hc1(8)notes
... • Classify a reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, singledisplacement, double-displacement, or combustion reaction. • Predict the products of simple reactions given the reactants. ...
... • Classify a reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, singledisplacement, double-displacement, or combustion reaction. • Predict the products of simple reactions given the reactants. ...
Chemical Reactions
... Pick up sock and board. Complete the Do Now via QR code or link I will be about 15-30 min late. This should be completed by the time I arrive. http://bit.ly/1LvB4ak ...
... Pick up sock and board. Complete the Do Now via QR code or link I will be about 15-30 min late. This should be completed by the time I arrive. http://bit.ly/1LvB4ak ...
syllabus for screening test (mcq type)
... Concentration dependence of rate of reaction, differential and integral rate equations for zeroth, first, second order reactions, rate equations involving reverse, parallel, consecutive and chain reactions, effect of temperature and pressure on rate constant, collision and transition state theories ...
... Concentration dependence of rate of reaction, differential and integral rate equations for zeroth, first, second order reactions, rate equations involving reverse, parallel, consecutive and chain reactions, effect of temperature and pressure on rate constant, collision and transition state theories ...
Big Idea 6
... – Quadratic equation – 5% rule (used when K is very small-compared to initial concentration) ...
... – Quadratic equation – 5% rule (used when K is very small-compared to initial concentration) ...
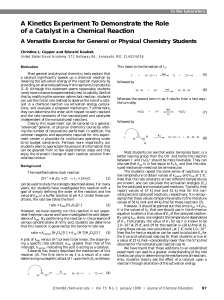
JCE0198 p0087 A Kinetics Experiment To Demonstrate the Role of
... better leaving group than the OH{ and hence the reaction between I{ and H3O 2+ should be more favorable. They can also see that kcat is in fact equal to K1 kH and that the catalyzed mechanism need not be termolecular. The students repeat the same series of reactions at a low temperature to obtain va ...
... better leaving group than the OH{ and hence the reaction between I{ and H3O 2+ should be more favorable. They can also see that kcat is in fact equal to K1 kH and that the catalyzed mechanism need not be termolecular. The students repeat the same series of reactions at a low temperature to obtain va ...
Grade 11 Chemistry Exam Review
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
Chemical Equations PowerPoint
... will require trial and error, the following guidelines may be helpful) a) balance the different types of atoms one at a time b) first, balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation ...
... will require trial and error, the following guidelines may be helpful) a) balance the different types of atoms one at a time b) first, balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation ...
111 Exam I Outline
... Key: You must have a balanced equation!! How many grams of chromic chloride reacts with 6.0 mole Cr? ...
... Key: You must have a balanced equation!! How many grams of chromic chloride reacts with 6.0 mole Cr? ...
Equilibrium
... ● Electronegativity: ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself; increases across a period and decreases down a family ● Ionization Energy: energy required to remove the valence electron from an atom; increases across a period and increases up a family ● Atomic Radius: ra ...
... ● Electronegativity: ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself; increases across a period and decreases down a family ● Ionization Energy: energy required to remove the valence electron from an atom; increases across a period and increases up a family ● Atomic Radius: ra ...
Chemical Equations and Reaction Types Lab
... molecular equations and as ionic equations. We shall only consider molecular equations in this exercise. ...
... molecular equations and as ionic equations. We shall only consider molecular equations in this exercise. ...
review CH5 chem121pikul
... • The reactant with the least number of moles AFTER mole ratio considered is the limiting reactant. • Use limiting reactant # moles to determine moles of products that form ...
... • The reactant with the least number of moles AFTER mole ratio considered is the limiting reactant. • Use limiting reactant # moles to determine moles of products that form ...
Chapter 3: Introduction to chemical formulas and reactivity
... More examples 1. A certain compound is 73.9% Hg and 26.1% Cl by mass. What is the empirical formula? 2. (BLB) A sample of a substance is analyzed and found to contain 5.28 g Sn and 3.37 g F. What is the empirical formula? 3. (BLB) A sample contains 11.66 Fe and 5.01 g oxygen. What is the empirical ...
... More examples 1. A certain compound is 73.9% Hg and 26.1% Cl by mass. What is the empirical formula? 2. (BLB) A sample of a substance is analyzed and found to contain 5.28 g Sn and 3.37 g F. What is the empirical formula? 3. (BLB) A sample contains 11.66 Fe and 5.01 g oxygen. What is the empirical ...
Rate
... Rate Law (Rate Expression)- Shows how the concentration of reactants affect the rate of the reaction. Rate of Reaction = k [Reactant 1]m [Reactant 2]n k = rate constant: the constant of proportionality The value of K changes with changing temperature. Reaction Order – The power to which the concent ...
... Rate Law (Rate Expression)- Shows how the concentration of reactants affect the rate of the reaction. Rate of Reaction = k [Reactant 1]m [Reactant 2]n k = rate constant: the constant of proportionality The value of K changes with changing temperature. Reaction Order – The power to which the concent ...
Chemical Reactions.
... study question 8 Which equation represents a single replacement reaction? • 2NaI(s) + Cl2(g) à 2NaCl(s) + I2(s) • 2NaI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) à 2NaNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) ...
... study question 8 Which equation represents a single replacement reaction? • 2NaI(s) + Cl2(g) à 2NaCl(s) + I2(s) • 2NaI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) à 2NaNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) ...
Chapter 8 Test Review
... 1.Count the valence electrons for all atoms 2.Put the least electronegative atom in the center. Hydrogen is always on outside 3.Assign 2 electrons to each atom 4.Complete octets on outside atoms 5.Put remaining electrons in pairs on central atom 6.If central atom doesn’t have an octet, move electron ...
... 1.Count the valence electrons for all atoms 2.Put the least electronegative atom in the center. Hydrogen is always on outside 3.Assign 2 electrons to each atom 4.Complete octets on outside atoms 5.Put remaining electrons in pairs on central atom 6.If central atom doesn’t have an octet, move electron ...
List Definition Chemistry - A Level / Secondary Chemistry Tuition
... The standard enthalpy change of solution of an ionic compound (Hsoln), is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic compound is dissolved in a large excess of water under standard conditions 25C and 1 atm. Entropy (S) measures the degree of disorder in a system. The entropy of a system increase ...
... The standard enthalpy change of solution of an ionic compound (Hsoln), is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic compound is dissolved in a large excess of water under standard conditions 25C and 1 atm. Entropy (S) measures the degree of disorder in a system. The entropy of a system increase ...
Chapter 6-student notes
... There's a problem with our skeleton equations.... Can you spot it? Example: CH4 + O2 -> CO2 + H2O Problem:______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ...
... There's a problem with our skeleton equations.... Can you spot it? Example: CH4 + O2 -> CO2 + H2O Problem:______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ...