Tehnici de optimizare – Programare Genetica
... large number of "training" hours for the network to be able to act for what it was designed for, cannot detect singular elements other than those for which it has been accustomed (3), it's hard to debug during operation and it is not scalable. Considering this aspects, we highlight some applications ...
... large number of "training" hours for the network to be able to act for what it was designed for, cannot detect singular elements other than those for which it has been accustomed (3), it's hard to debug during operation and it is not scalable. Considering this aspects, we highlight some applications ...
Neural Networks
... A neuron is a cell in the brain that collects, processes and disseminates electric signals On their own, neurons are not particularly complex Much of the brain’s information-processing capacity is thought to stem from the number of and interrelationships between the neurons. As such is an emergent p ...
... A neuron is a cell in the brain that collects, processes and disseminates electric signals On their own, neurons are not particularly complex Much of the brain’s information-processing capacity is thought to stem from the number of and interrelationships between the neurons. As such is an emergent p ...
Biological Implementation of the Temporal Difference Algorithm for
... same neuromodulatory signal (the TD error, which has been linked to the signaling of DA neurons) and almost the same learning rules in updating their synaptic weights. All the modifiable synapses require local memory to implement the necessary eligibility mechanism. Local memory ensures that the sam ...
... same neuromodulatory signal (the TD error, which has been linked to the signaling of DA neurons) and almost the same learning rules in updating their synaptic weights. All the modifiable synapses require local memory to implement the necessary eligibility mechanism. Local memory ensures that the sam ...
Building and Evaluating Models of Human-Level Intelligence Kenneth Forbus () Nicholas Cassimatis
... data and is therefore likely to at least approximate the actual mechanisms of cognition. To validate a model of (some aspects of) human level-intelligence, one must also demonstrate that it can behave at a human-level of competence. How do we demonstrate this? Three aspects of the human-level intell ...
... data and is therefore likely to at least approximate the actual mechanisms of cognition. To validate a model of (some aspects of) human level-intelligence, one must also demonstrate that it can behave at a human-level of competence. How do we demonstrate this? Three aspects of the human-level intell ...
Learning Text Similarity with Siamese Recurrent
... At each time step t ∈ {1, . . . , T }, the hiddenstate vector ht is updated by the equation ht = σ(W xt + U ht−1 ), in which xt is the input at time t, W is the weight matrix from inputs to the hidden-state vector and U is the weight matrix on the hidden-state vector from the previous time step ht−1 ...
... At each time step t ∈ {1, . . . , T }, the hiddenstate vector ht is updated by the equation ht = σ(W xt + U ht−1 ), in which xt is the input at time t, W is the weight matrix from inputs to the hidden-state vector and U is the weight matrix on the hidden-state vector from the previous time step ht−1 ...
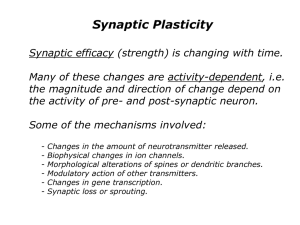
Neurons` Short-Term Plasticity Amplifies Signals
... that a specific neuron prefers, called its “place field,” the neuron responds with high-frequency bursts of spikes. As the rat’s familiarity with the maze increases over only a few minutes, so does the reliability by which hippocampal neurons respond to their preferred July 2006 | Volume 4 | Issue 7 | ...
... that a specific neuron prefers, called its “place field,” the neuron responds with high-frequency bursts of spikes. As the rat’s familiarity with the maze increases over only a few minutes, so does the reliability by which hippocampal neurons respond to their preferred July 2006 | Volume 4 | Issue 7 | ...
4-up pdf - Computer Sciences User Pages
... problems that often have their roots in some aspect of biological information processing. The goal of the subject is to identify solvable and interesting information processing problems, and solve them.” ...
... problems that often have their roots in some aspect of biological information processing. The goal of the subject is to identify solvable and interesting information processing problems, and solve them.” ...
Learning and Predicting Dynamic Network Behavior with Graphical
... of multiagent behavior modeling by introducing the history-dependent graphical multiagent models (hGMMs) that express multiagent behavior on a graph, and capture dynamic relations and strategic decisions by conditioning action on history [5]. However, information the modeler may have about the agent ...
... of multiagent behavior modeling by introducing the history-dependent graphical multiagent models (hGMMs) that express multiagent behavior on a graph, and capture dynamic relations and strategic decisions by conditioning action on history [5]. However, information the modeler may have about the agent ...
How Antidepressants Work - Rainsville Family Practice
... This may be related to genetic predisposition, chronic stress, or illness, certain medications, or by other factors we do not fully understand. In any event, the first neuron cannot secrete enough messengers to activate the receptor sites adequately on the next neuron, therefore the signal is muted. ...
... This may be related to genetic predisposition, chronic stress, or illness, certain medications, or by other factors we do not fully understand. In any event, the first neuron cannot secrete enough messengers to activate the receptor sites adequately on the next neuron, therefore the signal is muted. ...
nn2new-02
... Next we turn our attention to how to go from a group of local neurons to neural networks ...
... Next we turn our attention to how to go from a group of local neurons to neural networks ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Science (IOSR-JCE) e-ISSN: 2278-0661, p-ISSN: 2278-8727 PP 24-28 www.iosrjournals.org
... Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) [1] technology is a new and fast evolving field that seeks direct interaction between the human neural system and machines, aiming to augment human capabilities by enabling people (especially disabled) to communicate and control devices by mere “thinking” or expressing ...
... Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) [1] technology is a new and fast evolving field that seeks direct interaction between the human neural system and machines, aiming to augment human capabilities by enabling people (especially disabled) to communicate and control devices by mere “thinking” or expressing ...
ELEC 548
... Absence Policies: Class attendance is not required, however students will be responsible for the material covered during lecture. The slides presented during class will be available on the course website, and it is the responsibility of the student who missed class to work with other students to rev ...
... Absence Policies: Class attendance is not required, however students will be responsible for the material covered during lecture. The slides presented during class will be available on the course website, and it is the responsibility of the student who missed class to work with other students to rev ...
Distributed Model
... small world nodes at a certain value. 4. The connected nodes merge the local model with new knowledge in another model. 5. Update the connected global model knowledge, and propagate to all the local models in this small world. 6. Sum all the knowledge L3 collected, and update the G2, then repeat the ...
... small world nodes at a certain value. 4. The connected nodes merge the local model with new knowledge in another model. 5. Update the connected global model knowledge, and propagate to all the local models in this small world. 6. Sum all the knowledge L3 collected, and update the G2, then repeat the ...