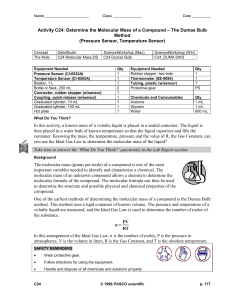
Determine the Molecular Mass of a Compound
... The molecular mass (grams per mole) of a compound is one of the most important variables needed to identify and characterize a chemical. The molecular mass of an unknown compound allows a chemist to determine the molecular formula of the compound. The molecular formula can then be used to determine ...
... The molecular mass (grams per mole) of a compound is one of the most important variables needed to identify and characterize a chemical. The molecular mass of an unknown compound allows a chemist to determine the molecular formula of the compound. The molecular formula can then be used to determine ...
Aquaporin - 3D Molecular Designs
... model, to pass through. This Aquaporin Mini Model can be purchased at 3dmoleculardesigns.com/Education-Products/Aquaporin-Mini-Model.htm. ...
... model, to pass through. This Aquaporin Mini Model can be purchased at 3dmoleculardesigns.com/Education-Products/Aquaporin-Mini-Model.htm. ...
Chapter 7_honors
... compounds. Exceptions include the peroxides (such as H2O2 => ox# = -1) and when combined with halogens (ex. OF2=> ox# = +2) ...
... compounds. Exceptions include the peroxides (such as H2O2 => ox# = -1) and when combined with halogens (ex. OF2=> ox# = +2) ...
Scientific visualization of chemical systems
... to provide a clearer view of the phenomenon. This is the ezploralion phase. Control and interaction need to be added to refine the simulation, extract useful information and explore newly discovered features. Good visualization environments will include advanced interactivity such as 3D cursors, pic ...
... to provide a clearer view of the phenomenon. This is the ezploralion phase. Control and interaction need to be added to refine the simulation, extract useful information and explore newly discovered features. Good visualization environments will include advanced interactivity such as 3D cursors, pic ...
File - Pomp
... the energy for all human action. These “metabolic engines” are known as the phosphagen pathway, the glycolytic pathway, and the oxidative pathway.The first, the phosphagen, dominates the highest-powered activities, those that last less than about ten seconds. The second pathway, the ...
... the energy for all human action. These “metabolic engines” are known as the phosphagen pathway, the glycolytic pathway, and the oxidative pathway.The first, the phosphagen, dominates the highest-powered activities, those that last less than about ten seconds. The second pathway, the ...
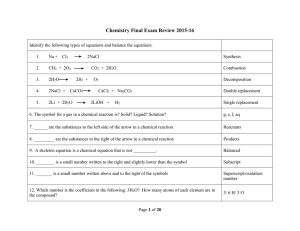
Exam Review_Key_All Topics.082
... 1. What is the purpose of a fractionating column and how does it work? A Fractionating column is used to separate a mixture into its component parts by differences in boiling points. The fractionating column is filled with beads that allow for condensation. The bottom of the flask is heated and the ...
... 1. What is the purpose of a fractionating column and how does it work? A Fractionating column is used to separate a mixture into its component parts by differences in boiling points. The fractionating column is filled with beads that allow for condensation. The bottom of the flask is heated and the ...
3 molecules
... How many oxygen atoms are there in 500. mL of a 30.0 % solution of H2SO4 with a density of 1.250 g/cm3 ? (MW = 98.1) ...
... How many oxygen atoms are there in 500. mL of a 30.0 % solution of H2SO4 with a density of 1.250 g/cm3 ? (MW = 98.1) ...
Writing Formulas Worksheet 1. sodium nitrate 16. aluminum sulfide
... hydrates. The number of moles of water present per mole of anhydrous salt (salt minus water of crystallization) is usually a whole number. One example is the hydrate of copper (II) sulfate. Its blue crystals look and feel dry. Yet each mole of hydrate contains 5 moles of water. Its formula is CuSO4 ...
... hydrates. The number of moles of water present per mole of anhydrous salt (salt minus water of crystallization) is usually a whole number. One example is the hydrate of copper (II) sulfate. Its blue crystals look and feel dry. Yet each mole of hydrate contains 5 moles of water. Its formula is CuSO4 ...
Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function A. Lipids: Water
... liver and has a role in some cell membranes, as well as in the digestion of other fats. • Some lipids function as vitamins, required for normal functioning, must be acquired from the diet. Figure 3.24 ...
... liver and has a role in some cell membranes, as well as in the digestion of other fats. • Some lipids function as vitamins, required for normal functioning, must be acquired from the diet. Figure 3.24 ...
word - My eCoach
... Cellulose and Chitin are polysaccharides that function to support and protect the organism. The cell walls of plants are composed of cellulose. The cell walls of fungi and the exoskeleton of arthropods are composed of chitin. Cellulose is composed of beta-glucose monomers; starch and glycogen are co ...
... Cellulose and Chitin are polysaccharides that function to support and protect the organism. The cell walls of plants are composed of cellulose. The cell walls of fungi and the exoskeleton of arthropods are composed of chitin. Cellulose is composed of beta-glucose monomers; starch and glycogen are co ...
Chem152
... 1. What is the term for the smallest particle that represents an element? A) atom B) entity C) formula unit D) molecule E) none of the above 2. What is the term for the number that identifies a particular element? A) atomic number B) element number C) mass number D) substance number E) none of the a ...
... 1. What is the term for the smallest particle that represents an element? A) atom B) entity C) formula unit D) molecule E) none of the above 2. What is the term for the number that identifies a particular element? A) atomic number B) element number C) mass number D) substance number E) none of the a ...
ECA Biochemistry Gizmos
... Organic Compounds • Contain carbon & found in living organisms o Inorganic Carbon compounds: CO2, o Many inorganics found in living organisms • Iron in blood ...
... Organic Compounds • Contain carbon & found in living organisms o Inorganic Carbon compounds: CO2, o Many inorganics found in living organisms • Iron in blood ...
AL COS #
... What term describes two liquids that can be mixed together but Immiscible separate shortly after you cease mixing them? What term describes two liquids that are soluble in each other? Miscible What is the substance that is dissolved in a solution? Solute What is the substance that dissolves a solute ...
... What term describes two liquids that can be mixed together but Immiscible separate shortly after you cease mixing them? What term describes two liquids that are soluble in each other? Miscible What is the substance that is dissolved in a solution? Solute What is the substance that dissolves a solute ...
Protein Lab 2012 PDF
... molecules into globules in the milk. You can’t see them because even though they are large molecules, molecules are still too small to see with the human eye. Because pH (the acidity of a liquid) and high temperature both disrupt chemical bonds, they can affect how a molecule forms or how it behaves ...
... molecules into globules in the milk. You can’t see them because even though they are large molecules, molecules are still too small to see with the human eye. Because pH (the acidity of a liquid) and high temperature both disrupt chemical bonds, they can affect how a molecule forms or how it behaves ...
Comparative Proteomics Kit I: Protein Profiler Module
... • Analyze protein profiles from a variety of fish • Study protein structure/function • Use polyacrylamide electrophoresis to separate proteins by size ...
... • Analyze protein profiles from a variety of fish • Study protein structure/function • Use polyacrylamide electrophoresis to separate proteins by size ...
Unit 2: Practice
... 17. Determine the number of molecules found in 5.00 mol water. 18. Determine the number of carbon atoms found in 2.50 mol methane, CH4. 19. Calculate the number of moles of lead present in 8.6 1017 atoms of Pb. 20. Determine the molar mass of mercury(II) sulfide. 21. Ammonium carbonate is commonly ...
... 17. Determine the number of molecules found in 5.00 mol water. 18. Determine the number of carbon atoms found in 2.50 mol methane, CH4. 19. Calculate the number of moles of lead present in 8.6 1017 atoms of Pb. 20. Determine the molar mass of mercury(II) sulfide. 21. Ammonium carbonate is commonly ...
AP Chemistry Unit 3 Test Review Topics Covered: Gases Liquids
... What effect do the volume and pressure changes have on the average kinetic energy of the molecules in the sample? (A) The average kinetic energy increases. (B) The average kinetic energy decreases. (C) The average kinetic energy stays the same. (D) It cannot be determined how the kinetic energy is a ...
... What effect do the volume and pressure changes have on the average kinetic energy of the molecules in the sample? (A) The average kinetic energy increases. (B) The average kinetic energy decreases. (C) The average kinetic energy stays the same. (D) It cannot be determined how the kinetic energy is a ...
Salting in and salting out of proteins and dialysis
... • After removing the precipitate by filtration or centrifugation, the desired protein can be precipitated by altering the salt concentration to the level at which the desired protein becomes insoluble. ...
... • After removing the precipitate by filtration or centrifugation, the desired protein can be precipitated by altering the salt concentration to the level at which the desired protein becomes insoluble. ...
Empirical is the
... composition! Take that value and multiple by the given amount of mass. That is the amount of Carbon in the Carbon dioxide that was given off. Repeat with the Hydrogen. Then use these values to convert to moles like in the previous problems. Divide by the the smallest mole value to get the ratios. Th ...
... composition! Take that value and multiple by the given amount of mass. That is the amount of Carbon in the Carbon dioxide that was given off. Repeat with the Hydrogen. Then use these values to convert to moles like in the previous problems. Divide by the the smallest mole value to get the ratios. Th ...
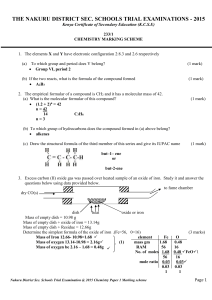
the nakuru district sec. schools trial examinations - 2015
... 8. Explain in terms of structure and bonding why silicon (IV) oxide exists as a solid of high melting point while sulphur (IV) oxide exists as a gas. (2 marks SiO2 has giant atomic structure 1 with strong covalent bonds between hence exists as a solid while SO2 has simple molecular structure 1 w ...
... 8. Explain in terms of structure and bonding why silicon (IV) oxide exists as a solid of high melting point while sulphur (IV) oxide exists as a gas. (2 marks SiO2 has giant atomic structure 1 with strong covalent bonds between hence exists as a solid while SO2 has simple molecular structure 1 w ...
Chemical Formulas and Formula Weight Calculations
... The Mole has its origins with a hypothesis formulated by the Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro (1776‐1856). In 1811, Avogadro pointed out that: “Gay‐Lussac has shown in an interesting Memoir (Mémoires de la Société d'Arcueil, Tome II.) that gases always unite in a very simple proportion by volume, ...
... The Mole has its origins with a hypothesis formulated by the Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro (1776‐1856). In 1811, Avogadro pointed out that: “Gay‐Lussac has shown in an interesting Memoir (Mémoires de la Société d'Arcueil, Tome II.) that gases always unite in a very simple proportion by volume, ...
Learning objectives
... 11. Explain why strong covalent bonds and weak bonds are both essential in living organisms. 12. Distinguish between hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions. 13. Give an example that illustrates how a molecule’s shape can determine its biological function. 14. Explain what is meant by a chemic ...
... 11. Explain why strong covalent bonds and weak bonds are both essential in living organisms. 12. Distinguish between hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions. 13. Give an example that illustrates how a molecule’s shape can determine its biological function. 14. Explain what is meant by a chemic ...
GMS BI 555/755 Lecture 3: Techniques for
... The Principle of Isoelectric Focusing. A pH gradient is established in a gel before loading the sample. (A) The sample is loaded and voltage is applied. The proteins will migrate to their isoelectric pH, the location at which they have no net charge. (B) The proteins form bands that can be excised a ...
... The Principle of Isoelectric Focusing. A pH gradient is established in a gel before loading the sample. (A) The sample is loaded and voltage is applied. The proteins will migrate to their isoelectric pH, the location at which they have no net charge. (B) The proteins form bands that can be excised a ...
Size-exclusion chromatography

Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size, and in some cases molecular weight. It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. Typically, when an aqueous solution is used to transport the sample through the column, the technique is known as gel-filtration chromatography, versus the name gel permeation chromatography, which is used when an organic solvent is used as a mobile phase. SEC is a widely used polymer characterization method because of its ability to provide good molar mass distribution (Mw) results for polymers.