AP CHEMISTRY Chang -Chemistry 9
... Chemical reactivity and products of chemical reactions Relationships in the periodic table: horizontal, vertical, and diagonal with examples from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and the first series of transition elements Introduction to organic chemistry: hydrocarbons and functional ...
... Chemical reactivity and products of chemical reactions Relationships in the periodic table: horizontal, vertical, and diagonal with examples from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and the first series of transition elements Introduction to organic chemistry: hydrocarbons and functional ...
Spectrum05
... Since there are no products there is no reverse reaction. As the forward reaction proceeds the reactants are used up so the forward reaction slows. The products build up, and the reverse reaction speeds up. ...
... Since there are no products there is no reverse reaction. As the forward reaction proceeds the reactants are used up so the forward reaction slows. The products build up, and the reverse reaction speeds up. ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
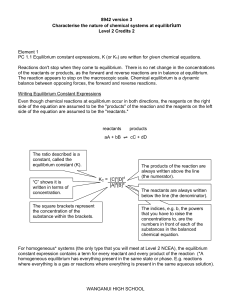
... arrow (→) separates the reactants from the products (arrow points to products) –Read as: “reacts to form” or yields The plus sign = “and” (s) after the formula = solid: Fe(s) (g) after the formula = gas: CO2(g) (l) after the formula = liquid: H2O(l) ...
... arrow (→) separates the reactants from the products (arrow points to products) –Read as: “reacts to form” or yields The plus sign = “and” (s) after the formula = solid: Fe(s) (g) after the formula = gas: CO2(g) (l) after the formula = liquid: H2O(l) ...
CH 11 Chemical Reaction WS #2 (Pre
... 1. What is the Great Barrier Reef and how was it formed? 2. Define chemical reaction3. How is a chemical reaction different from a physical one? Provide examples to support your explanation. 4. Explain how the appearance of the Statue of Liberty is an example of a chemical reaction: 5. What are stal ...
... 1. What is the Great Barrier Reef and how was it formed? 2. Define chemical reaction3. How is a chemical reaction different from a physical one? Provide examples to support your explanation. 4. Explain how the appearance of the Statue of Liberty is an example of a chemical reaction: 5. What are stal ...
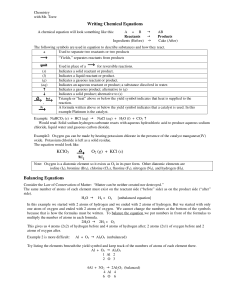
Writing Chemical Equations KClO3 O2 (g) + KCl (s) Balancing
... In this example we started with 2 atoms of hydrogen and we ended with 2 atoms of hydrogen. But we started with only one atom of oxygen and ended with 2 atoms of oxygen. We cannot change the numbers at the bottom of the symbols because that is how the formulas must be written. To balance the equation ...
... In this example we started with 2 atoms of hydrogen and we ended with 2 atoms of hydrogen. But we started with only one atom of oxygen and ended with 2 atoms of oxygen. We cannot change the numbers at the bottom of the symbols because that is how the formulas must be written. To balance the equation ...
2008 local exam - American Chemical Society
... Not valid for use as an ACS Olympiad Local Section Exam after March 29, 2008. STOCK CODE OL08 Distributed by the ACS DivCHED Examinations Institute, University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee, Milwaukee, WI. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. ...
... Not valid for use as an ACS Olympiad Local Section Exam after March 29, 2008. STOCK CODE OL08 Distributed by the ACS DivCHED Examinations Institute, University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee, Milwaukee, WI. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. ...
final exam review chapter 1-4
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
Reactions
... 7. Always consult the Activity Series of metals and non-metals before attempting to write equations for replacement reactions. 8. If a reactant or product is solid, place (s) after the formula 9. If the reactant or product is a liquid, place (l) after the formula 10. If the reactant or product is a ...
... 7. Always consult the Activity Series of metals and non-metals before attempting to write equations for replacement reactions. 8. If a reactant or product is solid, place (s) after the formula 9. If the reactant or product is a liquid, place (l) after the formula 10. If the reactant or product is a ...
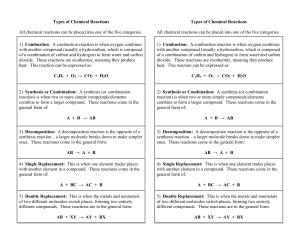
Types of Chemical Reactions
... general form of: A + BC → AC + B 5) Double Replacement: This is when the metals and nonmetals of two different molecules switch places, forming two entirely different compounds. These reactions are in the general form: ...
... general form of: A + BC → AC + B 5) Double Replacement: This is when the metals and nonmetals of two different molecules switch places, forming two entirely different compounds. These reactions are in the general form: ...
chemical reaction?
... • A catalyst is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up or changed very much. • Catalysts usually ____________ reaction rate by bringing together reactants • _____________ are an example of a catalyst found in living things ...
... • A catalyst is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up or changed very much. • Catalysts usually ____________ reaction rate by bringing together reactants • _____________ are an example of a catalyst found in living things ...
Presentation - Chem Rxns - stpats-sch3u-sem1-2013
... Coefficient = a whole number indicating the ratio of molecules of each substance involved in a chemical reaction ...
... Coefficient = a whole number indicating the ratio of molecules of each substance involved in a chemical reaction ...
Slide 1 - MrCard.Org
... given amt. of another material • catalyst – material that increases the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy • enzyme – a biological catalyst • inhibitor – material used to decrease rate of a reaction ...
... given amt. of another material • catalyst – material that increases the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy • enzyme – a biological catalyst • inhibitor – material used to decrease rate of a reaction ...