Crystal Optics
... propagating along the third pricipal axis of the crystal and choose thickness of crystal according to wavelenght of light ...
... propagating along the third pricipal axis of the crystal and choose thickness of crystal according to wavelenght of light ...
The Large-Scale Polarization Explorer (LSPE)
... extending our knowledge above 100 GHz. The main diffuse polarized emissions are synchrotron emission and thermal dust emission from non-spherical grains. Diffuse synchrotron emission is polarized around 10-20% on the average21, 22, the polarization of thermal dust is expected to be about 5% 23. Free ...
... extending our knowledge above 100 GHz. The main diffuse polarized emissions are synchrotron emission and thermal dust emission from non-spherical grains. Diffuse synchrotron emission is polarized around 10-20% on the average21, 22, the polarization of thermal dust is expected to be about 5% 23. Free ...
POLARIZATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
... The LPlp modes count the group of modes appearing together as a single mode and they are an example of pseudo-modes with the property of changing their cross-sectional intensity and polarization pattern as the mode propagates. However, the LPl p modes are superpositions of the true, generally hybrid ...
... The LPlp modes count the group of modes appearing together as a single mode and they are an example of pseudo-modes with the property of changing their cross-sectional intensity and polarization pattern as the mode propagates. However, the LPl p modes are superpositions of the true, generally hybrid ...
LS2520342037
... photonic crystal fiber are determined by the size, pattern of air holes rather than by the properties of optical glass[2]. Light is guided through small solid core PCFs, where high intensities can be maintained for interaction lengths of several meters resulting in large nonlinear effect. It has bee ...
... photonic crystal fiber are determined by the size, pattern of air holes rather than by the properties of optical glass[2]. Light is guided through small solid core PCFs, where high intensities can be maintained for interaction lengths of several meters resulting in large nonlinear effect. It has bee ...
Reflection of a Ray of Light Introduction: Purpose
... A "medium" refers to any change in the substance which interacts with the light. Some mediums are transparent meaning that _________________________, some mediums are translucent meaning that ________________________, and some mediums are opaque meaning that ________________________. Provide an ...
... A "medium" refers to any change in the substance which interacts with the light. Some mediums are transparent meaning that _________________________, some mediums are translucent meaning that ________________________, and some mediums are opaque meaning that ________________________. Provide an ...
John Kerr and his effects found in 1877 and 1878
... not envisage that, more than a hundred years later, we still speak of the polar Kerr effect, although horseshoe-shaped magnets are no longer used. Together with his second communication to the Philosophical Magazine [2] in March 1878, dealing with the Reflection of Polarized Light from the Equatoria ...
... not envisage that, more than a hundred years later, we still speak of the polar Kerr effect, although horseshoe-shaped magnets are no longer used. Together with his second communication to the Philosophical Magazine [2] in March 1878, dealing with the Reflection of Polarized Light from the Equatoria ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... phase defects, as well as to locate their positions with an accuracy no better than half the width of the interference fringe. However, the application of this method is rather limited if there are two (or more) dislocations in close proximity, because two vortices can be successfully resolved only ...
... phase defects, as well as to locate their positions with an accuracy no better than half the width of the interference fringe. However, the application of this method is rather limited if there are two (or more) dislocations in close proximity, because two vortices can be successfully resolved only ...
Analysis of Optical Systems I
... in Fig. (14.3b). This phenomenon is called total internal reflection. Several types of reflecting prisms operate this way. When total internal reflection occurs, there is no transmission of energy through the boundary. However, the fields of the wave do not abruptly go to zero at the boundary. There ...
... in Fig. (14.3b). This phenomenon is called total internal reflection. Several types of reflecting prisms operate this way. When total internal reflection occurs, there is no transmission of energy through the boundary. However, the fields of the wave do not abruptly go to zero at the boundary. There ...
Fabry-Perot Interferometer FABRYPEROT.TEX KB 20020122
... is more or less blocked. These conditions can be adjusted by changing the wavelength and/or the geometry. Thus Fabry-Perot plates can be used to measure or to control light wavelengths or to measure geometric properties. The geometric conditions are defined by several properties including thickness, ...
... is more or less blocked. These conditions can be adjusted by changing the wavelength and/or the geometry. Thus Fabry-Perot plates can be used to measure or to control light wavelengths or to measure geometric properties. The geometric conditions are defined by several properties including thickness, ...
02-01/02 Intro to Light and Electromagnetic waves Problem Set
... d. partially polarized. ____ 31. If two polarizing filters are held with their polarization axes at right angles to each other, the amount of light transmitted compared to when their axes are parallel is a. zero. b. half as much. c. the same. d. twice as much. Essay 32. Which waves are part of the e ...
... d. partially polarized. ____ 31. If two polarizing filters are held with their polarization axes at right angles to each other, the amount of light transmitted compared to when their axes are parallel is a. zero. b. half as much. c. the same. d. twice as much. Essay 32. Which waves are part of the e ...
Optical response of plasmonic relief meta-surfaces
... cut to a range of depths to achieve a variety of polarization- and viewing-angle-independent colours as shown in the upper row of optical microscope images, where each patterned (coloured) area measures 20 µm × 20 µm and is surrounded by unstructured silver. The inset shows an electron microscope im ...
... cut to a range of depths to achieve a variety of polarization- and viewing-angle-independent colours as shown in the upper row of optical microscope images, where each patterned (coloured) area measures 20 µm × 20 µm and is surrounded by unstructured silver. The inset shows an electron microscope im ...
Generalized Laws of Reflection and Refraction
... RESEARCH ARTICLES that of an individual straight antenna of length h (Fig. 2B, middle), and therefore the first-order antenna resonance occurs at h ≈ leff/2, where leff is the effective wavelength (14). In the antisymmetric mode, the current distribution in each arm approximates that of one half of ...
... RESEARCH ARTICLES that of an individual straight antenna of length h (Fig. 2B, middle), and therefore the first-order antenna resonance occurs at h ≈ leff/2, where leff is the effective wavelength (14). In the antisymmetric mode, the current distribution in each arm approximates that of one half of ...
Lectures on Theoretical Physics Linear Response Theory
... that the system has no chance to adapt, it remains away from equilibrium, and we speak of irreversibility. The most important application is optics. There is a medium which is exposed to an electromagnetic wave. The electric field changes so rapidly that matter within a region of micrometer dimensio ...
... that the system has no chance to adapt, it remains away from equilibrium, and we speak of irreversibility. The most important application is optics. There is a medium which is exposed to an electromagnetic wave. The electric field changes so rapidly that matter within a region of micrometer dimensio ...
(full text)
... 15. Z. Yan, A. H. Majedi, and S. Safavi-Naeini, “Physical Modeling of Hot-Electron Superconducting Single-Photon Detectors,” IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 17, 3789–3794 (2007). 16. While our fabrication process (see Refs. 9 and 10) leaves behind 10-40 nm of residual resist on top of the nanowires, we ...
... 15. Z. Yan, A. H. Majedi, and S. Safavi-Naeini, “Physical Modeling of Hot-Electron Superconducting Single-Photon Detectors,” IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 17, 3789–3794 (2007). 16. While our fabrication process (see Refs. 9 and 10) leaves behind 10-40 nm of residual resist on top of the nanowires, we ...
Tailored Complex Potentials and Friedel`s Law in Atom Optics
... of Friedel’s law due to fundamental optical principles in a very controlled system. Typically, diffraction phenomena are invariant under an inversion of the crystal, even when the elementary cell of the crystal possesses no symmetry. This empirical rule is generally referred to as Friedel’s law [1]. ...
... of Friedel’s law due to fundamental optical principles in a very controlled system. Typically, diffraction phenomena are invariant under an inversion of the crystal, even when the elementary cell of the crystal possesses no symmetry. This empirical rule is generally referred to as Friedel’s law [1]. ...
Light Measurement Handbook
... So, for a 2.2 mm thick filter, the external transmittance at 330 nm would be 36.1% ...
... So, for a 2.2 mm thick filter, the external transmittance at 330 nm would be 36.1% ...
39 Raman Scattering Spectroscopy Raman - Rose
... A third problem is that fluorescent signals (from the molecule of interest or from contaminants), which may have much higher intensity, will also be observed using standard instrumentation. This last problem can usually be solved by using long wavelength incident beams (such as the 514.5 nm waveleng ...
... A third problem is that fluorescent signals (from the molecule of interest or from contaminants), which may have much higher intensity, will also be observed using standard instrumentation. This last problem can usually be solved by using long wavelength incident beams (such as the 514.5 nm waveleng ...
Axial birefringence in high-numerical-aperture optical
... information layer through a protective cover layer of thickness d. To increase the information density the wavelength is decreased and the numerical aperture is increased, as the spot size scales with /NA. To that end the existing compact disk (CD) standard ( ⫽ 780 nm, NA ⫽ 0.45, d ⫽ 1.2 mm) is su ...
... information layer through a protective cover layer of thickness d. To increase the information density the wavelength is decreased and the numerical aperture is increased, as the spot size scales with /NA. To that end the existing compact disk (CD) standard ( ⫽ 780 nm, NA ⫽ 0.45, d ⫽ 1.2 mm) is su ...
Flat optics with designer metasurfaces
... phase associated with Fig. 4) are able to extend the phase response to cover the entire 2π range, which is necessary for a complete control of the wavefront. For example, in Fig. 1c the unit cell of the metasurface consisting of eight antennas produces a phase shift of the scattered light that incre ...
... phase associated with Fig. 4) are able to extend the phase response to cover the entire 2π range, which is necessary for a complete control of the wavefront. For example, in Fig. 1c the unit cell of the metasurface consisting of eight antennas produces a phase shift of the scattered light that incre ...
IJFTR 12(2) 100-102
... h, we could calculate the refractive indices from Eqs (2) and (8) of Presby 1 and Wilkes 7 (Table 1).The mean calculated values of n~'for the three polymeric fibres are more in agreement with those obtained by interferometric and the Becke-line methods" - 10 by Wilkes formula than with those by Pres ...
... h, we could calculate the refractive indices from Eqs (2) and (8) of Presby 1 and Wilkes 7 (Table 1).The mean calculated values of n~'for the three polymeric fibres are more in agreement with those obtained by interferometric and the Becke-line methods" - 10 by Wilkes formula than with those by Pres ...
Examples of convex lens
... silver chloride in each interval of the visible spectrum he got from a glass prism. He first found that blue light cause silver chloride to turn black more than red light did. Then he placed the silver chloride in to the region beyond violet, where no light could be seen by naked eye, but silver chl ...
... silver chloride in each interval of the visible spectrum he got from a glass prism. He first found that blue light cause silver chloride to turn black more than red light did. Then he placed the silver chloride in to the region beyond violet, where no light could be seen by naked eye, but silver chl ...
Polarization Model at 60 GHz
... The model for NLOS channel polarization matrix is defined based on the following considerations: It is known that reflection coefficients are different for E field components belonging (parallel) to the plane of incidence and for perpendicular to the plane of incidence. Also these coefficients depen ...
... The model for NLOS channel polarization matrix is defined based on the following considerations: It is known that reflection coefficients are different for E field components belonging (parallel) to the plane of incidence and for perpendicular to the plane of incidence. Also these coefficients depen ...
Reflection and Refraction of Plane Waves
... Principle of Reversibility • Referring to the figure, we can get • If we assume that the law of reflection and transmission holds for the time-averaged waves, we expect that the reversepropagating and must produce their own reflected waves and transmitted waves. ...
... Principle of Reversibility • Referring to the figure, we can get • If we assume that the law of reflection and transmission holds for the time-averaged waves, we expect that the reversepropagating and must produce their own reflected waves and transmitted waves. ...
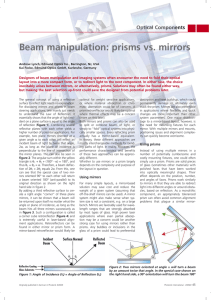
Beam manipulation: prisms vs. mirrors
... layout into a more compact form, or to redirect light to the next component. In either case, the choice inevitably arises between mirrors, or alternatively, prisms. Solutions may often be found either way, but making the best selection up-front could save the designer from potential problems later. ...
... layout into a more compact form, or to redirect light to the next component. In either case, the choice inevitably arises between mirrors, or alternatively, prisms. Solutions may often be found either way, but making the best selection up-front could save the designer from potential problems later. ...
Excitation wavelength dependence of the anomalous circular
... The ordinary circular photogalvanic effect (CPGE) has been applied widely to measure the Rashba and Dresselhaus spin-orbit coupling coefficient in semiconductors.10–12 According to CPGE, the oblique incidence of circularly polarized light induces a spin polarized charge current whose direction and m ...
... The ordinary circular photogalvanic effect (CPGE) has been applied widely to measure the Rashba and Dresselhaus spin-orbit coupling coefficient in semiconductors.10–12 According to CPGE, the oblique incidence of circularly polarized light induces a spin polarized charge current whose direction and m ...
Polarizer

A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization, polarized light. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers are used in many optical techniques and instruments, and polarizing filters find applications in photography and liquid crystal display technology. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.