S2014, BME 101L: Applied Circuits Lab 5a Characterizing
... Note: that the data sheet gives two different values in ohms: the impedance (actually, the magnitude of the impedance) and the DC resistance. In this lab you will measure both. The impedance is not really a single number though, but a function of frequency, and you will model the impedance of the lo ...
... Note: that the data sheet gives two different values in ohms: the impedance (actually, the magnitude of the impedance) and the DC resistance. In this lab you will measure both. The impedance is not really a single number though, but a function of frequency, and you will model the impedance of the lo ...
Current of electricity (Part 1)
... electrical energy (i.e. they supply electrical energy) batteries, electrical generators ...
... electrical energy (i.e. they supply electrical energy) batteries, electrical generators ...
Word
... The direction of the current depends on the motion of the magnet relative to the loop and changes when the magnet is reversed. The magnitude of the current depends on the speed of the motion, number of turns of wire and the 'angle' between the loop and the magnet. It doesn’t matter whether the coil ...
... The direction of the current depends on the motion of the magnet relative to the loop and changes when the magnet is reversed. The magnitude of the current depends on the speed of the motion, number of turns of wire and the 'angle' between the loop and the magnet. It doesn’t matter whether the coil ...
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS DARTMOUTH
... DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 201 CIRCUIT THEORY I EXTENDING THE RANGE OF AN ANALOG AMMETER ...
... DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 201 CIRCUIT THEORY I EXTENDING THE RANGE OF AN ANALOG AMMETER ...
R - Uplift North Hills Prep
... SHE accumulates a charge q1 of 2.0 x 10-5 C (sliding out of the seat of a car). HE has accumulated a charge q2 of – 8.0 x 10-5 C while waiting in the wind. What is the force between them a) when she opens the door 6.0 m from him and b) when their separation is reduced by a factor of 0.5? a) They ex ...
... SHE accumulates a charge q1 of 2.0 x 10-5 C (sliding out of the seat of a car). HE has accumulated a charge q2 of – 8.0 x 10-5 C while waiting in the wind. What is the force between them a) when she opens the door 6.0 m from him and b) when their separation is reduced by a factor of 0.5? a) They ex ...
AP_Physics_C_-_Resistivity_of_Wires
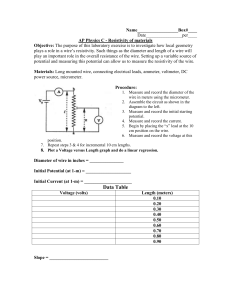
... plays a role in a wire’s resistivity. Such things as the diameter and length of a wire will play an important role in the overall resistance of the wire. Setting up a variable source of potential and measuring this potential can allow us to measure the resistivity of the wire. Materials: Long mounte ...
... plays a role in a wire’s resistivity. Such things as the diameter and length of a wire will play an important role in the overall resistance of the wire. Setting up a variable source of potential and measuring this potential can allow us to measure the resistivity of the wire. Materials: Long mounte ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.