Retarder Principles
... From the equations shown on the previous page, a true zeroorder quartz quarter waveplate for 550 nm operation is only 15 mm thick. Such a thin, fragile retarder presents handling difficulties in both fabrication and mounting. More commonly, multiple-order quartz retarders having a whole number of wa ...
... From the equations shown on the previous page, a true zeroorder quartz quarter waveplate for 550 nm operation is only 15 mm thick. Such a thin, fragile retarder presents handling difficulties in both fabrication and mounting. More commonly, multiple-order quartz retarders having a whole number of wa ...
幻灯片 1 - USTC, ICTS
... History of Nonautonomous Solitons Reason: A: The test of solitons in nonuniform media with time-dependent density gradients .(spatial soliton) B: The test of the core medium of the real fibers, which cannot be homogeneous, fiber loss is inevitable, and dissipation weakens the nonlinearity.(temporal ...
... History of Nonautonomous Solitons Reason: A: The test of solitons in nonuniform media with time-dependent density gradients .(spatial soliton) B: The test of the core medium of the real fibers, which cannot be homogeneous, fiber loss is inevitable, and dissipation weakens the nonlinearity.(temporal ...
Molten-core fabrication of novel optical fibers
... The resultant core glasses contain much higher yttria and alumina concentrations than would otherwise be possible, opening the door to “novel fibers from common materials” (just not common when it comes to optical fibers). For example, the YAG-derived fibers with high yttria and alumina contents hav ...
... The resultant core glasses contain much higher yttria and alumina concentrations than would otherwise be possible, opening the door to “novel fibers from common materials” (just not common when it comes to optical fibers). For example, the YAG-derived fibers with high yttria and alumina contents hav ...
Suppression of stimulated Brillouin scattering in
... Stokes pulse carries less than 0.1% of the pump energy in the forward direction and virtually no energy in the backward direction. In general, the grating needs a minimum value of κ before it is strong enough to suppress the SBS totally, and this minimum value increases with the pump peak power P0. ...
... Stokes pulse carries less than 0.1% of the pump energy in the forward direction and virtually no energy in the backward direction. In general, the grating needs a minimum value of κ before it is strong enough to suppress the SBS totally, and this minimum value increases with the pump peak power P0. ...
Initial demonstration of a local, evanescent, array coupled biosensor concept
... technique has been employed to study basic optical phenomena in waveguides such as propagation loss, spatial mode profiles, and modal interference [5-10]. In this work, NSOM is used for the first time to analyze a waveguide’s evanescent field change due to an adlayer. The measured results are shown ...
... technique has been employed to study basic optical phenomena in waveguides such as propagation loss, spatial mode profiles, and modal interference [5-10]. In this work, NSOM is used for the first time to analyze a waveguide’s evanescent field change due to an adlayer. The measured results are shown ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... where R is the reflectivity and k (k = αλ / 4π) is the extinction coefficient. The extinction coefficient k describes the properties of the material with respect to light of a given wavelength and indicates the absorption changes when the electromagnetic wave propagates through the material. Fig. (5 ...
... where R is the reflectivity and k (k = αλ / 4π) is the extinction coefficient. The extinction coefficient k describes the properties of the material with respect to light of a given wavelength and indicates the absorption changes when the electromagnetic wave propagates through the material. Fig. (5 ...
engineering of complex optical fields and its
... Fig. 4-2. SOPs evolution for second order FP beam at 1). z = -10zR, 2). z = -zR, 3). z = 0, 4). z = zR and 5). z = 10zR. ................................................................................................ 37 Fig. 4-3. One slice (shown in red) of the Poincaré sphere at fixed ϕ and r/w(z) ...
... Fig. 4-2. SOPs evolution for second order FP beam at 1). z = -10zR, 2). z = -zR, 3). z = 0, 4). z = zR and 5). z = 10zR. ................................................................................................ 37 Fig. 4-3. One slice (shown in red) of the Poincaré sphere at fixed ϕ and r/w(z) ...
Slow light in various media: a tutorial
... energy between the light and medium. One can get a better intuitive picture of the physical phenomena governing slow light propagation by plotting the dispersion curve in the absence of loss (i.e., ␥12 = 0) as the dashed curve in Fig. 1(d). This curve corresponds to a well-known coupled modes model, ...
... energy between the light and medium. One can get a better intuitive picture of the physical phenomena governing slow light propagation by plotting the dispersion curve in the absence of loss (i.e., ␥12 = 0) as the dashed curve in Fig. 1(d). This curve corresponds to a well-known coupled modes model, ...
Design and use of guided mode resonance filters for
... Even though the principles of diffraction had been known since the time of Newton, it was Rittenhouse who in 1786, produced the first man-made diffraction grating from hairs spaced by the threads of two fine screws [1]. Years later, in 1902, Wood noticed unexpected rapid intensity variations in ligh ...
... Even though the principles of diffraction had been known since the time of Newton, it was Rittenhouse who in 1786, produced the first man-made diffraction grating from hairs spaced by the threads of two fine screws [1]. Years later, in 1902, Wood noticed unexpected rapid intensity variations in ligh ...
THz Materials
... and cooled down to -45 ÷ -120° C depending on grade. PE has good dielectric characteristics, chemical resistance, and radioresistance. However it is unstable to UV-radiation, fats, and oils. PE is biologically inert and easy to be processed. Density (23°C) is 0.91-0.925 g/cm3. Tensile flow limit (23 ...
... and cooled down to -45 ÷ -120° C depending on grade. PE has good dielectric characteristics, chemical resistance, and radioresistance. However it is unstable to UV-radiation, fats, and oils. PE is biologically inert and easy to be processed. Density (23°C) is 0.91-0.925 g/cm3. Tensile flow limit (23 ...
characterization of nondiffracting bessel beams in the propagation
... [7] and free-space optical communications [8]. For these applications, the useful part of the Bessel beams is often limited to their near field. As a matter of fact, the central lobe persists as long as there are off-axis lobes to replenish its diffraction losses and prevent it from spreading [9, 10 ...
... [7] and free-space optical communications [8]. For these applications, the useful part of the Bessel beams is often limited to their near field. As a matter of fact, the central lobe persists as long as there are off-axis lobes to replenish its diffraction losses and prevent it from spreading [9, 10 ...
Gain-Flattening Filters Using Dielectric Multilayer Thin Film
... is 1550 nm. When the incident light is not normal to the thin film surface, the polarization-dependent loss (PDL) takes a finite value. Figure 2 shows the results of theoretical calculations for PDL for designs based in which the optical thickness is 1 and 3 times one quarter of the center wavelengt ...
... is 1550 nm. When the incident light is not normal to the thin film surface, the polarization-dependent loss (PDL) takes a finite value. Figure 2 shows the results of theoretical calculations for PDL for designs based in which the optical thickness is 1 and 3 times one quarter of the center wavelengt ...
PDF
... vortex lines in electron beams8 are hard to obtain and study but often can be understood by probing defects in other topologically similar but more easily accessible systems, such as LCs and laser beams1–5,8,14. A nematic LC is typically comprised of rod-like molecules that spontaneously orient them ...
... vortex lines in electron beams8 are hard to obtain and study but often can be understood by probing defects in other topologically similar but more easily accessible systems, such as LCs and laser beams1–5,8,14. A nematic LC is typically comprised of rod-like molecules that spontaneously orient them ...
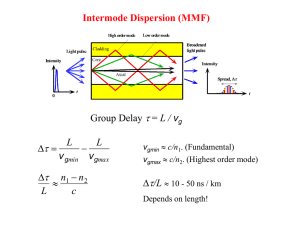
Waveguide Dispersion
... Combining intermodal and intramodal dispersions Consider a graded index fiber with a core diameter of 30 mm and a refractive index of 1.474 at the center of the core and a cladding refractive index of 1.453. Suppose that we use a laser diode emitter with a spectral linewidth of 3 nm to transmit alo ...
... Combining intermodal and intramodal dispersions Consider a graded index fiber with a core diameter of 30 mm and a refractive index of 1.474 at the center of the core and a cladding refractive index of 1.453. Suppose that we use a laser diode emitter with a spectral linewidth of 3 nm to transmit alo ...
T - International Journal of Electronics and Telecommunications
... COMSOL Multiphysics (version 4.2) has been used to arrange the structure of the fiber. Finite element method (FEM) with a perfectly matched layer (PML) has been used to study the propagation characteristics of the waveguide. The cladding of the fiber has a hexagonal distribution with three air hole ...
... COMSOL Multiphysics (version 4.2) has been used to arrange the structure of the fiber. Finite element method (FEM) with a perfectly matched layer (PML) has been used to study the propagation characteristics of the waveguide. The cladding of the fiber has a hexagonal distribution with three air hole ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).