Electronicsound
... terminals, an electric potential difference exists between them. The maximum potential difference is called the electromotive force* (emf) of the battery. The electric potential difference is also known as the voltage, V. The SI unit for voltage is the volt, after Alessandro Volta (17451827) who inv ...
... terminals, an electric potential difference exists between them. The maximum potential difference is called the electromotive force* (emf) of the battery. The electric potential difference is also known as the voltage, V. The SI unit for voltage is the volt, after Alessandro Volta (17451827) who inv ...
10 Transistor Inverter Applications II
... any relevant power ratings. Assuming that the given relay has been chosen correctly by the user, the only thing of concern is the power dissipation in the transistors. Before this is done, the mechanism of operation of the transistors should be looked at a little more closely. In the Darlington conf ...
... any relevant power ratings. Assuming that the given relay has been chosen correctly by the user, the only thing of concern is the power dissipation in the transistors. Before this is done, the mechanism of operation of the transistors should be looked at a little more closely. In the Darlington conf ...
Magnets and Magnetic Fields
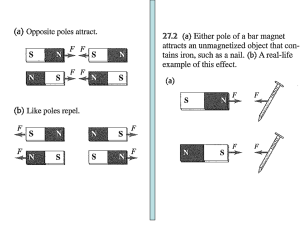
... • Magnets get their name from a stone found 3000 years ago in Magnesia, which is now modern day Greece. This stone is called Iodestone and is composed of magnetite. • Some material can be made into permanent magnets – You can change any piece of iron, such as a nail, into a permanent magnet by stro ...
... • Magnets get their name from a stone found 3000 years ago in Magnesia, which is now modern day Greece. This stone is called Iodestone and is composed of magnetite. • Some material can be made into permanent magnets – You can change any piece of iron, such as a nail, into a permanent magnet by stro ...
Electric Motors
... plastic comb in your wool sweater and then hold it over tiny pieces of paper, they are attracted to the comb. They are pulled together by the electrostatic force. Charged particles follow the same rule as magnets. Opposite charges attract and like charges repel each other. When charged particles mov ...
... plastic comb in your wool sweater and then hold it over tiny pieces of paper, they are attracted to the comb. They are pulled together by the electrostatic force. Charged particles follow the same rule as magnets. Opposite charges attract and like charges repel each other. When charged particles mov ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... • Unlike x-rays and computed tomographic (CT) scans, which use radiation, MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves. The MRI scanner contains the magnet. The magnetic field produced by an MRI is about 10 thousand times greater than the earth's. ...
... • Unlike x-rays and computed tomographic (CT) scans, which use radiation, MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves. The MRI scanner contains the magnet. The magnetic field produced by an MRI is about 10 thousand times greater than the earth's. ...
Syllabus_APHY112
... dielectrics, capacitor with parallel plates and dielectric, Energy stored inside an electric field Current and Resistances: Electric current, Resistance and Ohm's law, Resistivity of different conductors, Resistances in combination Direct Current Circuits: Electromotive force, Kirchhoff's rules, Pow ...
... dielectrics, capacitor with parallel plates and dielectric, Energy stored inside an electric field Current and Resistances: Electric current, Resistance and Ohm's law, Resistivity of different conductors, Resistances in combination Direct Current Circuits: Electromotive force, Kirchhoff's rules, Pow ...
615-0335 (10-152) Lenz`s Law Pendulum
... Introduction: What is Lenz’s Law? How does it apply to pendulums? Lenz’s Law gives the direction of the electromotive force caused by electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction is a phenomenon caused when a magnetic field interacts with a conductive material. As the material passes through ...
... Introduction: What is Lenz’s Law? How does it apply to pendulums? Lenz’s Law gives the direction of the electromotive force caused by electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction is a phenomenon caused when a magnetic field interacts with a conductive material. As the material passes through ...
... 1. A bulb cannot be used in place of a resister to verify ohms law. Justify this statement with reason. 2. What is meant by tropic movements? 3 . Name the component of a solar cooker that produces a green house effect inside it. 4. Give reason why white coloured silver chloride turns grey when kept ...
20-7 Transformers and the Transmission of Electricity
... What is a transformer good for? In general, transformers are used to change the voltage from a wall socket into a different voltage, which could be higher or lower, for use by a particular device. Some devices, such as microwave ovens and cathode ray tube televisions, require higher voltages than th ...
... What is a transformer good for? In general, transformers are used to change the voltage from a wall socket into a different voltage, which could be higher or lower, for use by a particular device. Some devices, such as microwave ovens and cathode ray tube televisions, require higher voltages than th ...
Magnetic force between parallel currents - Rose
... direction of B obeys a right-hand rule: if you point the thumb of your right hand along the current direction, its curled fingers indicate the direction of the field lines around the wire. The magnitude of B in this case is given by ...
... direction of B obeys a right-hand rule: if you point the thumb of your right hand along the current direction, its curled fingers indicate the direction of the field lines around the wire. The magnitude of B in this case is given by ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.