a new method to parallel two supplies
... A NEW METHOD TO PARALLEL TWO SUPPLIES This new document will present a way to parallel two supplies (the main board supply and a Li-Ion battery) in order to power a single output. While the Li-Ion battery is not in use, it will get recharged by sampling a small portion of the current from the main b ...
... A NEW METHOD TO PARALLEL TWO SUPPLIES This new document will present a way to parallel two supplies (the main board supply and a Li-Ion battery) in order to power a single output. While the Li-Ion battery is not in use, it will get recharged by sampling a small portion of the current from the main b ...
KA7500B Datasheet
... 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life the body, or (b) support or sustain life, or (c) whose support device or system, ...
... 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life the body, or (b) support or sustain life, or (c) whose support device or system, ...
Product Data Sheet: DEHNconnect SD2 DCO SD2 MD HF 5 (917 970)
... ■ Disconnection module for disconnecting signal circuits for maintenance work ■ For installation in conformity with the lightning protection zone concept at the boundaries from 0B –2 and higher ...
... ■ Disconnection module for disconnecting signal circuits for maintenance work ■ For installation in conformity with the lightning protection zone concept at the boundaries from 0B –2 and higher ...
EE 321 Analog Electronics, Fall 2013 Homework #13 solution
... 4.86. Figure P4.86 shows a scheme for coupling and amplifying a high-frequency pulse signal. The circuit utilizes two MOSFETs whose bias details are not shown and a 50-Ω coaxial cable. Transistor Q1 operates as a CS amplifier and Q2 as a CG amplifier. For proper operation, transistor Q2 is required ...
... 4.86. Figure P4.86 shows a scheme for coupling and amplifying a high-frequency pulse signal. The circuit utilizes two MOSFETs whose bias details are not shown and a 50-Ω coaxial cable. Transistor Q1 operates as a CS amplifier and Q2 as a CG amplifier. For proper operation, transistor Q2 is required ...
LVDS Driver
... switch. A matched ‘sink’ and ‘source’ current of ~3mA is provided by a simple current mirror scheme. Small differences in the output current can be expected due to differences in matching of the NMOS and PMOS current mirrors. Current Mirror masters for Low Level Driver - A simple resistor based mirr ...
... switch. A matched ‘sink’ and ‘source’ current of ~3mA is provided by a simple current mirror scheme. Small differences in the output current can be expected due to differences in matching of the NMOS and PMOS current mirrors. Current Mirror masters for Low Level Driver - A simple resistor based mirr ...
The Field Effect Transistor
... Redo the circuit replacing the computer-generated voltages with a power supply for VDD and a signal generator for the variable input voltage as shown in Figure 3. Choose a value of Rs to give the following circuit a good operating point. For a good operating point, the drain voltage is between 5 and ...
... Redo the circuit replacing the computer-generated voltages with a power supply for VDD and a signal generator for the variable input voltage as shown in Figure 3. Choose a value of Rs to give the following circuit a good operating point. For a good operating point, the drain voltage is between 5 and ...
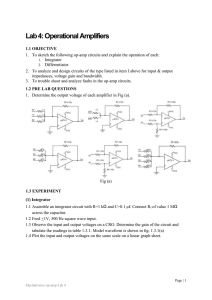
Sheet 4
... (1) Integrator 1.1 Assemble an integrator circuit with R=1 kΩ and C=0.1 µf. Connect Rf of value 1 MΩ across the capacitor. 1.2 Feed +1V, 500 Hz square wave input. 1.3 Observe the input and output voltages on a CRO. Determine the gain of the circuit and tabulate the readings in table 1.3.1. Model wav ...
... (1) Integrator 1.1 Assemble an integrator circuit with R=1 kΩ and C=0.1 µf. Connect Rf of value 1 MΩ across the capacitor. 1.2 Feed +1V, 500 Hz square wave input. 1.3 Observe the input and output voltages on a CRO. Determine the gain of the circuit and tabulate the readings in table 1.3.1. Model wav ...
L45-kirchhoff- Jan13-ch5
... The sum of the drops in potential difference equals the potential difference at the source (Remember the loop rule?) The voltage in each loop is the same as the source of potential: Equation: ...
... The sum of the drops in potential difference equals the potential difference at the source (Remember the loop rule?) The voltage in each loop is the same as the source of potential: Equation: ...
Solutions - UF Physics
... figure, we see that from point A all the possible three roads that this current can take look exactly symmetrical. Therefore, all three wires that start from A must carry the same current, i.e. I/3 since the sum ought to sum up to I. Take one of these roads. When you hit the next node, you see that ...
... figure, we see that from point A all the possible three roads that this current can take look exactly symmetrical. Therefore, all three wires that start from A must carry the same current, i.e. I/3 since the sum ought to sum up to I. Take one of these roads. When you hit the next node, you see that ...
Here the input voltage to the circuit is given by v(t) - Rose
... Here the input voltage to the circuit is given by v(t). The capacitor is fully discharged at time 0. We want to find the ideal op amp’s output voltage. For ideal op amp, the voltages of the input terminals are equal. The inverted terminal is grounded, so it’s at 0 V. This means that the non-invertin ...
... Here the input voltage to the circuit is given by v(t). The capacitor is fully discharged at time 0. We want to find the ideal op amp’s output voltage. For ideal op amp, the voltages of the input terminals are equal. The inverted terminal is grounded, so it’s at 0 V. This means that the non-invertin ...
Time Delay Relay Using IC 555
... which drives (opens/closes) an electric switch that is capable of carrying much larger current amounts. Or a circuit which operates the coil or electronic actuator from one source and uses a separate power source to drive an isolated device. Relays are used throughout the automobile. A typical vehic ...
... which drives (opens/closes) an electric switch that is capable of carrying much larger current amounts. Or a circuit which operates the coil or electronic actuator from one source and uses a separate power source to drive an isolated device. Relays are used throughout the automobile. A typical vehic ...
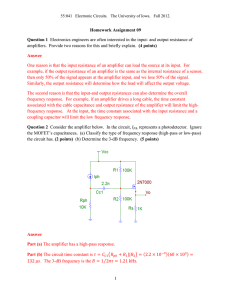
1 Homework Assignment 09 Question 1 Electronics engineers are
... 55:041 Electronic Circuits. The University of Iowa. Fall 2012. ...
... 55:041 Electronic Circuits. The University of Iowa. Fall 2012. ...
Wilson current mirror

A Wilson current mirror is a three-terminal circuit (Fig. 1) that accepts an input current at the input terminal and provides a ""mirrored"" current source or sink output at the output terminal. The mirrored current is a precise copy of the input current. It may be used as a Wilson current source by applying a constant bias current to the input branch as in Fig. 2. The circuit is named after George R. Wilson, an integrated circuit design engineer who worked for Tektronix. Wilson devised this configuration in 1967 when he and Barrie Gilbert challenged each other to find an improved current mirror overnight that would use only three transistors. Wilson won the challenge.