cell emerges linearly polarized but in an orthogonal direction resulting in a bright appearance. The 90o twist in the cell is lost when a sufficiently strong electric field is applied to th ...
... gradually rotates the plane of polarization of light by 90o . Hence a linearly polarized light incident on the cell emerges linearly polarized but in an orthogonal direction resulting in a bright appearance. The 90o twist in the cell is lost when a sufficiently strong electric field is applied to th ...
A Study of the Phenomenon of Spontaneous Parametric Down
... A diagram of the experimental setup is illustrated in Fig. 2. The setup consists of a pump laser diode that was used to emit a photon beam having wavelength 405 nm which was directed using a mirror, which was designed to reflect light having wavelengths between 400 nm and 750 nm, through a uniaxial, ...
... A diagram of the experimental setup is illustrated in Fig. 2. The setup consists of a pump laser diode that was used to emit a photon beam having wavelength 405 nm which was directed using a mirror, which was designed to reflect light having wavelengths between 400 nm and 750 nm, through a uniaxial, ...
The creation and annihilation of optical vortices using cascade
... convert a circularly polarised light beam with σ = +1ħ to a beam with = +2ħ with a very high efficiency (up to 98%), but can have problems with mode quality [7]. Several groups have shown internal conical diffraction (ICD) using a single biaxial crystal provides an efficient means for the convers ...
... convert a circularly polarised light beam with σ = +1ħ to a beam with = +2ħ with a very high efficiency (up to 98%), but can have problems with mode quality [7]. Several groups have shown internal conical diffraction (ICD) using a single biaxial crystal provides an efficient means for the convers ...
A review of metasurfaces: physics and applications
... 2. Anomalous reflection and refraction 2.1. Generalized laws of reflection and refraction When a plane electromagnetic wave encounters a boundary between two homogeneous media with different refractive indices, it is split into a reflected beam that propagates back to the first medium and a transmit ...
... 2. Anomalous reflection and refraction 2.1. Generalized laws of reflection and refraction When a plane electromagnetic wave encounters a boundary between two homogeneous media with different refractive indices, it is split into a reflected beam that propagates back to the first medium and a transmit ...
Guided-Wave Optical Biosensors
... Fig. 6 shows both Raman scattering mechanisms. In case of Raman to Stokes scattering, the molecule is at the lowest energetic level S 0 0 . When an electromagnetic beam strikes the sample, the molecule passes to a higher energetic level and then it returns to a lower energetic level S 01 by emitting ...
... Fig. 6 shows both Raman scattering mechanisms. In case of Raman to Stokes scattering, the molecule is at the lowest energetic level S 0 0 . When an electromagnetic beam strikes the sample, the molecule passes to a higher energetic level and then it returns to a lower energetic level S 01 by emitting ...
Four Aces of Refractive Surgery: Aberrations
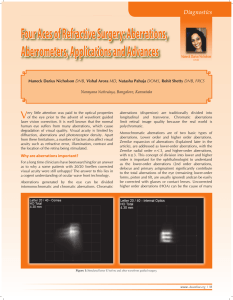
... Shack principle. It is a technique developed by Johannes Hartmann in 1900 and modified by Shack and Platt in the late 1960s. Numerous other methodologies and applications have since arisen.The first measurements of HOAs were conducted by Smirov using a psychophysical method, in 19618. All aberromete ...
... Shack principle. It is a technique developed by Johannes Hartmann in 1900 and modified by Shack and Platt in the late 1960s. Numerous other methodologies and applications have since arisen.The first measurements of HOAs were conducted by Smirov using a psychophysical method, in 19618. All aberromete ...
Unit4
... Consists of a tunable bandpass filter and an optical power meter The light from the input fibre is collimated and applied to the diffraction grating The diffraction grating separates the input light into different angles depending on wavelength The light from the grating is then focused onto an outp ...
... Consists of a tunable bandpass filter and an optical power meter The light from the input fibre is collimated and applied to the diffraction grating The diffraction grating separates the input light into different angles depending on wavelength The light from the grating is then focused onto an outp ...
Fast Light, Slow Light and Optical Precursors: What
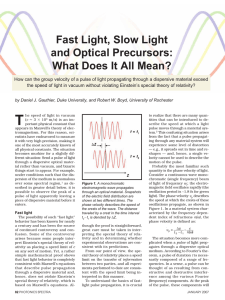
... to realize that there are many quantities that can be introduced to describe the speed at which a light pulse moves through a material system.2 This confusing situation arises from the fact that a pulse propagating through any material system will experience some level of distortion — e.g., it sprea ...
... to realize that there are many quantities that can be introduced to describe the speed at which a light pulse moves through a material system.2 This confusing situation arises from the fact that a pulse propagating through any material system will experience some level of distortion — e.g., it sprea ...
TS2
... band gap guidance. Although the first (solid core) photonic band gap fiber was reported in 1998 (27) (Fig. 3, E and F), hollow-core guidance had Fig. 3. An assortment of optical (OM) and scanning electron (SEM) to wait until the technolomicrographs of PCF structures. (A) SEM of an endlessly single-m ...
... band gap guidance. Although the first (solid core) photonic band gap fiber was reported in 1998 (27) (Fig. 3, E and F), hollow-core guidance had Fig. 3. An assortment of optical (OM) and scanning electron (SEM) to wait until the technolomicrographs of PCF structures. (A) SEM of an endlessly single-m ...
How optics has changed data communications
... In the backbone of today’s high performance networks, optical fibers provide enormous point-to-point communications capacity. To accommodate the rapidly growing volume of communications traffic, each fiber’s capacity can be augmented by using “Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)”, Commerci ...
... In the backbone of today’s high performance networks, optical fibers provide enormous point-to-point communications capacity. To accommodate the rapidly growing volume of communications traffic, each fiber’s capacity can be augmented by using “Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)”, Commerci ...
Phase Mismatch–Free Nonlinear Propagation in Optical Zero
... fishnet of 20 layers. In contrast, for thin fishnets (fewer than five layers), the forward/backward ratio is unity regardless of the index of refraction, indicating that phase matching is not important in these structures (23–26). The nonlinear simulation is performed with nonlinear scattering theor ...
... fishnet of 20 layers. In contrast, for thin fishnets (fewer than five layers), the forward/backward ratio is unity regardless of the index of refraction, indicating that phase matching is not important in these structures (23–26). The nonlinear simulation is performed with nonlinear scattering theor ...
The Equation of Number the Total Internal of Reflection Angles
... close to the axis and at various angles, allowing efficient coupling of light into the fiber .However, this high numerical aperture increases the amount of dispersion as rays at different angles have different path length and therefore take different times to traverse the fiber.In graded – index fib ...
... close to the axis and at various angles, allowing efficient coupling of light into the fiber .However, this high numerical aperture increases the amount of dispersion as rays at different angles have different path length and therefore take different times to traverse the fiber.In graded – index fib ...
Light scattering models of white blood cells and back
... 9–12 μm in a medium one; and 13–20 μm in a large one. The lymphocytes in the blood are mostly the small ones. The nucleus is round-shaped and a shallow concavity often appears on one side of it. The chromatin with a small amount of cytoplasm is densely shaped as lumpy masses and forms a narrow band ...
... 9–12 μm in a medium one; and 13–20 μm in a large one. The lymphocytes in the blood are mostly the small ones. The nucleus is round-shaped and a shallow concavity often appears on one side of it. The chromatin with a small amount of cytoplasm is densely shaped as lumpy masses and forms a narrow band ...
Wave Optics
... Thin-Film Interference For light, as for any electromagnetic wave, wavelength, frequency, and speed are related by ...
... Thin-Film Interference For light, as for any electromagnetic wave, wavelength, frequency, and speed are related by ...
Wave Optics
... Thin-Film Interference For light, as for any electromagnetic wave, wavelength, frequency, and speed are related by ...
... Thin-Film Interference For light, as for any electromagnetic wave, wavelength, frequency, and speed are related by ...
Optical study of lead borosilicate glasses
... related to their applicability in the field of optics and electronics. It was found that, the optical non-linearity is caused by the electronic polarization of a material upon its exposure to intense light beams, thus, the non-linear response of the material is governed by the ...
... related to their applicability in the field of optics and electronics. It was found that, the optical non-linearity is caused by the electronic polarization of a material upon its exposure to intense light beams, thus, the non-linear response of the material is governed by the ...
Theoretical and empirical comparison of coupling coefficient and
... Wherever the two curves intersect, we have the same refractive index at certain separation fiber for both core and cladding. This occurs since the change of d, n1 and n2 attain the same κ. It also expresses that refractive indices are proportional to κ. The curve calculation is in a wide range of d ...
... Wherever the two curves intersect, we have the same refractive index at certain separation fiber for both core and cladding. This occurs since the change of d, n1 and n2 attain the same κ. It also expresses that refractive indices are proportional to κ. The curve calculation is in a wide range of d ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Tip-tilt mirror and sensor configuration
... Off-axis object is equivalent to having a de-centered ray bundle Spherical surface ...
... Off-axis object is equivalent to having a de-centered ray bundle Spherical surface ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).