Chemistry Review 3
... 17. A gas sample is at 25oC and 1.0 atmosphere. Which changes in temperature and pressure will cause this sample to behave more like an ideal gas? 1. decreased temperature and increased pressure 3. increased temperature and increased pressure 2. decreased temperature and decreased pressure 4. increa ...
... 17. A gas sample is at 25oC and 1.0 atmosphere. Which changes in temperature and pressure will cause this sample to behave more like an ideal gas? 1. decreased temperature and increased pressure 3. increased temperature and increased pressure 2. decreased temperature and decreased pressure 4. increa ...
Final exam questions for Chemical Engineer BSc
... solutions. Measurement of conductivity. Molar conductivity and its dependence on concentration: weak and strong electrolytes. The Kohlrausch law of the independent migration of ions. Ionic motion in electric field: mobility and molar conductivity. Electrolysis: definition and measurement of transpor ...
... solutions. Measurement of conductivity. Molar conductivity and its dependence on concentration: weak and strong electrolytes. The Kohlrausch law of the independent migration of ions. Ionic motion in electric field: mobility and molar conductivity. Electrolysis: definition and measurement of transpor ...
Kémiai technológia I
... solutions. Measurement of conductivity. Molar conductivity and its dependence on concentration: weak and strong electrolytes. The Kohlrausch law of the independent migration of ions. Ionic motion in electric field: mobility and molar conductivity. Electrolysis: definition and measurement of transpor ...
... solutions. Measurement of conductivity. Molar conductivity and its dependence on concentration: weak and strong electrolytes. The Kohlrausch law of the independent migration of ions. Ionic motion in electric field: mobility and molar conductivity. Electrolysis: definition and measurement of transpor ...
50 Frequently Forgotten Facts
... 26) Molecular compounds tend to be soft, have low melting points and high vapor pressures. Hydrogen bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular forces (when the H of one polar molecule attracts the N, O or F of another polar molecule), followed by dipole (where the more electronegative end of one ...
... 26) Molecular compounds tend to be soft, have low melting points and high vapor pressures. Hydrogen bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular forces (when the H of one polar molecule attracts the N, O or F of another polar molecule), followed by dipole (where the more electronegative end of one ...
File
... Thus there are two effects of increasing temperature: greater collision intensity and more frequent collisions. Activation Energy -minimum energy needed for a reaction to take place. A higher temp, a greater fraction of the molecules have KE > = the Ea. So this just says to have a reaction you need ...
... Thus there are two effects of increasing temperature: greater collision intensity and more frequent collisions. Activation Energy -minimum energy needed for a reaction to take place. A higher temp, a greater fraction of the molecules have KE > = the Ea. So this just says to have a reaction you need ...
GENERAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
... For example, CsBr is named cesium bromide. Binary Ionic Compounds, where the metal ion has variable oxidation state (Transition elements) 1. the oxidation state on the metal ion is specified by Roman Numeral in brackets 2. monoatomic anions are named as before For example, CuCl and CuCl2 are named a ...
... For example, CsBr is named cesium bromide. Binary Ionic Compounds, where the metal ion has variable oxidation state (Transition elements) 1. the oxidation state on the metal ion is specified by Roman Numeral in brackets 2. monoatomic anions are named as before For example, CuCl and CuCl2 are named a ...
FREQUENTLY FORGOTTEN FACTS
... 26) Molecular compounds tend to be soft, have low melting points and high vapor pressures. Hydrogen bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular forces (when the H of one polar molecule attracts the N, O or F of another polar molecule), followed by dipole (where the more electronegative end of one ...
... 26) Molecular compounds tend to be soft, have low melting points and high vapor pressures. Hydrogen bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular forces (when the H of one polar molecule attracts the N, O or F of another polar molecule), followed by dipole (where the more electronegative end of one ...
Solution
... = -4.75 x 105 J d) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction at 25°C. Are products or reactants favored at equilibrium under standard conditions? Is this consistent with part (c)? Explain your answer. dG = -RT*lnK K = e-dG/RT = e-(-4.75 x 105 J/(8.31J/(K*mol)*298 K) = 1.83 x 1083, this is ...
... = -4.75 x 105 J d) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction at 25°C. Are products or reactants favored at equilibrium under standard conditions? Is this consistent with part (c)? Explain your answer. dG = -RT*lnK K = e-dG/RT = e-(-4.75 x 105 J/(8.31J/(K*mol)*298 K) = 1.83 x 1083, this is ...
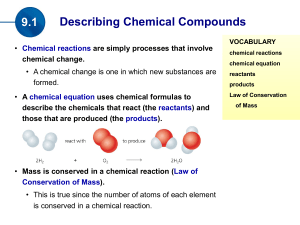
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... coefficients as required throughout the equation so that atoms are conserved. Subscripts are never changed. • For example when the number of atoms of the reactant element(s) are the same as the number of atoms of the product element(s), the equation is balanced. ...
... coefficients as required throughout the equation so that atoms are conserved. Subscripts are never changed. • For example when the number of atoms of the reactant element(s) are the same as the number of atoms of the product element(s), the equation is balanced. ...
CHM1 Exam 16 Name 2222222222222222222222222222 Multiple
... (1) the Pb (s) to the Cu (s) (2) the Cu (s) to the Pb (s) (3) the Pb2+ (aq) to the Pb (s) (4) the Cu2+ (aq) to the Cu (s) 24. Shown below are the reduction potentials for four half-reactions under standard ...
... (1) the Pb (s) to the Cu (s) (2) the Cu (s) to the Pb (s) (3) the Pb2+ (aq) to the Pb (s) (4) the Cu2+ (aq) to the Cu (s) 24. Shown below are the reduction potentials for four half-reactions under standard ...
Midterm 2 from Summer 2012
... A 30.5g sample of an alloy at 93.0oC is placed into 55.0g of Water at 22.0oC in an insulated coffee cup calorimeter. I the final temperature of the system is 31.4oC, what is the Specific Heat of the alloy? Assume the calorimeter absorbs no heat. ...
... A 30.5g sample of an alloy at 93.0oC is placed into 55.0g of Water at 22.0oC in an insulated coffee cup calorimeter. I the final temperature of the system is 31.4oC, what is the Specific Heat of the alloy? Assume the calorimeter absorbs no heat. ...
Free response review
... 2. The molecular formula of an unknown compound is determined by combustion analysis and freezing point depression. A solution containing 0.496 g of benzoic acid, C6H5COOH, and 25.0 g of camphor, C10H16O, freezes at 173.3° C. The freezing point of pure camphor is 179.8° C. An unknown molecular compo ...
... 2. The molecular formula of an unknown compound is determined by combustion analysis and freezing point depression. A solution containing 0.496 g of benzoic acid, C6H5COOH, and 25.0 g of camphor, C10H16O, freezes at 173.3° C. The freezing point of pure camphor is 179.8° C. An unknown molecular compo ...
普通化学 (全英文) 教学大纲
... Be able to write rate laws for Zero-order, and First-order reactions Half-life (t1/2): At t = t1/2, C = 0.5 C0 For the first-order reaction, t1/2 is independent of initial concentration: t1/2 = (ln 2) / k Units of rate constant k for different order of reactions 11.4.Reaction mechanism (a).E ...
... Be able to write rate laws for Zero-order, and First-order reactions Half-life (t1/2): At t = t1/2, C = 0.5 C0 For the first-order reaction, t1/2 is independent of initial concentration: t1/2 = (ln 2) / k Units of rate constant k for different order of reactions 11.4.Reaction mechanism (a).E ...
Michaelis-Menten kinetic theory of enzyme action 1. Effect of
... a. If Km is set equal to [S] and substituted into equation, then v = 1/2Vmax. Therefore, Km is equal to the substrate concentration at which the velocity is half-maximal. b. Km is not a true dissociation constant, but it does provide a measure of the affinity of an enzyme for its substrate. The lowe ...
... a. If Km is set equal to [S] and substituted into equation, then v = 1/2Vmax. Therefore, Km is equal to the substrate concentration at which the velocity is half-maximal. b. Km is not a true dissociation constant, but it does provide a measure of the affinity of an enzyme for its substrate. The lowe ...
Molecular and Empirical Formulas
... Appears after the formula, the compound or molecule is in the SOLID state. ...
... Appears after the formula, the compound or molecule is in the SOLID state. ...
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation Introductory Chemistry Basic
... the relative numbers of molecules of reactants and products. – Can be used to determine mass relationships Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
... the relative numbers of molecules of reactants and products. – Can be used to determine mass relationships Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
NSCC Chem 121 chapter5
... CHEMICAL EQUATIONS • Chemical equations are a convenient way to represent chemical reactions. Chemical equations are written in terms of reactants and products. • A symbol is written in parentheses to the right of each reactant and product to indicate the state or form in which the substance exists ...
... CHEMICAL EQUATIONS • Chemical equations are a convenient way to represent chemical reactions. Chemical equations are written in terms of reactants and products. • A symbol is written in parentheses to the right of each reactant and product to indicate the state or form in which the substance exists ...
Amounts of Reactants and Products
... product that can be formed It is important to figure out which reactant is the limiting one so that you can correctly calculate the products that will be formed. Steps for Solving problems involving Limiting reactants: 1. Write and balance the equation for the reaction. 2. Convert known masses of ...
... product that can be formed It is important to figure out which reactant is the limiting one so that you can correctly calculate the products that will be formed. Steps for Solving problems involving Limiting reactants: 1. Write and balance the equation for the reaction. 2. Convert known masses of ...
Reaction Rate Graphs C12-3
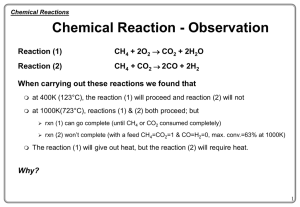
... to form new substances. Not all chemical reactions take place at the same rate. Some reactions are very fast (eg. explosions), while others are very slow (eg. the rusting of iron). The Collision Theory states that: Chemical reactions involve collisions of reactant particles. Not all collisions l ...
... to form new substances. Not all chemical reactions take place at the same rate. Some reactions are very fast (eg. explosions), while others are very slow (eg. the rusting of iron). The Collision Theory states that: Chemical reactions involve collisions of reactant particles. Not all collisions l ...