Document
... electricity and current electricity? Static electricity is stationary or collects on the surface of an object, whereas current electricity is flowing very rapidly through a conductor. The flow of electricity in current electricity has electrical pressure or voltage. Electric charges flow from an are ...
... electricity and current electricity? Static electricity is stationary or collects on the surface of an object, whereas current electricity is flowing very rapidly through a conductor. The flow of electricity in current electricity has electrical pressure or voltage. Electric charges flow from an are ...
Attraction of Electric Charges Charging by Conduction Charging by
... that uses wire loops between two points rotating in a in a circuit magnetic field to expressed in volts generate electricity (aka potential difference) ...
... that uses wire loops between two points rotating in a in a circuit magnetic field to expressed in volts generate electricity (aka potential difference) ...
Worksheet
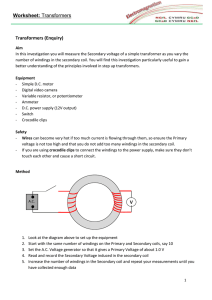
... - Digital video camera - Variable resistor, or potentiometer - Ammeter - D.C. power supply (12V output) - Switch - Crocodile clips Safety - Wires can become very hot if too much current is flowing through them, so ensure the Primary voltage is not too high and that you do not add too many windings i ...
... - Digital video camera - Variable resistor, or potentiometer - Ammeter - D.C. power supply (12V output) - Switch - Crocodile clips Safety - Wires can become very hot if too much current is flowing through them, so ensure the Primary voltage is not too high and that you do not add too many windings i ...
Magnetic Flux and Faraday`s Law of Induction
... conductor depends on the current in the wire and the resistance of the wire (PLoss = I2R) The resistance of the wire used in power transmission is set by the type of material used (usually aluminum), cross-sectional area of the wire, and the length of the wire. This is very difficult to change once ...
... conductor depends on the current in the wire and the resistance of the wire (PLoss = I2R) The resistance of the wire used in power transmission is set by the type of material used (usually aluminum), cross-sectional area of the wire, and the length of the wire. This is very difficult to change once ...
Direct current voltage increment due to ac coupling in a high Tc
... This general equation takes into account the possibility that I ac(t) is nonsinusoidal, with a nonvanishing average. However, in our experimental setup ^ I ac& 50, since I ac is induced by ac coupling of the HTS coil to the ac source. Also note that the dc current through the coil is supplied by a c ...
... This general equation takes into account the possibility that I ac(t) is nonsinusoidal, with a nonvanishing average. However, in our experimental setup ^ I ac& 50, since I ac is induced by ac coupling of the HTS coil to the ac source. Also note that the dc current through the coil is supplied by a c ...
Lodestones Magnetic Poles
... Draw field lines so that compass always points tangent to the field lines. Field lines point from N to S outside the magnet Field lines point from S to N inside the magnet Field lines form closed loops Field lines never intersect ...
... Draw field lines so that compass always points tangent to the field lines. Field lines point from N to S outside the magnet Field lines point from S to N inside the magnet Field lines form closed loops Field lines never intersect ...
Solution Set 11 - 6911norfolk.com
... oscillators. It can be regarded as a simple LC circuit. The inductance is that of a toroid with one turn. Find an expression for the resonant frequency of this circuit and show by a sketch the configuration of the magnetic and electric fields. ...
... oscillators. It can be regarded as a simple LC circuit. The inductance is that of a toroid with one turn. Find an expression for the resonant frequency of this circuit and show by a sketch the configuration of the magnetic and electric fields. ...
Section 22.1 - CPO Science
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
Thin wire A long nail = 10p is a good size (10P = 10-penny
... magnetic field twists with the coiled wire, causing the magnetic field lines to concentrate inside the coil. This creates a powerful magnetic effect inside the coil called an electromagnet. The magnetic field inside the coil causes the tiny magnetic fields in the metal of the nail to be aligned in o ...
... magnetic field twists with the coiled wire, causing the magnetic field lines to concentrate inside the coil. This creates a powerful magnetic effect inside the coil called an electromagnet. The magnetic field inside the coil causes the tiny magnetic fields in the metal of the nail to be aligned in o ...
Chapter 26: Magnetism - University of Colorado Boulder
... • Gauss’s law ensures that magnetic field lines have no beginnings or endings, but generally form closed loops. • If monopoles are ever discovered, the right-hand side of Gauss’s law for magnetism would be nonzero. ...
... • Gauss’s law ensures that magnetic field lines have no beginnings or endings, but generally form closed loops. • If monopoles are ever discovered, the right-hand side of Gauss’s law for magnetism would be nonzero. ...
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
... magnetic field in the iron. The energy of the magnetic field. Electric field. The intensity of the electric field, dielectric permittivity. Capacitors - capacitance, serial and parallel connections of capacitors. Electrical induction. Energy of the electric field. Alternating current. Basic concept ...
... magnetic field in the iron. The energy of the magnetic field. Electric field. The intensity of the electric field, dielectric permittivity. Capacitors - capacitance, serial and parallel connections of capacitors. Electrical induction. Energy of the electric field. Alternating current. Basic concept ...
Chapter 13
... coupling (k=1). • It has two or more turns with a large number of windings on a core of high permeability. • The ideal transformer has: 1. Coils with very large reactance (L1, L2, M →) 2. Coupling coefficient is equal to unity. 3. Primary and secondary coils are lossless ...
... coupling (k=1). • It has two or more turns with a large number of windings on a core of high permeability. • The ideal transformer has: 1. Coils with very large reactance (L1, L2, M →) 2. Coupling coefficient is equal to unity. 3. Primary and secondary coils are lossless ...
PC795 - Picker Components
... Terminal Plating N: Nickel Plated Terminals Standard on all Plug in Models; Nil: PC Pin Version RoHS Compliant: -X ...
... Terminal Plating N: Nickel Plated Terminals Standard on all Plug in Models; Nil: PC Pin Version RoHS Compliant: -X ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.