JAY McCLELLAND
... Another key property of the model • Sensitivity to coherent covariation can be domain- and property-type specific, and such sensitivity is acquired as differentiation occurs. • Obviates the need for initial domain-specific biases to account for domain-specific patterns of generalization and inferen ...
... Another key property of the model • Sensitivity to coherent covariation can be domain- and property-type specific, and such sensitivity is acquired as differentiation occurs. • Obviates the need for initial domain-specific biases to account for domain-specific patterns of generalization and inferen ...
Slide ()
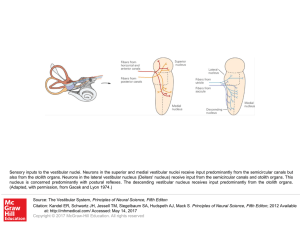
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
hebbRNN: A Reward-Modulated Hebbian Learning Rule for
... and Gerstner 2014; Carnevale et al. 2015; Laje, Buonomano, and Buonomano 2013). However, training these networks to produce meaningful behavior has proven difficult. Furthermore, the most common methods are generally not biologically-plausible and rely on information not local to the synapses of ind ...
... and Gerstner 2014; Carnevale et al. 2015; Laje, Buonomano, and Buonomano 2013). However, training these networks to produce meaningful behavior has proven difficult. Furthermore, the most common methods are generally not biologically-plausible and rely on information not local to the synapses of ind ...
UNDERSTANDING OF DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS
... Help experts build on ideas for new models or vary hyper-parameters to obtain a stateof-the-art model. Paper: Understanding Neural Networks Through Deep Visualization provides two such tools to help users that build DNNs to understand them better, Interactively plots the activations produced o ...
... Help experts build on ideas for new models or vary hyper-parameters to obtain a stateof-the-art model. Paper: Understanding Neural Networks Through Deep Visualization provides two such tools to help users that build DNNs to understand them better, Interactively plots the activations produced o ...
Random Variables - CEDAR
... Generative Model of data allows data to be generated from the model ...
... Generative Model of data allows data to be generated from the model ...
Principles of Sensory Coding
... color scheme, white corresponds to no activity above the spontaneous level. Erchova, 2004 ...
... color scheme, white corresponds to no activity above the spontaneous level. Erchova, 2004 ...
Work toward real-time control of a cortical neural prothesis
... Neurons in the cerebral cortex typically display broad cosine tuning, and those in the motor cortex have been shown to be broadly tuned to the direction of hand movement [1]–[3]. These neurons will fire most rapidly for movements in their “preferred direction,” and least when the motion of the hand ...
... Neurons in the cerebral cortex typically display broad cosine tuning, and those in the motor cortex have been shown to be broadly tuned to the direction of hand movement [1]–[3]. These neurons will fire most rapidly for movements in their “preferred direction,” and least when the motion of the hand ...
Analyzing EEG data from the brain computer interface with
... feature extraction is to find the most linearly independent signals possible based on the original signal. Blind source separation is a method for calculating an original signal based on a mixed signal and with no knowledge of the mixing process or the original signal. ...
... feature extraction is to find the most linearly independent signals possible based on the original signal. Blind source separation is a method for calculating an original signal based on a mixed signal and with no knowledge of the mixing process or the original signal. ...
File
... Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
... Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
Document
... • Compute probability by summing over extensions of all paths leading to current cell. • An extension of a path from a state i at time t-1 to state j at t is computed by multiplying together: i. previous path probability from the previous cell forward[t-1,i], ii. transition probability aij from prev ...
... • Compute probability by summing over extensions of all paths leading to current cell. • An extension of a path from a state i at time t-1 to state j at t is computed by multiplying together: i. previous path probability from the previous cell forward[t-1,i], ii. transition probability aij from prev ...
Learning multiple layers of representation
... Learning feature detectors To enable the perceptual system to make the fine distinctions that are required to control behavior, sensory cortex needs an efficient way of adapting the synaptic weights of multiple layers of feature-detecting neurons. The backpropagation learning procedure [1] iterative ...
... Learning feature detectors To enable the perceptual system to make the fine distinctions that are required to control behavior, sensory cortex needs an efficient way of adapting the synaptic weights of multiple layers of feature-detecting neurons. The backpropagation learning procedure [1] iterative ...
here
... This course assembles the latest numerical finite difference methods (FDM) for solving PDEs found in financial engineering. Topics covered includes one-step and multi-step finite difference method which includes the implicit Euler scheme, explicit Euler scheme and CrankNicolson scheme, Runge-Kutta m ...
... This course assembles the latest numerical finite difference methods (FDM) for solving PDEs found in financial engineering. Topics covered includes one-step and multi-step finite difference method which includes the implicit Euler scheme, explicit Euler scheme and CrankNicolson scheme, Runge-Kutta m ...
linear system
... applied before and /or after t1. Hence, if an input u[t1,) is applied to a system, unless we know the input applied before t1, we will obtain different output y[t1,) , although the same input u[t1,) is applied. ...
... applied before and /or after t1. Hence, if an input u[t1,) is applied to a system, unless we know the input applied before t1, we will obtain different output y[t1,) , although the same input u[t1,) is applied. ...
Synaptic Transmission
... message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
... message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
Unsupervised Learning What is clustering for?
... according to their content similarities, – To produce a topic hierarchy ...
... according to their content similarities, – To produce a topic hierarchy ...
09-unsupervised - The University of Iowa
... applied to a neural network, the weight matrix will eventually converge. The same problem exists for k-means or vector quantitation. • Present a modified type of competitive learning, called Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART), which is a collection of models for unsupervised learning and designed to ov ...
... applied to a neural network, the weight matrix will eventually converge. The same problem exists for k-means or vector quantitation. • Present a modified type of competitive learning, called Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART), which is a collection of models for unsupervised learning and designed to ov ...