Hardy Weinberg equation questions
... Two genes control the type of comb; each gene has a dominant and a recessive allele. The two genes are inherited independently, but interact to produce the four types of comb. ...
... Two genes control the type of comb; each gene has a dominant and a recessive allele. The two genes are inherited independently, but interact to produce the four types of comb. ...
transplantation
... Bone marrow transplantation Thymus transplantation Spleen transplantation Blood transfusion of neonate In most cases the reaction is ...
... Bone marrow transplantation Thymus transplantation Spleen transplantation Blood transfusion of neonate In most cases the reaction is ...
The Lung Immunology Group Department of Biological Sciences
... associated with ulcerative colitis CXCR-1 (+2607)GC genotype associated with 8.3-fold increased susceptibility to bronchiectasis associated with UC • CXCR-1 (+2607 G/C) -AA substitution from serine to threonine at residue of CXCR-1 critical for ligand binding - alters binding of IL-8 to CXCR-1 • Air ...
... associated with ulcerative colitis CXCR-1 (+2607)GC genotype associated with 8.3-fold increased susceptibility to bronchiectasis associated with UC • CXCR-1 (+2607 G/C) -AA substitution from serine to threonine at residue of CXCR-1 critical for ligand binding - alters binding of IL-8 to CXCR-1 • Air ...
Full Text in English - Health Science Journals: Indonesia
... CD is acquired within the family and a good example of disease related to HLA alleles.4 CD is likely to occur in 10% of first degree of relatives. Concordance in identical twins is around 70%.1,4,6 Several studies reported that HLA-DQ2 (DQA1*0501/DQB1*0201) and in some extent to HLA-DQ8 (DQA1*0301/D ...
... CD is acquired within the family and a good example of disease related to HLA alleles.4 CD is likely to occur in 10% of first degree of relatives. Concordance in identical twins is around 70%.1,4,6 Several studies reported that HLA-DQ2 (DQA1*0501/DQB1*0201) and in some extent to HLA-DQ8 (DQA1*0301/D ...
Week 8 Lab: SNP Detection, SNP Discussion
... cut with Hpa II. The remaining six lanes will consist of cut and uncut DNA from each student in the lab group. The loading dye they’re using this week will only contain the larger dye, so we don’t have interference with the smaller dye band and the DNA bands we’re interested in. ***At the end of lab ...
... cut with Hpa II. The remaining six lanes will consist of cut and uncut DNA from each student in the lab group. The loading dye they’re using this week will only contain the larger dye, so we don’t have interference with the smaller dye band and the DNA bands we’re interested in. ***At the end of lab ...
The nature of the antigen determine the type of immune response
... a. Epitopes are very small (e.g., just four or five amino acid or monosaccharide residues). b. The epitopes on an antigen can be linear (i.e., continuous within the amino acid sequence of hr molecule) or conformational (i.e., containing amino acids that end up in the same area on the surface of the ...
... a. Epitopes are very small (e.g., just four or five amino acid or monosaccharide residues). b. The epitopes on an antigen can be linear (i.e., continuous within the amino acid sequence of hr molecule) or conformational (i.e., containing amino acids that end up in the same area on the surface of the ...
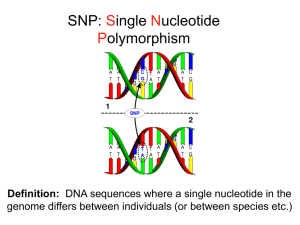
SNP presentation
... ACTN3 is a protein that is only turned on in fast-twitch muscle fibers (the kind of muscles use in power sports like sprinting and weightlifting) C allele- functional protein (CC & CT are power athletes) T allele- nonsense SNP. People with two T alleles have no functional alpha-actin-3 (TT are endur ...
... ACTN3 is a protein that is only turned on in fast-twitch muscle fibers (the kind of muscles use in power sports like sprinting and weightlifting) C allele- functional protein (CC & CT are power athletes) T allele- nonsense SNP. People with two T alleles have no functional alpha-actin-3 (TT are endur ...
chapter fourteen
... In the flower-color example, the F1 plants inherited a purple-flower allele from one parent and a white-flower allele from the other. They had purple flowers because the allele for that trait is dominant. 4. 4. Mendel’s law of segregation states that the two alleles for a heritable character sep ...
... In the flower-color example, the F1 plants inherited a purple-flower allele from one parent and a white-flower allele from the other. They had purple flowers because the allele for that trait is dominant. 4. 4. Mendel’s law of segregation states that the two alleles for a heritable character sep ...
CHAPTER 14 MENDEL AND THE GENE IDEA
... ° In the flower-color example, the F1 plants inherited a purple-flower allele from one parent and a white-flower allele from the other. ° They had purple flowers because the allele for that trait is dominant. 4. 4. Mendel’s law of segregation states that the two alleles for a heritable character sep ...
... ° In the flower-color example, the F1 plants inherited a purple-flower allele from one parent and a white-flower allele from the other. ° They had purple flowers because the allele for that trait is dominant. 4. 4. Mendel’s law of segregation states that the two alleles for a heritable character sep ...
Update in Endocrine Autoimmunity
... Rapid advances in human genetics have afforded the opportunity to identify new risk alleles associated with common diseases, like type 1 diabetes and thyroiditis, that have previously been elusive. This has been due to a number of factors, including the completion of the human genome sequence, the d ...
... Rapid advances in human genetics have afforded the opportunity to identify new risk alleles associated with common diseases, like type 1 diabetes and thyroiditis, that have previously been elusive. This has been due to a number of factors, including the completion of the human genome sequence, the d ...
Chapter 14 – Mendel and the Gene Idea
... He studied at the University of Vienna from 1851 to 1853, where he was influenced by a physicist who encouraged experimentation and the application of mathematics to science and by a botanist who stimulated Mendel’s interest in the causes of variation in ...
... He studied at the University of Vienna from 1851 to 1853, where he was influenced by a physicist who encouraged experimentation and the application of mathematics to science and by a botanist who stimulated Mendel’s interest in the causes of variation in ...
population genetics
... The way a trait is determined by the alleles for a gene depends on how the alleles, and the proteins they make, interact with each other. Obviously, if an individual is homozygous for a gene/locus (i.e., having two of the same allele), that allele determines the trait. If an individual is heterozygo ...
... The way a trait is determined by the alleles for a gene depends on how the alleles, and the proteins they make, interact with each other. Obviously, if an individual is homozygous for a gene/locus (i.e., having two of the same allele), that allele determines the trait. If an individual is heterozygo ...
Traits and Families
... b. Random chance determines which of the two genes is passed to each offspring. ...
... b. Random chance determines which of the two genes is passed to each offspring. ...
Document
... version of a trait to pass on or homozygous. • Sometimes we refer to homozygous organisms as being a “pure bred”. • If a pea plant came from parents that were tall, it is tall and all of its offspring are tall when crossed with other pea plants that are “true-breeding”, we can be fairly certain that ...
... version of a trait to pass on or homozygous. • Sometimes we refer to homozygous organisms as being a “pure bred”. • If a pea plant came from parents that were tall, it is tall and all of its offspring are tall when crossed with other pea plants that are “true-breeding”, we can be fairly certain that ...
14_DetailLectOut_jkAR
... In the flower-color example, the F1 plants inherited a purple-flower allele from one parent and a white-flower allele from the other. They had purple flowers because the allele for that trait is dominant. 4. 4. Mendel’s law of segregation states that the two alleles for a heritable character sep ...
... In the flower-color example, the F1 plants inherited a purple-flower allele from one parent and a white-flower allele from the other. They had purple flowers because the allele for that trait is dominant. 4. 4. Mendel’s law of segregation states that the two alleles for a heritable character sep ...
Linkage and Linkage Disequilibrium
... •Selection: When an individual’s genotype influences his/her reproductive fitness. For example, if two alleles interact to decrease reproductive fitness, the alleles will tend to be negatively associated. •Stratification: Some populations consist of two or more subgroups that, for cultural or other ...
... •Selection: When an individual’s genotype influences his/her reproductive fitness. For example, if two alleles interact to decrease reproductive fitness, the alleles will tend to be negatively associated. •Stratification: Some populations consist of two or more subgroups that, for cultural or other ...
Early frameshift alleles of zebrafish tbx5a that fail to
... potential translation of N-terminal Tbx5a protein remnants that could retain function. Further indicating that targeting this region could result in loss-of-function alleles, the corresponding amino acid sequence is highly conserved between zebrafish and humans (indicating functional conservation) a ...
... potential translation of N-terminal Tbx5a protein remnants that could retain function. Further indicating that targeting this region could result in loss-of-function alleles, the corresponding amino acid sequence is highly conserved between zebrafish and humans (indicating functional conservation) a ...
Lab 8 - Population Genetics and Evolution
... offspring, so all four cards must be reshuffled and the process repeated to produce a second offspring. 2. The other partner should then record the genotype of the second offspring on the Data Page. The very short reproductive career of this generation is over. You and your partner now become t ...
... offspring, so all four cards must be reshuffled and the process repeated to produce a second offspring. 2. The other partner should then record the genotype of the second offspring on the Data Page. The very short reproductive career of this generation is over. You and your partner now become t ...
Name Date Class
... In a test cross, the organism with the trait controlled by a dominant allele is crossed with an organism with a trait controlled by a recessive allele. If all offspring have the trait controlled by the dominant allele, then the parent is probably a purebred. If any offspring has the recessive strait ...
... In a test cross, the organism with the trait controlled by a dominant allele is crossed with an organism with a trait controlled by a recessive allele. If all offspring have the trait controlled by the dominant allele, then the parent is probably a purebred. If any offspring has the recessive strait ...
CHAPTER 14 MENDEL AND THE GENE IDEA
... In the flower-color example, the F1 plants inherited a purple-flower allele from one parent and a white-flower allele from the other. They had purple flowers because the allele for that trait is dominant. 4. 4. Mendel’s law of segregation states that the two alleles for a heritable character sep ...
... In the flower-color example, the F1 plants inherited a purple-flower allele from one parent and a white-flower allele from the other. They had purple flowers because the allele for that trait is dominant. 4. 4. Mendel’s law of segregation states that the two alleles for a heritable character sep ...
7.014 Genetics Section Problems
... iii) To be type B, individual 3 must have gotten an io ALK- chromosome from Dad and an I B ALK+ chromosome from Mom. iv) Individual 4 got an IA ALK- chromosome from Mom and an io ALK- chromosome from Dad. If no recombination occurred, then for this impending child the chance of getting I B ALK+ chro ...
... iii) To be type B, individual 3 must have gotten an io ALK- chromosome from Dad and an I B ALK+ chromosome from Mom. iv) Individual 4 got an IA ALK- chromosome from Mom and an io ALK- chromosome from Dad. If no recombination occurred, then for this impending child the chance of getting I B ALK+ chro ...
Name Introduction to Genetics Genetics: I. Genes and
... A. Mendel needed to answer one more question: When alleles are being segregated during gamete formation, does the segregation of one pair alleles have any affect on the segregation of a different pair of alleles? In other words, does the gene that determines if a pea plant is tall or dwarf have any ...
... A. Mendel needed to answer one more question: When alleles are being segregated during gamete formation, does the segregation of one pair alleles have any affect on the segregation of a different pair of alleles? In other words, does the gene that determines if a pea plant is tall or dwarf have any ...
Bean Bunny Evolution
... so that each partner has a chance to select the beans and record the results. 11. Determine the gene frequency of F and f for each generation and record them in the chart in the columns labeled “Gene Frequency F” and “Gene Frequency f.” To find the gene frequency of F, divide the number of F by the ...
... so that each partner has a chance to select the beans and record the results. 11. Determine the gene frequency of F and f for each generation and record them in the chart in the columns labeled “Gene Frequency F” and “Gene Frequency f.” To find the gene frequency of F, divide the number of F by the ...
Human-specific evolution of killer cell immunoglobulin
... populations and species. Modulating these functions are conserved and variable NK-cell receptors that recognize epitopes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. In humans, for example, recognition of human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-E by the CD94:NKG2A receptor is conserved, wherea ...
... populations and species. Modulating these functions are conserved and variable NK-cell receptors that recognize epitopes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. In humans, for example, recognition of human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-E by the CD94:NKG2A receptor is conserved, wherea ...
GENETICS & EVOLUTION : Inheritance - mf011
... red blood cells: IA, IB, and i. The enzyme encoded by the IA allele adds the A carbohydrate, whereas the enzyme encoded by the IB allele adds the B carbohydrate; the enzyme encoded by the i allele adds neither ...
... red blood cells: IA, IB, and i. The enzyme encoded by the IA allele adds the A carbohydrate, whereas the enzyme encoded by the IB allele adds the B carbohydrate; the enzyme encoded by the i allele adds neither ...
Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is the locus of genes that encode for proteins on the surface of cells that are responsible for regulation of the immune system in humans. This group of genes resides on chromosome 6 (exception: the gene for β2-microglobulin which is located on chromosome 15), and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins and has many other functions. The HLA genes are the human versions of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes that are found in most vertebrates (and thus are the most studied of the MHC genes). The proteins encoded by certain genes are also known as antigens, as a result of their historic discovery as factors in organ transplants. The major HLAs are essential elements for immune function. Different classes have different functions:HLAs corresponding to MHC class I (A, B, and C) present peptides from inside the cell. For example, if the cell is infected by a virus, the HLA system brings fragments of the virus to the surface of the cell so that the cell can be destroyed by the immune system. These peptides are produced from digested proteins that are broken down in the proteasomes. In general, these particular peptides are small polymers, about 9 amino acids in length. Foreign antigens presented by MHC class I attract killer T-cells (also called CD8 positive- or cytotoxic T-cells) that destroy cells.HLAs corresponding to MHC class II (DP, DM, DOA, DOB, DQ, and DR) present antigens from outside of the cell to T-lymphocytes. These particular antigens stimulate the multiplication of T-helper cells, which in turn stimulate antibody-producing B-cells to produce antibodies to that specific antigen. Self-antigens are suppressed by regulatory T cells.HLAs corresponding to MHC class III encode components of the complement system.HLAs have other roles. They are important in disease defense. They are the major cause of organ transplant rejections. They may protect against or fail to protect (if down-regulated by an infection) against cancers. Mutations in HLA may be linked to autoimmune disease (examples: type I diabetes, coeliac disease). HLA may also be related to people's perception of the odor of other people, and may be involved in mate selection, as at least one study found a lower-than-expected rate of HLA similarity between spouses in an isolated community.Aside from the genes encoding the 6 major antigen-presenting proteins, there are a large number of other genes, many involved in immune function, located on the HLA complex. Diversity of HLAs in the human population is one aspect of disease defense, and, as a result, the chance of two unrelated individuals with identical HLA molecules on all loci is very low. HLA genes have historically been identified as a result of the ability to successfully transplant organs between HLA-similar individuals.