KHARKOV STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
... The first triad is known as ferrous metals. Iron and cobalt exhibit oxidation states of +3 and +2 in their compounds while nickel compounds are generally in the +2 oxidation state. The elements of second and third triads - are collectively called platinum metals. Ions of iron, cobalt, nickel, and pl ...
... The first triad is known as ferrous metals. Iron and cobalt exhibit oxidation states of +3 and +2 in their compounds while nickel compounds are generally in the +2 oxidation state. The elements of second and third triads - are collectively called platinum metals. Ions of iron, cobalt, nickel, and pl ...
Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry
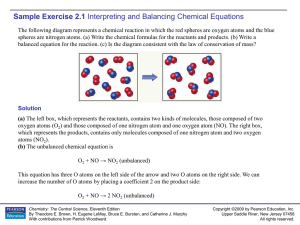
... HE AMOUNT OF PRODUCT FORMED IN A CHEMICAL REACTION is related to the amount of reactant that is consumed. This concept makes sense intuitively, but how do we describe and understand this relationship more ...
... HE AMOUNT OF PRODUCT FORMED IN A CHEMICAL REACTION is related to the amount of reactant that is consumed. This concept makes sense intuitively, but how do we describe and understand this relationship more ...
tro2_ppt_lecture_04 - Louisiana Tech University
... The concentration [M] for the diluted solution is 0.50 M, which contains 0.15 moles of NaOH in 0.30 liters. (0.50 mol/L)(0.300 L) = 0.15 moles NaOH The original solution concentration was 3.0 M, which contains 0.15 moles of NaOH in 0.050 L, and the dilute solution also contains 0.15 moles of NaOH, b ...
... The concentration [M] for the diluted solution is 0.50 M, which contains 0.15 moles of NaOH in 0.30 liters. (0.50 mol/L)(0.300 L) = 0.15 moles NaOH The original solution concentration was 3.0 M, which contains 0.15 moles of NaOH in 0.050 L, and the dilute solution also contains 0.15 moles of NaOH, b ...
doc - Dartmouth College
... from part (a). You will also need to know that aspirin's Ka = 2.75 10–5. Question 2 Methanol (CH3OH) can be made by passing CO and H2 at high temperature over a catalyst according to CO(g) + 2 H2(g) CH3OH(g). If 1.00 mol of CO(g) and 2.00 mol of H2(g) are introduced over the catalyst at 500 K and ...
... from part (a). You will also need to know that aspirin's Ka = 2.75 10–5. Question 2 Methanol (CH3OH) can be made by passing CO and H2 at high temperature over a catalyst according to CO(g) + 2 H2(g) CH3OH(g). If 1.00 mol of CO(g) and 2.00 mol of H2(g) are introduced over the catalyst at 500 K and ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... • Aqueous reactions cannot take place without water. What do you already know about water that will help us understand aqueous reactions? Aqueous Reactions ...
... • Aqueous reactions cannot take place without water. What do you already know about water that will help us understand aqueous reactions? Aqueous Reactions ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... How many moles of the excess reactant remain after the completion of the reaction? 1) use L.R. to determine quantity of excess reactant used. 2)subtract to find quantity that remains. ...
... How many moles of the excess reactant remain after the completion of the reaction? 1) use L.R. to determine quantity of excess reactant used. 2)subtract to find quantity that remains. ...
Ch 10 Practice Problems 1. Consider the process A(l) A(s). Which
... C) A reaction that exhibits a negative value of S cannot be spontaneous. D) At constant pressure and temperature, a decrease in free energy ensures an increase in the entropy of the system. E) none of these ...
... C) A reaction that exhibits a negative value of S cannot be spontaneous. D) At constant pressure and temperature, a decrease in free energy ensures an increase in the entropy of the system. E) none of these ...
1 - KFUPM Faculty List
... 15. Which of the following is a strong electrolyte solution? A) KMnO4(aq) KMnO4 is a normal salt, and thus this is a strong electrolyte solution B) C2H5OH(aq) This is a dissolved polar molecule (an alcohol) and thus it is a non-electrolyte solution C) NH3(aq) This is a weak base solution and thus a ...
... 15. Which of the following is a strong electrolyte solution? A) KMnO4(aq) KMnO4 is a normal salt, and thus this is a strong electrolyte solution B) C2H5OH(aq) This is a dissolved polar molecule (an alcohol) and thus it is a non-electrolyte solution C) NH3(aq) This is a weak base solution and thus a ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • In this type of reaction two or more substances react to form one product. • Examples: – 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) – N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) – C3H6 (g) + Br2 (l) C3H6Br2 (l) ...
... • In this type of reaction two or more substances react to form one product. • Examples: – 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) – N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) – C3H6 (g) + Br2 (l) C3H6Br2 (l) ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • In this type of reaction two or more substances react to form one product. • Examples: – 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) – N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) – C3H6 (g) + Br2 (l) C3H6Br2 (l) ...
... • In this type of reaction two or more substances react to form one product. • Examples: – 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) – N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) – C3H6 (g) + Br2 (l) C3H6Br2 (l) ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and
... • In this type of reaction two or more substances react to form one product. • Examples: – 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) – N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) – C3H6 (g) + Br2 (l) C3H6Br2 (l) ...
... • In this type of reaction two or more substances react to form one product. • Examples: – 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) – N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) – C3H6 (g) + Br2 (l) C3H6Br2 (l) ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • In this type of reaction two or more substances react to form one product. • Examples: – 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) – N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) – C3H6 (g) + Br2 (l) C3H6Br2 (l) ...
... • In this type of reaction two or more substances react to form one product. • Examples: – 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) – N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) – C3H6 (g) + Br2 (l) C3H6Br2 (l) ...
chemistry - Ethiopian Ministry of Education
... dissociation of atoms. We can describe the transformation both qualitatively and quantitatively with the help of chemical equations for the reaction. Some of the examples of chemical change include oxidation of matter (rusting, burning), fermentation, changing milk in to yogurt, and addition of wate ...
... dissociation of atoms. We can describe the transformation both qualitatively and quantitatively with the help of chemical equations for the reaction. Some of the examples of chemical change include oxidation of matter (rusting, burning), fermentation, changing milk in to yogurt, and addition of wate ...
Answers - University of Waterloo
... 5. Carefully detach the last page. It is the datasheet. 6. Now answer the exam questions. Questions are not in order of difficulty. Indicate your choice on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet by marking one letter beside the question number. • Mark only one answer for each question. • Questions are all of th ...
... 5. Carefully detach the last page. It is the datasheet. 6. Now answer the exam questions. Questions are not in order of difficulty. Indicate your choice on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet by marking one letter beside the question number. • Mark only one answer for each question. • Questions are all of th ...
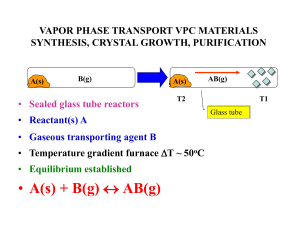
vapor phase transport vpc materials synthesis, crystal growth
... The reactor consists of three inner quartz tubes, which supply the reactive gases, InCl3, GaCl3 (N2 carrier) and NH3, and an outer quartz tube, which supplies inert gas (N2) and houses the reaction in a horizontal tube furnace. Two independently controlled heating tapes were used to tune the vapour ...
... The reactor consists of three inner quartz tubes, which supply the reactive gases, InCl3, GaCl3 (N2 carrier) and NH3, and an outer quartz tube, which supplies inert gas (N2) and houses the reaction in a horizontal tube furnace. Two independently controlled heating tapes were used to tune the vapour ...
Carefully detach the last page. It is the Data Sheet.
... 40 Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, is a weak acid in water. What happens when 0.01 moles of HCl are added to a 0.1 mol L−1 solution of ethanoic acid? ...
... 40 Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, is a weak acid in water. What happens when 0.01 moles of HCl are added to a 0.1 mol L−1 solution of ethanoic acid? ...