Reactions Balancing Chemical Equations uses Law of conservation
... Net Ionic Equation H+(aq) + HCO3"(aq) ! CO2(g)+ H2O(l) ...
... Net Ionic Equation H+(aq) + HCO3"(aq) ! CO2(g)+ H2O(l) ...
Electrochemistry
... Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers (In order of priority): 1. The oxidation number of any pure element is _________. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is __________ to its charge. 3. The ______ of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if ____________, or equal to the ___________ if ...
... Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers (In order of priority): 1. The oxidation number of any pure element is _________. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is __________ to its charge. 3. The ______ of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if ____________, or equal to the ___________ if ...
CHE 106 Chapter 5
... Things to remember: DH is as state function, so we are allowed to apply Hess’s Law and add together appropriate reactions to calculate the DHof ...
... Things to remember: DH is as state function, so we are allowed to apply Hess’s Law and add together appropriate reactions to calculate the DHof ...
Lecture Notes in Physical Chemistry Semester 2: Kinetics and
... satisfies this requirement, that a product of functions of different arguments is equal to a single function involving a sum of functions of the arguments? There’s only one function that does that: the exponential, because e a e b e c = e a+b+c . In this case a must be v x2 and so on, so the candida ...
... satisfies this requirement, that a product of functions of different arguments is equal to a single function involving a sum of functions of the arguments? There’s only one function that does that: the exponential, because e a e b e c = e a+b+c . In this case a must be v x2 and so on, so the candida ...
15equil1pp
... “If the concentrations of all the substances present at equilibrium are raised to the power of the number of moles they appear in the equation, the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants is a constant, provided the temperature rema ...
... “If the concentrations of all the substances present at equilibrium are raised to the power of the number of moles they appear in the equation, the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants is a constant, provided the temperature rema ...
LECTURE_Solutions2013(1)
... • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
... • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
AP Chemistry: Total Notes Review
... o Elements in the same group on the Periodic Table have the same type of electron arrangement in their outermost shells ex) F, [He]2s22p5; and Cl[Ne]3s23p5 ~ Outer-shell electrons: those that lie outside the orbitals occupied in the nextlowest noble gas element ex)[He]2s22p5 ~ Valence electrons: out ...
... o Elements in the same group on the Periodic Table have the same type of electron arrangement in their outermost shells ex) F, [He]2s22p5; and Cl[Ne]3s23p5 ~ Outer-shell electrons: those that lie outside the orbitals occupied in the nextlowest noble gas element ex)[He]2s22p5 ~ Valence electrons: out ...
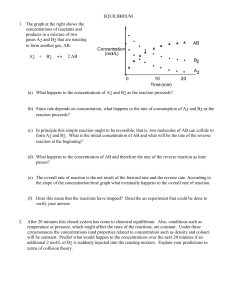
EQUILIBRIUM - SCH4U1-CCVI
... 1. Once a system has reached equilibrium, are the following true or false? a. The reaction is finished, no more products are forming. __________ b. The concentrations of the reactants and the products are equal. ______________ c. The concentrations are no longer changing. ___________ d. The reaction ...
... 1. Once a system has reached equilibrium, are the following true or false? a. The reaction is finished, no more products are forming. __________ b. The concentrations of the reactants and the products are equal. ______________ c. The concentrations are no longer changing. ___________ d. The reaction ...
PPT
... “Flash Photolysis” – e.g., Bryukov et al., J. Phys. Chem. A., 2004, v. 108, 10464-10472. OH + CH4 H2O + CH3 Basic requirements: A fast (ms to ms) method for detecting and quantifying [OH], as it decays via reaction with CH4. Generally, detection is via absorption or fluorescence-based methodologie ...
... “Flash Photolysis” – e.g., Bryukov et al., J. Phys. Chem. A., 2004, v. 108, 10464-10472. OH + CH4 H2O + CH3 Basic requirements: A fast (ms to ms) method for detecting and quantifying [OH], as it decays via reaction with CH4. Generally, detection is via absorption or fluorescence-based methodologie ...
Follow Along Notes - Jackson County School System
... Which of the following statements about the reaction quotient, Q is false? a. The value of Q can be used to predict equilibrium concentrations. b. It has the same expression as Kc. c. Its value is calculated using nonequilibrium concentrations. d. If Q > Kc, the reaction must move to equilibrium by ...
... Which of the following statements about the reaction quotient, Q is false? a. The value of Q can be used to predict equilibrium concentrations. b. It has the same expression as Kc. c. Its value is calculated using nonequilibrium concentrations. d. If Q > Kc, the reaction must move to equilibrium by ...
all practice examples
... A) Show that the reaction is first order by plotting the appropriate graph for first order reactions. B) What is the value of the rate constant, k? C) What is [A] at t = 750 s? ...
... A) Show that the reaction is first order by plotting the appropriate graph for first order reactions. B) What is the value of the rate constant, k? C) What is [A] at t = 750 s? ...
Chemistry 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. A 10.0 g sample of a substance has 34.8 J of energy added to it and its temperature increases by 25.0°C. What is the specific heat capacity of the substance? A. 0.139 J/g°C B. 0.338 J/g°C C. 0.718 J/g°C D. 0.870 J/g°C 3. If the ΔH for a reaction is positive, which of the following statements is t ...
... 2. A 10.0 g sample of a substance has 34.8 J of energy added to it and its temperature increases by 25.0°C. What is the specific heat capacity of the substance? A. 0.139 J/g°C B. 0.338 J/g°C C. 0.718 J/g°C D. 0.870 J/g°C 3. If the ΔH for a reaction is positive, which of the following statements is t ...
Practice problems
... Now we can use the summary in Figure 20.6 to help us describe the voltaic cell. The first half-reaction is the reduction process (electrons shown on the reactant side of the equation), and by definition, this process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation (electrons shown o ...
... Now we can use the summary in Figure 20.6 to help us describe the voltaic cell. The first half-reaction is the reduction process (electrons shown on the reactant side of the equation), and by definition, this process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation (electrons shown o ...
CHEM 30 REDOX
... A redox reaction is a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred. Number of electrons lost by one species equals number of electrons gained by the other species. Reduction is a process in which e- are gained. Oxidation is a process in which e- are lost A reducing agent donates e- and is ox ...
... A redox reaction is a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred. Number of electrons lost by one species equals number of electrons gained by the other species. Reduction is a process in which e- are gained. Oxidation is a process in which e- are lost A reducing agent donates e- and is ox ...