Types of Chemical Reactions
... 5. What is the net ionic equation for the reaction between aqueous calcium hydroxide and nitric acid? The products of this reaction are aqueous calcium nitrate and water. How does this net ionic equation compare to the net ionic equation shown at the top of this page? Hint: you may want to begin wit ...
... 5. What is the net ionic equation for the reaction between aqueous calcium hydroxide and nitric acid? The products of this reaction are aqueous calcium nitrate and water. How does this net ionic equation compare to the net ionic equation shown at the top of this page? Hint: you may want to begin wit ...
Notes - Text
... • At room temperature, it decomposes to brown NO2. N2O4(g) → 2NO2(g) • At some time, the color stops changing and we have a mixture of N2O4 and NO2. • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the concentrations of all species are constant. • Assume that both the forward and reverse reactions are e ...
... • At room temperature, it decomposes to brown NO2. N2O4(g) → 2NO2(g) • At some time, the color stops changing and we have a mixture of N2O4 and NO2. • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the concentrations of all species are constant. • Assume that both the forward and reverse reactions are e ...
CBSE/12th Class/2010/CHEMISTRY
... couple or Fe3+/Fe2+ couple.Because Mn3+ has the outer electronic configuration of 3d4 and Mn2+ has the outer electronic configuration of 3d5. Thus, the conversion of Mn3+ to Mn2+ will be a favourable reaction since 3d5 is a very stable configuration as it is half filled configuration. Hence, Eo valu ...
... couple or Fe3+/Fe2+ couple.Because Mn3+ has the outer electronic configuration of 3d4 and Mn2+ has the outer electronic configuration of 3d5. Thus, the conversion of Mn3+ to Mn2+ will be a favourable reaction since 3d5 is a very stable configuration as it is half filled configuration. Hence, Eo valu ...
Chemistry Syllabus - Madison County Schools
... 2f. Compare different types of intermolecular forces and explain the relationship between intermolecular forces, boiling points, and vapor pressure when comparing differences in properties of pure substances. (DOK 1) 2g. Develop a three-dimensional model of molecular structure. (DOK 2) Lewis dot s ...
... 2f. Compare different types of intermolecular forces and explain the relationship between intermolecular forces, boiling points, and vapor pressure when comparing differences in properties of pure substances. (DOK 1) 2g. Develop a three-dimensional model of molecular structure. (DOK 2) Lewis dot s ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... 2a. Describe and classify matter based on physical and chemical properties and interactions between molecules or atoms. (DOK 1) Physical properties (e.g., melting points, densities, boiling points) of a variety of substances Substances and mixtures Three states of matter in terms of internal e ...
... 2a. Describe and classify matter based on physical and chemical properties and interactions between molecules or atoms. (DOK 1) Physical properties (e.g., melting points, densities, boiling points) of a variety of substances Substances and mixtures Three states of matter in terms of internal e ...
chemical equation - HCC Learning Web
... • Writing chemical equations The law of conservation of mass dictates that the total number of atoms of each element on both sides of a chemical equation must match. The equation is then said to be balanced. ...
... • Writing chemical equations The law of conservation of mass dictates that the total number of atoms of each element on both sides of a chemical equation must match. The equation is then said to be balanced. ...
Student Review packet
... NH4Cl(s) NH3(g) + HCl(g) for this reaction, ΔH = +42.1 kilocalories Suppose the substances in the reaction above are at equilibrium at 600 K in volume V and at pressure P. State whether the partial pressure of NH3(g) will have increased, decreased, or remained the same when equilibrium is reestabl ...
... NH4Cl(s) NH3(g) + HCl(g) for this reaction, ΔH = +42.1 kilocalories Suppose the substances in the reaction above are at equilibrium at 600 K in volume V and at pressure P. State whether the partial pressure of NH3(g) will have increased, decreased, or remained the same when equilibrium is reestabl ...
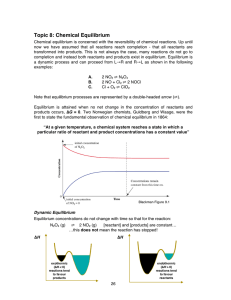
Topic 8: Chemical Equilibrium
... For the above systems which compounds are favoured at equilibrium? Hint: remember that K = P[prod.] / P[react.] Small Keq: Equilibrium favours ________________ Large Keq: Equilibrium favours ________________ Medium Keq; ________________________________are present at equilibrium The Reaction Quotient ...
... For the above systems which compounds are favoured at equilibrium? Hint: remember that K = P[prod.] / P[react.] Small Keq: Equilibrium favours ________________ Large Keq: Equilibrium favours ________________ Medium Keq; ________________________________are present at equilibrium The Reaction Quotient ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment 2016
... Predict whether the following combinations will result in a reaction. Write a balanced reaction for those reactions. Indicate you understand the specific reactions by writing the net ionic equation for the reaction. Hopefully you would have memorized the solubility rules before attempting to answer ...
... Predict whether the following combinations will result in a reaction. Write a balanced reaction for those reactions. Indicate you understand the specific reactions by writing the net ionic equation for the reaction. Hopefully you would have memorized the solubility rules before attempting to answer ...
The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry Part I – Multiple
... 20. What mass of Au is produced when 0.0500 mol of Au2S3 is reduced completely with excess H2 ? (A) 9.85 g (B) 19.7 g (C) 24.5 g (D) 39.4 g (E) 48.9 g ... C10H12O4S(s ) + ... O2(g) ... CO2(g) + ... SO2(g) + ... H2O(g) 26. When the equation above is balanced and all coefficients are reduced to thei ...
... 20. What mass of Au is produced when 0.0500 mol of Au2S3 is reduced completely with excess H2 ? (A) 9.85 g (B) 19.7 g (C) 24.5 g (D) 39.4 g (E) 48.9 g ... C10H12O4S(s ) + ... O2(g) ... CO2(g) + ... SO2(g) + ... H2O(g) 26. When the equation above is balanced and all coefficients are reduced to thei ...
H3AsO4 + 3 I- + 2 H3O+ H3AsO3 + I3- + H2O
... the orientation of the electron's magnetic field and has two possible values +½ and –½. The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same spin in the same orbital. This principle limits the number of electrons that occupy any one atomic orbital to two. Electron ...
... the orientation of the electron's magnetic field and has two possible values +½ and –½. The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same spin in the same orbital. This principle limits the number of electrons that occupy any one atomic orbital to two. Electron ...
AP Chemistry: Chapter 13 Gaseous Equilibrium Section 1: Multiple
... A rigid container holds a mixture of graphite pellets (C(s)), H2O(g), CO(g), and H2(g) at equilibrium. State whether the number of moles of CO(g) in the container will increase, decrease, or remain the same after each of the following disturbances is applied to the original mixture. For each case, a ...
... A rigid container holds a mixture of graphite pellets (C(s)), H2O(g), CO(g), and H2(g) at equilibrium. State whether the number of moles of CO(g) in the container will increase, decrease, or remain the same after each of the following disturbances is applied to the original mixture. For each case, a ...
reaction rate - davis.k12.ut.us
... • Key factors that influence the rate of chemical reactions include reactivity, concentration, surface area, temperature, and catalysts. • Raising the temperature of a reaction generally increases the rate of the reaction by increasing the collision frequency and the number of collisions that ...
... • Key factors that influence the rate of chemical reactions include reactivity, concentration, surface area, temperature, and catalysts. • Raising the temperature of a reaction generally increases the rate of the reaction by increasing the collision frequency and the number of collisions that ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... oxidation number of +3. (Cu does not have oxidation numbers greater than +3.) Give only integer oxidation numbers. Answer: The oxidation numbers for Y, Ba, and O are +3, +2, and −2, respectively. Therefore, the sum of the oxidation numbers for the three Cu atoms must be +7. Two Cu atoms must have +2 ...
... oxidation number of +3. (Cu does not have oxidation numbers greater than +3.) Give only integer oxidation numbers. Answer: The oxidation numbers for Y, Ba, and O are +3, +2, and −2, respectively. Therefore, the sum of the oxidation numbers for the three Cu atoms must be +7. Two Cu atoms must have +2 ...
Higher Chemistry Learning Outcomes
... The modern Periodic Table is based on the work of Mendeleev who arranged the known elements in order of increasing atomic masses in conjunction with similar chemical properties, leaving gaps for undiscovered elements. There are variations in the densities, melting points and boiling points of th ...
... The modern Periodic Table is based on the work of Mendeleev who arranged the known elements in order of increasing atomic masses in conjunction with similar chemical properties, leaving gaps for undiscovered elements. There are variations in the densities, melting points and boiling points of th ...
Stoichiometry
... smallest number that you can multiply by all the mol amounts you have just calculated to get them to be all whole numbers or within .1 of a whole number. ...
... smallest number that you can multiply by all the mol amounts you have just calculated to get them to be all whole numbers or within .1 of a whole number. ...
Review
... Use of the definition of the Chemical Potentials, at equil the chemical potentials of a species in all phases must be equal to each other Processes move from a higher chemical potential to a lower one. Expression for the molar Gibbs free energy, the chemical potential, of a gas Calculation of the E ...
... Use of the definition of the Chemical Potentials, at equil the chemical potentials of a species in all phases must be equal to each other Processes move from a higher chemical potential to a lower one. Expression for the molar Gibbs free energy, the chemical potential, of a gas Calculation of the E ...