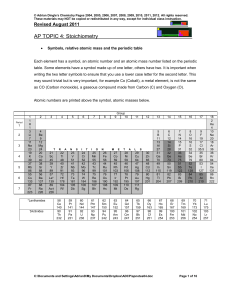
RES8_chemcontentchecklist
... State the formulae of the common acids: hydrochloric, sulfuric and nitric acids. State that common bases are metal oxides, metal hydroxides and ammonia. State that an alkali is a soluble base that releases OH– ions in aqueous solution. State the formulae of the common alkalis: sodium hydroxide, pota ...
... State the formulae of the common acids: hydrochloric, sulfuric and nitric acids. State that common bases are metal oxides, metal hydroxides and ammonia. State that an alkali is a soluble base that releases OH– ions in aqueous solution. State the formulae of the common alkalis: sodium hydroxide, pota ...
Analyzing ITC Data for the Enthalpy of Binding Metal Ions to Ligands
... The enthalpy, ΔHITC, reported from the fit of titration curve represents the overall heat in the reaction cell. In order to account for all of the processes during a reaction it is recommended to analyze the data and account for each separate chemical event. Analysis may seem overwhelming at first, ...
... The enthalpy, ΔHITC, reported from the fit of titration curve represents the overall heat in the reaction cell. In order to account for all of the processes during a reaction it is recommended to analyze the data and account for each separate chemical event. Analysis may seem overwhelming at first, ...
PREPARATORY PROBLEMS (Theoretical)
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, DG. This is the universal principle. If DG < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, DG. This is the universal principle. If DG < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
Chapter 4: Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
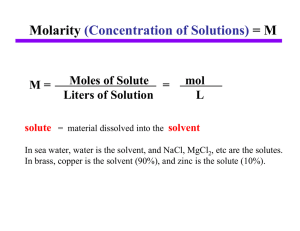
... weighs out a known mass (and, therefore, number of moles) of the solute. The solute is added to a volumetric flask, and solvent is added to the line on the neck of the flask. ...
... weighs out a known mass (and, therefore, number of moles) of the solute. The solute is added to a volumetric flask, and solvent is added to the line on the neck of the flask. ...
What is equilibrium?
... BaSO4 is an insoluble salt that has medical applications. Doctors use it as an X-ray contrast medium (Ba absorbs more radiation than most atoms). Ba ions are poisonous and in order to make sure they are not digested, a soluble salt like Na2SO4 is given with the Ba. As SO4 ions increase the Ba ion ...
... BaSO4 is an insoluble salt that has medical applications. Doctors use it as an X-ray contrast medium (Ba absorbs more radiation than most atoms). Ba ions are poisonous and in order to make sure they are not digested, a soluble salt like Na2SO4 is given with the Ba. As SO4 ions increase the Ba ion ...
Chemical equilibrium and the kinetic theory of gases
... The partial pressures (in bar) of H2O, CO and CO2 in an equilibrium reached in a reaction vessel at 700 K were: H2O: 0.72; CO: 1.21; CO2: 2.10. Calculate the partial pressure of H2. 2 Esters, used in the food industry as flavourings, are manufactured by reacting carboxylic acids and alcohols. The e ...
... The partial pressures (in bar) of H2O, CO and CO2 in an equilibrium reached in a reaction vessel at 700 K were: H2O: 0.72; CO: 1.21; CO2: 2.10. Calculate the partial pressure of H2. 2 Esters, used in the food industry as flavourings, are manufactured by reacting carboxylic acids and alcohols. The e ...
chm 434f/1206f solid state materials chemistry
... • Reactivity of solids • Fundamental aspect of solid state chemistry • Chemical reactivity of solid state materials depends on form and physical dimensions as well as structure and imperfections of reactants and products • Factors governing solid state reactivity underpin concepts and methods for th ...
... • Reactivity of solids • Fundamental aspect of solid state chemistry • Chemical reactivity of solid state materials depends on form and physical dimensions as well as structure and imperfections of reactants and products • Factors governing solid state reactivity underpin concepts and methods for th ...
1 - Berkeley City College
... (d) HNO3: H3O+ (or simply H+) and NO3–; strong electrolyte (b) C2H5OH (ethanol): C2H3OH; nonelectrolyte (c) C6H12O6(glucose): C6H12O6; nonelectrolyte (f) HC2H3O2: HC2H3O2 (mostly), H3O+, and C2H3O2–; Peak electrolyte (e) NaOH: Na+ & OH–; strong electrolyte ...
... (d) HNO3: H3O+ (or simply H+) and NO3–; strong electrolyte (b) C2H5OH (ethanol): C2H3OH; nonelectrolyte (c) C6H12O6(glucose): C6H12O6; nonelectrolyte (f) HC2H3O2: HC2H3O2 (mostly), H3O+, and C2H3O2–; Peak electrolyte (e) NaOH: Na+ & OH–; strong electrolyte ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... ___________________________________________ which says that there is a ________________________________ between the concentrations of the products and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium ...
... ___________________________________________ which says that there is a ________________________________ between the concentrations of the products and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium ...
Chapter 8 and 9 – Energy Balances
... where Vˆ i is the specific volume of pure species i. Enthalpies of mixing are often expressed in terms of heat of solution ∆ Hˆ s (T , r ) . ∆ Hˆ s (T , r ) is the change in enthalpy that results from dissolving one mole of solute in r moles of liquid solvent at constant T. In the limit when 1 mole ...
... where Vˆ i is the specific volume of pure species i. Enthalpies of mixing are often expressed in terms of heat of solution ∆ Hˆ s (T , r ) . ∆ Hˆ s (T , r ) is the change in enthalpy that results from dissolving one mole of solute in r moles of liquid solvent at constant T. In the limit when 1 mole ...
XIX. Chemistry, High School
... • Show all your work (diagrams, tables, or computations) in your Student Answer Booklet. • If you do the work in your head, explain in writing how you did the work. Write your answer to question 11 in the space provided in your Student Answer Booklet. ID:273070 273070_notebookpage.eps Common EQ ...
... • Show all your work (diagrams, tables, or computations) in your Student Answer Booklet. • If you do the work in your head, explain in writing how you did the work. Write your answer to question 11 in the space provided in your Student Answer Booklet. ID:273070 273070_notebookpage.eps Common EQ ...
Table of contents
... which family in the periodic table does the unknown element likely belong. Explain your reasoning please. I1 = 896 kj/mol I2 = 1752 kj/mol I3 = 14807 kj/mol I4 = 17948 kj/mol” ▪ To solve this, look for the spike in ionization energies. Notice the jump from I2 to I3 is massive compared to the rest (I ...
... which family in the periodic table does the unknown element likely belong. Explain your reasoning please. I1 = 896 kj/mol I2 = 1752 kj/mol I3 = 14807 kj/mol I4 = 17948 kj/mol” ▪ To solve this, look for the spike in ionization energies. Notice the jump from I2 to I3 is massive compared to the rest (I ...
Equilibrium and Pressure
... decreased slightly as the reaction proceeded. This is an example of Le Châtelier’s principle, which is the tendency of a system in equilibrium to shift in response to a change. ...
... decreased slightly as the reaction proceeded. This is an example of Le Châtelier’s principle, which is the tendency of a system in equilibrium to shift in response to a change. ...