Study Guide for Quiz II
... In general: Be able to identify the type of reaction, predict products, write correct formulas, and balance equations. Know the colors of all the copper containing products. Review the experiment and your results. Make sure you understand each step that you performed. For example, why was reaction 1 ...
... In general: Be able to identify the type of reaction, predict products, write correct formulas, and balance equations. Know the colors of all the copper containing products. Review the experiment and your results. Make sure you understand each step that you performed. For example, why was reaction 1 ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... __ Na2S + __ AgNO3 _ NaNO3 + _ Ag2S ___ Mg + ___ HCl ___ H2 + ___ MgCl2 ...
... __ Na2S + __ AgNO3 _ NaNO3 + _ Ag2S ___ Mg + ___ HCl ___ H2 + ___ MgCl2 ...
Chapter 5 – Chemical Reactions
... reaction will be synthesis. Two metals will not combine chemically Noble gases will not combine Write the symbol for the more positive element first and then use the criss-cross method to determine the formula. ...
... reaction will be synthesis. Two metals will not combine chemically Noble gases will not combine Write the symbol for the more positive element first and then use the criss-cross method to determine the formula. ...
Study Guide
... Calculate average reaction rates and instantaneous reaction rates from graphs. Calculate the rate of reactant consumption and product formation in reactions. Identify postulates of collision theory. Apply collision theory to explain reaction rates and factors affecting reaction rates. Explain how su ...
... Calculate average reaction rates and instantaneous reaction rates from graphs. Calculate the rate of reactant consumption and product formation in reactions. Identify postulates of collision theory. Apply collision theory to explain reaction rates and factors affecting reaction rates. Explain how su ...
General Equilibrium
... where K is the equilibrium constant, and aX is the activity of X and described by the activity coefficient X and [X]: aX = X[X] In dilute solutions, the activity coefficient approaches unity. Often, experimental conditions allow us to assume activity coefficients of one so that concentrations can ...
... where K is the equilibrium constant, and aX is the activity of X and described by the activity coefficient X and [X]: aX = X[X] In dilute solutions, the activity coefficient approaches unity. Often, experimental conditions allow us to assume activity coefficients of one so that concentrations can ...
I PUC Chemistry Mock Paper
... 11. How many atoms of gold are present in 49.25g of gold ( Atomic mass of gold = 197). 12. Define a) surface tension b) Boyle temperature. 13. What is Hydrogen bonding? Illustrate with an example. 14. How is plaster of paris prepared from gypsum? Give equation 15. Write any two differences between d ...
... 11. How many atoms of gold are present in 49.25g of gold ( Atomic mass of gold = 197). 12. Define a) surface tension b) Boyle temperature. 13. What is Hydrogen bonding? Illustrate with an example. 14. How is plaster of paris prepared from gypsum? Give equation 15. Write any two differences between d ...
2. Covalent network
... 1. When the rate of the forward reaction is equivalent to the rate of the reverse reaction the system is at equilibrium. 2. jA+kB<-->lC+mD a. j, j, l, and m are coefficient. b.A and B are the concentrations of the reactants c. C and D are the concentrations of the products k= [C]^l x [D]^m [A]^j x [ ...
... 1. When the rate of the forward reaction is equivalent to the rate of the reverse reaction the system is at equilibrium. 2. jA+kB<-->lC+mD a. j, j, l, and m are coefficient. b.A and B are the concentrations of the reactants c. C and D are the concentrations of the products k= [C]^l x [D]^m [A]^j x [ ...
Honors Chemistry
... 2. In single and double replacement reactions, reactants that are compounds are always aqueous. 3. In single and double replacement reactions, products that are compounds should have their phases identified using a solubility chart (aqueous vs. precipitate) 4. In synthesis and decomposition reaction ...
... 2. In single and double replacement reactions, reactants that are compounds are always aqueous. 3. In single and double replacement reactions, products that are compounds should have their phases identified using a solubility chart (aqueous vs. precipitate) 4. In synthesis and decomposition reaction ...
Making Connections - SCH4U1-CCVI
... eg. Calculate the enthalpy change for a combustion reaction which results in the temperature of 500. mL of water in a 0.250 kg Al (cAl = 0.900 J/g•°C) tea kettle rising from 20.0 °C to 95.0 °C. ∆H = - (mc∆TH2O + mc∆TAl) ; = - (mcH2O + mcAl) ∆T ...
... eg. Calculate the enthalpy change for a combustion reaction which results in the temperature of 500. mL of water in a 0.250 kg Al (cAl = 0.900 J/g•°C) tea kettle rising from 20.0 °C to 95.0 °C. ∆H = - (mc∆TH2O + mc∆TAl) ; = - (mcH2O + mcAl) ∆T ...
IB Chemistry Brakke ECA - Topic 15 T15D12
... The absolute entropy values, S, at 238 K for N2(g), H2(g) and NH3(g) are 192, 131 and 193 J K ο ο respectively. Calculate ∆S for the reaction and explain the sign of ∆S . ...
... The absolute entropy values, S, at 238 K for N2(g), H2(g) and NH3(g) are 192, 131 and 193 J K ο ο respectively. Calculate ∆S for the reaction and explain the sign of ∆S . ...
Order and Half-life Equations
... The order (and thus the rate law) is determined by linear regression analysis of three graphs. The graph with the best straight line (r2 closest to 1) determines the order. Note that the absolute value of the slope is the value of the rate constant. The graphs (y vs x): - Zeroeth Order: [A] vs. t ha ...
... The order (and thus the rate law) is determined by linear regression analysis of three graphs. The graph with the best straight line (r2 closest to 1) determines the order. Note that the absolute value of the slope is the value of the rate constant. The graphs (y vs x): - Zeroeth Order: [A] vs. t ha ...
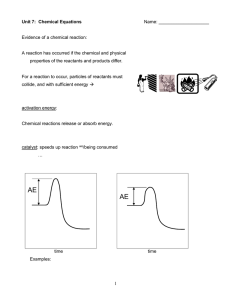
equilibrium and activation energy
... product or a reactant. Energy is a product in exothermic reaction (– H) Energy is a reactant in endothermic reactions (+ H). Increasing temperature increases the "concentration of energy." ...
... product or a reactant. Energy is a product in exothermic reaction (– H) Energy is a reactant in endothermic reactions (+ H). Increasing temperature increases the "concentration of energy." ...
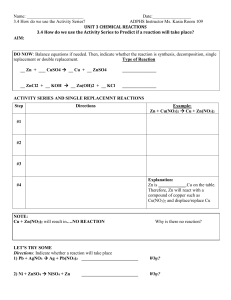
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
Ch. 6: Chemical Reactions Study Guide
... A change of color is a sign that a chemical reaction is taking place. The changes that are visible during a chemical reaction are signs that the atoms in the reactants have been rearranged. A substance is said to be reduced when it gains electrons. A sign that a chemical reaction is taking place is ...
... A change of color is a sign that a chemical reaction is taking place. The changes that are visible during a chemical reaction are signs that the atoms in the reactants have been rearranged. A substance is said to be reduced when it gains electrons. A sign that a chemical reaction is taking place is ...
Kinetics - Chemistry Geek
... The experimental rate law for the reaction between NO2 and CO to produce NO and CO2 is rate = k[NO2]2. The reaction is believed to occur via two steps: ...
... The experimental rate law for the reaction between NO2 and CO to produce NO and CO2 is rate = k[NO2]2. The reaction is believed to occur via two steps: ...
Chemistry 11 - Sardis Secondary
... - identifying limiting and excess reagents in a chemical reaction - calculating the amount of excess reactant - calculating the amount of product formed in a reaction using the limiting reactant C. Percent Yield (text pgs. 365-373) - calculating the efficiency of a chemical reaction from percent yie ...
... - identifying limiting and excess reagents in a chemical reaction - calculating the amount of excess reactant - calculating the amount of product formed in a reaction using the limiting reactant C. Percent Yield (text pgs. 365-373) - calculating the efficiency of a chemical reaction from percent yie ...
A reaction - 固体表面物理化学国家重点实验室
... The overall order of the reaction is K p i 1 ni k must have the units [concentration]-(p-1)[time]-1 • Elementary reactions may be described by their molecularity, which specifies the number of reactants that are involved in the reaction step. • If a reactant spontaneously decomposes to yield pro ...
... The overall order of the reaction is K p i 1 ni k must have the units [concentration]-(p-1)[time]-1 • Elementary reactions may be described by their molecularity, which specifies the number of reactants that are involved in the reaction step. • If a reactant spontaneously decomposes to yield pro ...
Chemical Reactions
... 1. Determine the correct formulas for all 4. Balance the elements one at a time by the reactants and products. using coefficients. When no coefficient is written, it is assumed to be 1. Begin by 2. Write the skeleton equation by placing the formulas for the reactants on the left balancing elements t ...
... 1. Determine the correct formulas for all 4. Balance the elements one at a time by the reactants and products. using coefficients. When no coefficient is written, it is assumed to be 1. Begin by 2. Write the skeleton equation by placing the formulas for the reactants on the left balancing elements t ...