Chapter 15
... charges would experience a force and accelerate along the surface and it would not be in equilibrium The net flux through the surface is through only the flat face outside the conductor The field here is perpendicular to the surface ...
... charges would experience a force and accelerate along the surface and it would not be in equilibrium The net flux through the surface is through only the flat face outside the conductor The field here is perpendicular to the surface ...
Gr. 11 Chemistry Student Workbook (Spring 2016)
... reduce any risks. Teachers will assess the readiness level of students to protect everyone in the class. If a student is considered unready, he or she will not be able to participate in the activity. If no other opportunity to participate can be arranged, then the student’s development of hands-on s ...
... reduce any risks. Teachers will assess the readiness level of students to protect everyone in the class. If a student is considered unready, he or she will not be able to participate in the activity. If no other opportunity to participate can be arranged, then the student’s development of hands-on s ...
AP-C Electric Potential
... d. Calculate the potential difference between two points in a uniform electric field, and state which point is at the higher potential. e. Calculate how much work is required to move a test charge from one location to another in the field of fixed point charges. f. Calculate the electrostatic potent ...
... d. Calculate the potential difference between two points in a uniform electric field, and state which point is at the higher potential. e. Calculate how much work is required to move a test charge from one location to another in the field of fixed point charges. f. Calculate the electrostatic potent ...
Graded Potentials - Root
... K+ channels start to close. Because positive ions are both concentrated on the outside of the axon, the outside is now more positive than when the axon is at rest. In other words, the inside is more negative than resting. ...
... K+ channels start to close. Because positive ions are both concentrated on the outside of the axon, the outside is now more positive than when the axon is at rest. In other words, the inside is more negative than resting. ...
On the combination of a linear field free trap with a time-of
... injection, i.e., the ions are typically decelerated into the trap to energies below 50 meV in order to prevent collision induced excitation or dissociation. Interaction with a buffer gas couples finally the ion temperature to that of the surrounding walls. Two phases of a rf voltage applied to the t ...
... injection, i.e., the ions are typically decelerated into the trap to energies below 50 meV in order to prevent collision induced excitation or dissociation. Interaction with a buffer gas couples finally the ion temperature to that of the surrounding walls. Two phases of a rf voltage applied to the t ...
... - Do not turn on the fixture if it has been through severe temperature differences. Damage may occur to the fixture. Wait until unit is at room temperature to operate. - The unit should be protected from any vibration or agitation during transport. - Do not expose the fixture in any excessive heat w ...
Delay Time and Gate Delays
... To drive large load capacitances such as long buses, I/O buffers, pads and off chip capacitive loads a chain of inverters can be used. With this configuration each successive gate is made large than the previous one until the last inverter in the chain can drive the large load within the required ti ...
... To drive large load capacitances such as long buses, I/O buffers, pads and off chip capacitive loads a chain of inverters can be used. With this configuration each successive gate is made large than the previous one until the last inverter in the chain can drive the large load within the required ti ...
Chem 11 Notes Booklet (pdf version)
... ◘ Metals are separated from nonmetals by the “staircase line”. metals - shiny, malleable, ductile, conductors of heat and electricity. ◘ The columns are families (groups) of elements having similar chemical properties. Some of these families have names to memorize (see sheet). ◘ The rows are called ...
... ◘ Metals are separated from nonmetals by the “staircase line”. metals - shiny, malleable, ductile, conductors of heat and electricity. ◘ The columns are families (groups) of elements having similar chemical properties. Some of these families have names to memorize (see sheet). ◘ The rows are called ...
Ch 4 Student
... Types of Aqueous Solutions and Solubility Dissolution of an Molecular Solid in Water • Sucrose is a molecular solid. Not composed of ions. • How does is dissolve in water? • Sugar molecules have areas that are polar – just like water • The partial positive and negative charges on the sugar interact ...
... Types of Aqueous Solutions and Solubility Dissolution of an Molecular Solid in Water • Sucrose is a molecular solid. Not composed of ions. • How does is dissolve in water? • Sugar molecules have areas that are polar – just like water • The partial positive and negative charges on the sugar interact ...
Electricity Part 2 (ppt)
... Exercise: a potential difference of 200 V is applied across a pair of parallel plates 0.012 m apart. (b) an electron is placed between the plates, next to the negative plate. Calculate the force on the electron, the acceleration of the electron, and the time it takes to reach the other plate. Force ...
... Exercise: a potential difference of 200 V is applied across a pair of parallel plates 0.012 m apart. (b) an electron is placed between the plates, next to the negative plate. Calculate the force on the electron, the acceleration of the electron, and the time it takes to reach the other plate. Force ...
Lecture 17 Fluid Dynamics: handouts
... No ∆P in normal direction Lateral flow has Poiseuille like velocity profile Gas obeys Ideal Gas Law No change in T ∂( Ph ) ...
... No ∆P in normal direction Lateral flow has Poiseuille like velocity profile Gas obeys Ideal Gas Law No change in T ∂( Ph ) ...
TAP 126- 4: Charging capacitors
... capacitance as the ratio of charge to potential difference. They should also be familiar with the farad as the unit of capacitance but also the submultiples of ‘milli’ and ‘micro’ as more common variants since the farad is such a large unit. The first questions refer to a capacitor having being char ...
... capacitance as the ratio of charge to potential difference. They should also be familiar with the farad as the unit of capacitance but also the submultiples of ‘milli’ and ‘micro’ as more common variants since the farad is such a large unit. The first questions refer to a capacitor having being char ...
Data Sheet Features General Description
... PMOSFET and NMOSFET switches. Both the DC bias current and gate charge losses are proportional to the VIN and this effect will be more serious at higher input voltages. ...
... PMOSFET and NMOSFET switches. Both the DC bias current and gate charge losses are proportional to the VIN and this effect will be more serious at higher input voltages. ...
Chapter 3 Molecules Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical
... no individual molecule units units, instead they have a three-dimensional array of cations and anions made of formula units many contain polyatomic ions several atoms attached together in one ion ...
... no individual molecule units units, instead they have a three-dimensional array of cations and anions made of formula units many contain polyatomic ions several atoms attached together in one ion ...
Filament Work Function (2001 Vossen Winner)
... the filament is low. As current flows through a circuit of two dissimilar metals heat is absorbed at one junction and given up at the other. It has recently been discovered that if the metals used have low work functions this process (known as the Peltier Effect) can occur at an efficiency of 70-80% ...
... the filament is low. As current flows through a circuit of two dissimilar metals heat is absorbed at one junction and given up at the other. It has recently been discovered that if the metals used have low work functions this process (known as the Peltier Effect) can occur at an efficiency of 70-80% ...
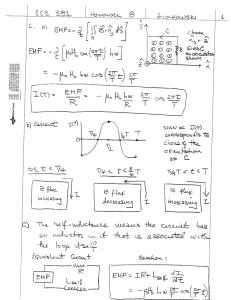
KEY - Rose
... before the switch is closed. A basic property of an ideal inductor is that the current through it cannot change instantaneously. This is because the potential difference VL –L(dI/dt) would become infinite for an instantaneous change of current, and that is not physically possible. Because the cur ...
... before the switch is closed. A basic property of an ideal inductor is that the current through it cannot change instantaneously. This is because the potential difference VL –L(dI/dt) would become infinite for an instantaneous change of current, and that is not physically possible. Because the cur ...
Technical Glossary
... cranking current rating is used for sizing batteries, cables, and battery switches. current see amperage Current is a flow of electrical charge carriers, usually electrons or electron-deficient atoms. The common symbol for current is the uppercase letter I. The standard unit is the ampere, symbolize ...
... cranking current rating is used for sizing batteries, cables, and battery switches. current see amperage Current is a flow of electrical charge carriers, usually electrons or electron-deficient atoms. The common symbol for current is the uppercase letter I. The standard unit is the ampere, symbolize ...
Nanofluidic circuitry
Nanofluidic circuitry is a nanotechnology aiming for control of fluids in nanometer scale. Due to the effect of an electrical double layer within the fluid channel, the behavior of nanofluid is observed to be significantly different compared with its microfluidic counterparts. Its typical characteristic dimensions fall within the range of 1–100 nm. At least one dimension of the structure is in nanoscopic scale. Phenomena of fluids in nano-scale structure are discovered to be of different properties in electrochemistry and fluid dynamics.