Theoretical neuroscience: Single neuron dynamics and computation
... • Dynamics: Neural systems are dynamical systems. • Coding: Neural systems are information processing systems. • Learning and memory: Neural systems are information storage devices. • Computing: Neural systems are computing devices. ...
... • Dynamics: Neural systems are dynamical systems. • Coding: Neural systems are information processing systems. • Learning and memory: Neural systems are information storage devices. • Computing: Neural systems are computing devices. ...
SOLARcief2003
... Computes statistical information (for example, entropy based information deficiency) in its subspaces. Makes associations with other neurons. ...
... Computes statistical information (for example, entropy based information deficiency) in its subspaces. Makes associations with other neurons. ...
File
... -- an axon carries nerve impulses AWAY from the cell body. -- if an action potential is generated, it will originate within the axon hillock, which will then pass the signal on to the axon. -- the axon carries the action potential from the cell body/axon hillock to its bulb-like synaptic endings (lo ...
... -- an axon carries nerve impulses AWAY from the cell body. -- if an action potential is generated, it will originate within the axon hillock, which will then pass the signal on to the axon. -- the axon carries the action potential from the cell body/axon hillock to its bulb-like synaptic endings (lo ...
Intrusion detection pattern recognition using an Artificial Neural
... • Myelin: Fundamental, which prevents neurons to enter into short circuit surrounds the axon. On the other hand contributes to the message transmission speed. ...
... • Myelin: Fundamental, which prevents neurons to enter into short circuit surrounds the axon. On the other hand contributes to the message transmission speed. ...
Memories of punishment and relief in a mini-brain - Schram
... odour as a signal for the “painful” punishment. When the timing of odour and shock are reversed, such that the odour follows shock, this odour is subsequently approached as it signals a “feeling of relief”. Thus, an experience with shock leaves the flies with two opposite memories, about stimuli tha ...
... odour as a signal for the “painful” punishment. When the timing of odour and shock are reversed, such that the odour follows shock, this odour is subsequently approached as it signals a “feeling of relief”. Thus, an experience with shock leaves the flies with two opposite memories, about stimuli tha ...
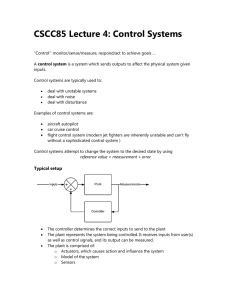
CSCC85 Lecture 4: Control Systems
... Neural networks are comprised of various neuron nodes combining multiple inputs using different weights to approximate some unknown ...
... Neural networks are comprised of various neuron nodes combining multiple inputs using different weights to approximate some unknown ...
File
... The brain regulates body functions, behaviors, and emotions. Neurons are the cells that fulfill these functions. How do neurons do this? Refer to handout, Master 2.3 How Do Neurons Communicate? Discuss with a partner about the diagrams, and then write a summary of how you think the neurons are inter ...
... The brain regulates body functions, behaviors, and emotions. Neurons are the cells that fulfill these functions. How do neurons do this? Refer to handout, Master 2.3 How Do Neurons Communicate? Discuss with a partner about the diagrams, and then write a summary of how you think the neurons are inter ...
Signal Averaging
... Fundamental to the idea of a graphical model is the notion of modularity – a complex system is built by combining simpler parts. Many of the classical multivariate probabilistic systems studied in fields such as statistics, systems engineering, information theory, pattern recognition and statist ...
... Fundamental to the idea of a graphical model is the notion of modularity – a complex system is built by combining simpler parts. Many of the classical multivariate probabilistic systems studied in fields such as statistics, systems engineering, information theory, pattern recognition and statist ...
BN4402 - ECE@NUS
... This course allows students to familiarize with the evolving field of Neuroengineering and introduces the concepts of Neuronal modeling. Neuronal Modeling is a technique that Computational Neuroscientists use to explore the behavior of neurons. Typically invitro experiments are conducted on brain sl ...
... This course allows students to familiarize with the evolving field of Neuroengineering and introduces the concepts of Neuronal modeling. Neuronal Modeling is a technique that Computational Neuroscientists use to explore the behavior of neurons. Typically invitro experiments are conducted on brain sl ...
Brain(annotated)
... A more likely view is that the information is encoded in exact spike times (and also the strength of synaptic connections). Thus neurons are communicating by sending numbers (times) to each other, and interpreting that information via synaptic strengths. ...
... A more likely view is that the information is encoded in exact spike times (and also the strength of synaptic connections). Thus neurons are communicating by sending numbers (times) to each other, and interpreting that information via synaptic strengths. ...
SM-718: Artificial Intelligence and Neural Networks Credits: 4 (2-1-2)
... using propositional to Web Mining . predicate logic, comparison of propositional and 2 predicate logic, Resolution, refutation, deduction, theorem proving, inferencing. monotonic and non-monotonic reasoning, Semantic 2 networks, scripts, schemas, frames, conceptual dependency, forward and backward r ...
... using propositional to Web Mining . predicate logic, comparison of propositional and 2 predicate logic, Resolution, refutation, deduction, theorem proving, inferencing. monotonic and non-monotonic reasoning, Semantic 2 networks, scripts, schemas, frames, conceptual dependency, forward and backward r ...
Black Box Methods – Neural Networks and Support Vector
... The primary detail that differentiates among these activation functions is the output signal range. Typically, this is one of (0, 1), (-1, +1), or (-inf, +inf). The choice of activation function biases the neural network such that it may fit certain types of data more appropriately, allowing the con ...
... The primary detail that differentiates among these activation functions is the output signal range. Typically, this is one of (0, 1), (-1, +1), or (-inf, +inf). The choice of activation function biases the neural network such that it may fit certain types of data more appropriately, allowing the con ...
Modeling Student Learning: Binary or Continuous Skill?
... binary latent variable (either learned or unlearned). Figure 1 illustrates the model; the illustration is done in a nonstandard way to stress the relation of the model to the model with continuous skill. The estimated skill is updated using a Bayes rule based on the observed answers; the prediction ...
... binary latent variable (either learned or unlearned). Figure 1 illustrates the model; the illustration is done in a nonstandard way to stress the relation of the model to the model with continuous skill. The estimated skill is updated using a Bayes rule based on the observed answers; the prediction ...
Synapses and neuronal signalling
... • Different combinations of ion channels, transmitter receptors • Enzymes and genes for different transmitters • Other proteins that influence excitability and synaptic function, adaptability • Changes in expression of particular genes can modify the strength of particular synaptic inputs and output ...
... • Different combinations of ion channels, transmitter receptors • Enzymes and genes for different transmitters • Other proteins that influence excitability and synaptic function, adaptability • Changes in expression of particular genes can modify the strength of particular synaptic inputs and output ...
Artificial Intelligence Support for Scientific Model
... language, scientists can use SIGMA’sgraphical interface to "program" visually using a high-level data flow modeling language. The terms in this modelinglanguage involve scientific concepts (e.g., physical quantities, scientific equations, and datasets) rather than general programmingconcepts (e.g., ...
... language, scientists can use SIGMA’sgraphical interface to "program" visually using a high-level data flow modeling language. The terms in this modelinglanguage involve scientific concepts (e.g., physical quantities, scientific equations, and datasets) rather than general programmingconcepts (e.g., ...