Paper
... regard the angular dependence of superradiant Raman scattering as a dependence on the intensity of the component of the incident light, which scales as cos2 ␣, where ␣ is the angle between the electric-field vector and the axis. Indeed, the rescaled data of Fig. 4 nicely matches the other data sho ...
... regard the angular dependence of superradiant Raman scattering as a dependence on the intensity of the component of the incident light, which scales as cos2 ␣, where ␣ is the angle between the electric-field vector and the axis. Indeed, the rescaled data of Fig. 4 nicely matches the other data sho ...
Bessel Beam Theory - u.arizona.edu
... Diffraction is a feature of the wave nature of light. It can occur anytime a beam of light passes through an aperture that is large with respect to its wavelength1. According to the Huygens-Fresnel Principle2, every point of the wavefront that is unobstructed by the hindrance serves as a source of s ...
... Diffraction is a feature of the wave nature of light. It can occur anytime a beam of light passes through an aperture that is large with respect to its wavelength1. According to the Huygens-Fresnel Principle2, every point of the wavefront that is unobstructed by the hindrance serves as a source of s ...
Lecture 7
... • Since there is no perfect way to present them (they all tie into each other) we’ll just start somewhere and get going… Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math ...
... • Since there is no perfect way to present them (they all tie into each other) we’ll just start somewhere and get going… Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math ...
Snell`s Law
... The rays (directions of propagation) are straight lines perpendicular to the wave fronts The above assumption is valid only when the size of the barrier (or the size of the media) is much larger than the wavelength of light ...
... The rays (directions of propagation) are straight lines perpendicular to the wave fronts The above assumption is valid only when the size of the barrier (or the size of the media) is much larger than the wavelength of light ...
Nonlocal Labeling of Paths in a Single-Photon Interferometer
... NONLOCAL LABELING OF PATHS IN A SINGLE-… ...
... NONLOCAL LABELING OF PATHS IN A SINGLE-… ...
Diffraction
... Large number of small zones, each with a width y. Phase difference between adjacent zones: = (2/)y sin Total electric filed E at point P: EP = Esin(t) + Esin(t+) +…+ Esin(t+N) It can be shown that: EP =(NE)[sin(/2)/(/2)]sin(t+), where = N = (2/) a sin. Light intensity ...
... Large number of small zones, each with a width y. Phase difference between adjacent zones: = (2/)y sin Total electric filed E at point P: EP = Esin(t) + Esin(t+) +…+ Esin(t+N) It can be shown that: EP =(NE)[sin(/2)/(/2)]sin(t+), where = N = (2/) a sin. Light intensity ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... no matter what other interdependencies may exist between the variables. But if we look at Eq. (3) of [1], we see that the implicit premise is that ...
... no matter what other interdependencies may exist between the variables. But if we look at Eq. (3) of [1], we see that the implicit premise is that ...
Optical Prescriptions Spectacle Lenses
... Any vibrations which are perpendicular to the polarization axis are blocked by the filter. Thus, a Polaroid filter with its long-chain molecules aligned horizontally will have a polarization axis aligned vertically. ...
... Any vibrations which are perpendicular to the polarization axis are blocked by the filter. Thus, a Polaroid filter with its long-chain molecules aligned horizontally will have a polarization axis aligned vertically. ...
MICROWAVE AND LIGHT INTERFERENCE - Galileo
... Electromagnetic waves carry energy. The energy density at any point is proportional to the square of the net electric field. The intensity (what we can observe) is the time average of the energy density. Important Note: To find the intensity of the electromagnetic waves at any point, we must first a ...
... Electromagnetic waves carry energy. The energy density at any point is proportional to the square of the net electric field. The intensity (what we can observe) is the time average of the energy density. Important Note: To find the intensity of the electromagnetic waves at any point, we must first a ...
reflection and refraction
... (A) Lead ball will float with ~ 83% of volume below mercury surface (B) Lead ball will float with 100% of volume below mercury surface (C) Lead ball will float with ~17% of volume below mercury surface (D) Lead ball will sink ...
... (A) Lead ball will float with ~ 83% of volume below mercury surface (B) Lead ball will float with 100% of volume below mercury surface (C) Lead ball will float with ~17% of volume below mercury surface (D) Lead ball will sink ...
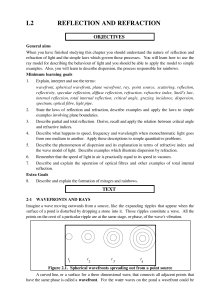
L2 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
... Colours of objects can be explained by supposing that their surfaces reflect different proportions of the various frequency (or wavelength) components of the incident light. Different mixes of these components produce the different visual sensations that we call colour. It is worth noting in passing ...
... Colours of objects can be explained by supposing that their surfaces reflect different proportions of the various frequency (or wavelength) components of the incident light. Different mixes of these components produce the different visual sensations that we call colour. It is worth noting in passing ...
1 L2: Reflection and Refraction c3.L2 REFLECTION AND
... Colours of objects can be explained by supposing that their surfaces reflect different proportions of the various frequency (or wavelength) components of the incident light. Different mixes of these components produce the different visual sensations that we call colour. It is worth noting in passing ...
... Colours of objects can be explained by supposing that their surfaces reflect different proportions of the various frequency (or wavelength) components of the incident light. Different mixes of these components produce the different visual sensations that we call colour. It is worth noting in passing ...
Polarized Light Assessment of Complex Turbid
... We have recently developed and validated an expanded Mueller matrix decomposition approach for extraction, quantification and unique interpretation of individual intrinsic polarimetry characteristics in complex tissue-like turbid media [17,18]. The ability of this approach to delineate individual in ...
... We have recently developed and validated an expanded Mueller matrix decomposition approach for extraction, quantification and unique interpretation of individual intrinsic polarimetry characteristics in complex tissue-like turbid media [17,18]. The ability of this approach to delineate individual in ...
Experimental demonstration of a narrowband, angular tolerant
... strength between the incident field and the eigenmode. In the usual case where the eigenmode is excited through the first order of the grating, this coupling strength is related to the first Fourier harmonic of the grating permittivity, ⑀1. When two counterpropagative modes are excited (e.g., in nor ...
... strength between the incident field and the eigenmode. In the usual case where the eigenmode is excited through the first order of the grating, this coupling strength is related to the first Fourier harmonic of the grating permittivity, ⑀1. When two counterpropagative modes are excited (e.g., in nor ...
Excitation of Surface Plasma Wave in Layered Structure of Au/Ap
... couple directly with light in air, i.e. SPW is non-radiative in this model. However, if a spacer-layer with dielectric constant es is introduced between the dielectric medium and the metal film such that the dielectric constant of the incident medium, er, is greater than E,, then the evanescent wave ...
... couple directly with light in air, i.e. SPW is non-radiative in this model. However, if a spacer-layer with dielectric constant es is introduced between the dielectric medium and the metal film such that the dielectric constant of the incident medium, er, is greater than E,, then the evanescent wave ...
CHAPTER 10
... 10.4 Red light, =600nm, enters a glass block whereupon its velocity is two-thirds that of its velocity in vacuum. Find the refractive index of the glass for this wavelength and the wavelength in the glass. 10.5 A ray of monochromatic light is incident at 40 on a plane air/glass boundary. If the r ...
... 10.4 Red light, =600nm, enters a glass block whereupon its velocity is two-thirds that of its velocity in vacuum. Find the refractive index of the glass for this wavelength and the wavelength in the glass. 10.5 A ray of monochromatic light is incident at 40 on a plane air/glass boundary. If the r ...
Part 4 - MZA Associates Corporation
... Modeling Localized Optical Effects In wave optics simulation all optical effects, with the sole exception of optical propagation through vacuum or an ideal dielectric medium, are modeled as if they occurred at discrete planes. This is an approximation of course, since many important effects, such a ...
... Modeling Localized Optical Effects In wave optics simulation all optical effects, with the sole exception of optical propagation through vacuum or an ideal dielectric medium, are modeled as if they occurred at discrete planes. This is an approximation of course, since many important effects, such a ...
Holography - Princeton University
... desired intensity. Higher intensities (consistent with a suitable reference/object ratio), will need shorter exposure times, and, will, in general, produce better holograms. Check that the reference beam is smooth across the film. In addition, you should make sure that the optical surfaces are clean ...
... desired intensity. Higher intensities (consistent with a suitable reference/object ratio), will need shorter exposure times, and, will, in general, produce better holograms. Check that the reference beam is smooth across the film. In addition, you should make sure that the optical surfaces are clean ...
Birefringence dispersion in fused silica for DUV lithography
... where q11 and q12 are the tensor components describing the material photoelastic effect. To understand the dispersion of birefringence in the DUV we have examined the dispersion of the stress optical coefficient in Corning’s HPFS® synthetic silica glass. In a birefringent optical element the refract ...
... where q11 and q12 are the tensor components describing the material photoelastic effect. To understand the dispersion of birefringence in the DUV we have examined the dispersion of the stress optical coefficient in Corning’s HPFS® synthetic silica glass. In a birefringent optical element the refract ...
DISPERSIVE BIREFRINGENT FILTERS Pochi YEH 1. Introduction
... These include cadmium sulfide (5 150-5400 A) [8], magnesium fluoride (1150-l 500 A) [9] and sapphire (1430 - 1530 A) [9]. In fact, there is even a change of sign of the birefringence (zero-crossing) after passing through zero, in the case of magnesium fluoride and cadmium sulfide. The operation of b ...
... These include cadmium sulfide (5 150-5400 A) [8], magnesium fluoride (1150-l 500 A) [9] and sapphire (1430 - 1530 A) [9]. In fact, there is even a change of sign of the birefringence (zero-crossing) after passing through zero, in the case of magnesium fluoride and cadmium sulfide. The operation of b ...
Measuring cellular structure at submicrometer scale with light
... diluting the stock suspension with de-ionized and distilled water to obtain the required optical density. Fig. 3 summarizes the experimental results obtained for polystyrene particles. To demonstrate the symmetry of the A/LSS scattering patterns, the parallel-polarized component of the backscattered ...
... diluting the stock suspension with de-ionized and distilled water to obtain the required optical density. Fig. 3 summarizes the experimental results obtained for polystyrene particles. To demonstrate the symmetry of the A/LSS scattering patterns, the parallel-polarized component of the backscattered ...
srep04093-s1
... The laser beam from a He-Ne laser (λ = 633 nm) first passes through a spatial light filter and is then expanded into a plane-wave-like beam with a diameter of approximately 10 mm. The two spiral phase plates and a metal rod were aligned along the beam propagation as shown in Fig. 3(c). We exper ...
... The laser beam from a He-Ne laser (λ = 633 nm) first passes through a spatial light filter and is then expanded into a plane-wave-like beam with a diameter of approximately 10 mm. The two spiral phase plates and a metal rod were aligned along the beam propagation as shown in Fig. 3(c). We exper ...
Influence of polarization direction, incidence angle, and geometry on
... al.[5] observed significant antenna-like plasmon resonances in Au and Cu nanowires, which have been applied as metallic nano waveguides.[6] Underlying these applications is localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) in the metal nanoparticles, the collective oscillations of conduction electrons induc ...
... al.[5] observed significant antenna-like plasmon resonances in Au and Cu nanowires, which have been applied as metallic nano waveguides.[6] Underlying these applications is localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) in the metal nanoparticles, the collective oscillations of conduction electrons induc ...
Enpolarization and depolarization of light
... the random phasors sum [26]. It was recently shown that this phenomenological model is relevant for strongly scattering medium, such as an inhomogeneous bulk with high optical index variations or a rough surface with steep slopes or peak to valley heights larger than the wavelength. In accordance wi ...
... the random phasors sum [26]. It was recently shown that this phenomenological model is relevant for strongly scattering medium, such as an inhomogeneous bulk with high optical index variations or a rough surface with steep slopes or peak to valley heights larger than the wavelength. In accordance wi ...
Holography
... Holographic gratings are made by recording the interference intensity patten of two plane waves onto a light sensitive material. Holographic gratings are much more popular than conventional rule gratings nowadays because they are easy to make at low cost; they have smaller scattering loss; can be ma ...
... Holographic gratings are made by recording the interference intensity patten of two plane waves onto a light sensitive material. Holographic gratings are much more popular than conventional rule gratings nowadays because they are easy to make at low cost; they have smaller scattering loss; can be ma ...
Polarizer

A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization, polarized light. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers are used in many optical techniques and instruments, and polarizing filters find applications in photography and liquid crystal display technology. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.