Humoral and Cellular Immunity
... (Hence the name: humoral immunity. Humoral comes from the Greek chymos, a key concept in ancient Greek medicine. In this view, people were made out of four fluids: blood, black bile, yellow bile and mucus (phlegma). Being healthy meant that the four humors were balanced. Having too much of a humor m ...
... (Hence the name: humoral immunity. Humoral comes from the Greek chymos, a key concept in ancient Greek medicine. In this view, people were made out of four fluids: blood, black bile, yellow bile and mucus (phlegma). Being healthy meant that the four humors were balanced. Having too much of a humor m ...
Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells Effector T cells
... NK cells protect against intracellular bacteria which tend to infect macrophages. (e.g. Listeria Toxoplasma, Leishmania) ...
... NK cells protect against intracellular bacteria which tend to infect macrophages. (e.g. Listeria Toxoplasma, Leishmania) ...
Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells Effector T cells
... NK cells activation is controlled by the balance between activating and inhibitory receptors. Inhibitory receptors bind MHC class I molecules and prevent inappropriate lysis of self cells. NK cells are activated by “missing self”, which can occur when viruses or tumor cells downregulate MHC class I ...
... NK cells activation is controlled by the balance between activating and inhibitory receptors. Inhibitory receptors bind MHC class I molecules and prevent inappropriate lysis of self cells. NK cells are activated by “missing self”, which can occur when viruses or tumor cells downregulate MHC class I ...
Innate immunity - Fadel Muhammad Garishah, MD
... substances produced at epithelial surfaces; – (2) phagocytic cells (neutrophils, macrophages) and NK (natural killer) cells; – (3) blood proteins, including members of the complement system and other mediators of inflammation; and – (4) proteins called cytokines that regulate and coordinate many of ...
... substances produced at epithelial surfaces; – (2) phagocytic cells (neutrophils, macrophages) and NK (natural killer) cells; – (3) blood proteins, including members of the complement system and other mediators of inflammation; and – (4) proteins called cytokines that regulate and coordinate many of ...
PAP System Interaction Reading
... infections it has encountered. The specific B and T cells that have been stimulated by a particular antigen grow and divide to form a pool of “memory” cells ready for a second encounter with the same antigen. If pathogens carrying the same antigens appear again, much larger numbers of cells are read ...
... infections it has encountered. The specific B and T cells that have been stimulated by a particular antigen grow and divide to form a pool of “memory” cells ready for a second encounter with the same antigen. If pathogens carrying the same antigens appear again, much larger numbers of cells are read ...
Bioanalytical chemistry
... ends of its two arms. However, a Fab or ScFv would only have a valence of one. Antigen will be precipitated only if it has several antibody-binding sites. This condition is usually satisfied in macromolecular antigens, which have a complex surface with binding sites for several different antibodies. ...
... ends of its two arms. However, a Fab or ScFv would only have a valence of one. Antigen will be precipitated only if it has several antibody-binding sites. This condition is usually satisfied in macromolecular antigens, which have a complex surface with binding sites for several different antibodies. ...
Margot Shields
... monocytes and lymphocytes). • The body cannot respond adequately to invading antigens without a minimum number of each type of immune cell. An optimum response requires a proper balance of the various types of cells. • However, changes found in the PNI literature are usually quite small and whether ...
... monocytes and lymphocytes). • The body cannot respond adequately to invading antigens without a minimum number of each type of immune cell. An optimum response requires a proper balance of the various types of cells. • However, changes found in the PNI literature are usually quite small and whether ...
PDF of this dashboard
... blood and bone marrow as treatment proceeds. It will also monitor the treatment’s effect on the level of disease and follow each patient for two years. ...
... blood and bone marrow as treatment proceeds. It will also monitor the treatment’s effect on the level of disease and follow each patient for two years. ...
Slide 1
... 6 or 7 steps to cancer • In the early 1950s epidemiological studies showed that cancer incidence increases with the 6th power of age – Though risk from mutagen exposure is linear (but also delayed) ...
... 6 or 7 steps to cancer • In the early 1950s epidemiological studies showed that cancer incidence increases with the 6th power of age – Though risk from mutagen exposure is linear (but also delayed) ...
understanding the immune system and laboratory values in multiple
... the normal (non-myeloma) immunoglobulins ...
... the normal (non-myeloma) immunoglobulins ...
III. Immunology and Complement
... First antibody to be produced and is of greatest importance in the first few days of a primary immune response to an infecting organism. Does not cross the placenta. Many blood group antibodies that are capable of agglutinating antigen positive RBCs suspended in saline in tests performed at 22 C are ...
... First antibody to be produced and is of greatest importance in the first few days of a primary immune response to an infecting organism. Does not cross the placenta. Many blood group antibodies that are capable of agglutinating antigen positive RBCs suspended in saline in tests performed at 22 C are ...
Cells
... fatty acids are located • These molecules role is membrane fluidity, which changes with temperature • Fluidity is the rate that objects can past through the membrane, higher the temperature the more easily things can past through ...
... fatty acids are located • These molecules role is membrane fluidity, which changes with temperature • Fluidity is the rate that objects can past through the membrane, higher the temperature the more easily things can past through ...
Raulet, D.H., and F. Melchers. 2001. Lymphocyte development. Curr Opin Immunol 13:163-165.
... B cell depends on the specificity of its BCR. If that receptor recognizes an autoantigen in the environment with high avidity, it is negatively selected — deleted by accelerated apoptosis. If it has a BCR with low avidity for autoantigens, it can be positively selected. Such cells undergo activation ...
... B cell depends on the specificity of its BCR. If that receptor recognizes an autoantigen in the environment with high avidity, it is negatively selected — deleted by accelerated apoptosis. If it has a BCR with low avidity for autoantigens, it can be positively selected. Such cells undergo activation ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... Like B cells, T cells have unique antigen receptors, called the T cell receptor, or TCR. However, the receptors of cytotoxic and helper T cells cannot recognize antigen present in the tissues, lymph, or blood. Instead, antigen must be presented to them by an antigen-presenting cell (APC). When an AP ...
... Like B cells, T cells have unique antigen receptors, called the T cell receptor, or TCR. However, the receptors of cytotoxic and helper T cells cannot recognize antigen present in the tissues, lymph, or blood. Instead, antigen must be presented to them by an antigen-presenting cell (APC). When an AP ...
Document
... xenograft – from a lower animal to a human being or from an animal of one species to one of another species ...
... xenograft – from a lower animal to a human being or from an animal of one species to one of another species ...
The Immune system
... • CD4 + helper T cells (TH); further subdivided into type 1 and type 2, also known as Th1 and Th2. The differentiation of Th cells into Th1 and Th2 occurs only after these cells have been activated during an immune response, in the peripheral lymphoid system. - Only recognize antigen bound to MHC cl ...
... • CD4 + helper T cells (TH); further subdivided into type 1 and type 2, also known as Th1 and Th2. The differentiation of Th cells into Th1 and Th2 occurs only after these cells have been activated during an immune response, in the peripheral lymphoid system. - Only recognize antigen bound to MHC cl ...
Unit 3 Biochemistry - The Naked Science Society
... Biochemists study the structures and physical properties of biological molecules. ...
... Biochemists study the structures and physical properties of biological molecules. ...
The Body`s Defenses
... When the body is invaded, four important nonspecific defenses take action: the inflammatory response; the temperature response; proteins that kill or inhibit pathogens; and white blood cells, which attack and kill pathogens. Inflammatory Response: Injury or local infection, such as a cut or a scrape ...
... When the body is invaded, four important nonspecific defenses take action: the inflammatory response; the temperature response; proteins that kill or inhibit pathogens; and white blood cells, which attack and kill pathogens. Inflammatory Response: Injury or local infection, such as a cut or a scrape ...
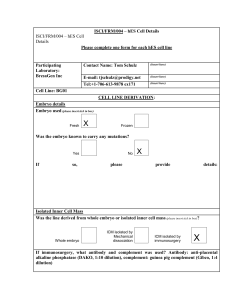
ISCI/FRM/004 – hES Cell Details
... If YES, please provide details: (Culture conditions) BG01 cells were first isolated in a 20% FBS containing medium. Subsequent passaging was performed in hESC medium (above) or hESC medium conditioned on MEFs prior to use (MEF-CM above). (karyotype) We have observed trisomies of chromosomes 12, 17 a ...
... If YES, please provide details: (Culture conditions) BG01 cells were first isolated in a 20% FBS containing medium. Subsequent passaging was performed in hESC medium (above) or hESC medium conditioned on MEFs prior to use (MEF-CM above). (karyotype) We have observed trisomies of chromosomes 12, 17 a ...
Laboratory Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment of Bacte rial Infection
... Nonselective (noninhibitory) media permit the growth of many microorganisms. Selective media contain inhibitory substances that permit the isolation of specific types of microorganisms. Microbial Identification: Colony and cellular morphology may permit preliminary identification. Growth characteris ...
... Nonselective (noninhibitory) media permit the growth of many microorganisms. Selective media contain inhibitory substances that permit the isolation of specific types of microorganisms. Microbial Identification: Colony and cellular morphology may permit preliminary identification. Growth characteris ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.