Immune Memory and Vaccines
... • Two ways to acquire this kind of active immunity* (active because the body actively produces antibodies to trigger a quick secondary response) – Naturally acquired active immunity: example— common cold viruses – “Artificially” acquired active immunity: Vaccines… *Passive immunity: Antibodies come ...
... • Two ways to acquire this kind of active immunity* (active because the body actively produces antibodies to trigger a quick secondary response) – Naturally acquired active immunity: example— common cold viruses – “Artificially” acquired active immunity: Vaccines… *Passive immunity: Antibodies come ...
Basics of Cancer Immunology for StaQsQcians and ComputaQonal
... – CD3+CD8+ is a cytotoxic (killer) T cell – CD19, CD20, CD22 are B cell markers • CD stands for cluster of differen:a:on ...
... – CD3+CD8+ is a cytotoxic (killer) T cell – CD19, CD20, CD22 are B cell markers • CD stands for cluster of differen:a:on ...
Third Semester M.Sc. Degree Examination (CSS)
... Explain the role of MHC proteins in cell mediated lysis. Give an account on the applications of monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reactions. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasitic infections. Discuss the role of secondary lymphoid orga ...
... Explain the role of MHC proteins in cell mediated lysis. Give an account on the applications of monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reactions. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasitic infections. Discuss the role of secondary lymphoid orga ...
Chapter 4.3: Tissues
... Most abundant Produce and maintain connective tissue Macrophages Engulf damaged cells and wastes Adipocytes Fat cells Mast Cells Release chemicals to start immune response ...
... Most abundant Produce and maintain connective tissue Macrophages Engulf damaged cells and wastes Adipocytes Fat cells Mast Cells Release chemicals to start immune response ...
Lymphatic System - Sizemore's Site
... an environmental substance that can produce a hypersensitive reaction in the body but may not be intrinsically harmful. Common allergens include pollen, animal dander, house dust, feathers, and various foods. Studies indicate that one of six Americans is hypersensitive to one or more allergens. ...
... an environmental substance that can produce a hypersensitive reaction in the body but may not be intrinsically harmful. Common allergens include pollen, animal dander, house dust, feathers, and various foods. Studies indicate that one of six Americans is hypersensitive to one or more allergens. ...
Chapter 19a
... • First exposure to antigen called “allergen” sensitized, second - over reaction • Skin testing • Desensitization can help improve reaction in about 70% of individuals. – Produce IgG to antigen (allergen) and hide it from Mast cells and IgE’s ...
... • First exposure to antigen called “allergen” sensitized, second - over reaction • Skin testing • Desensitization can help improve reaction in about 70% of individuals. – Produce IgG to antigen (allergen) and hide it from Mast cells and IgE’s ...
Immune System
... within the body, then your white blood cells (WBCs) begin their attack - WBCs normally circulate throughout the blood, but will enter the body’s ...
... within the body, then your white blood cells (WBCs) begin their attack - WBCs normally circulate throughout the blood, but will enter the body’s ...
Immune System - Mr. Mazza's BioResource
... cell-mediated immunity Cytotoxic T-cells (Tc) kill only cells that are infected with a virus Helper T-cells (Th) release chemicals called cytokines to activate B-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, and macrophages Suppressor T-cells (TS) slow down activity of B and T cells once the antigen has been destroyed ...
... cell-mediated immunity Cytotoxic T-cells (Tc) kill only cells that are infected with a virus Helper T-cells (Th) release chemicals called cytokines to activate B-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, and macrophages Suppressor T-cells (TS) slow down activity of B and T cells once the antigen has been destroyed ...
Immune system II
... ! Lymphocyte stem cells (B cells and others) differentiate to become potential antibody producing cells, each capable of producing one antibody (of random specificity). ! Presence of antigen stimulates cell division of the cell(s) that make antibodies that react with that antigen to produce a clone ...
... ! Lymphocyte stem cells (B cells and others) differentiate to become potential antibody producing cells, each capable of producing one antibody (of random specificity). ! Presence of antigen stimulates cell division of the cell(s) that make antibodies that react with that antigen to produce a clone ...
Humoral Immunity Antibodies.
... • There are 5 major types of C regions which correspond to the 5 different classes of antibodies. • All plasma cells in the body are producing one of these classes of antibodies. • A particular plasma cell may switch the particular class of Antibody that it is producing in order to fight an infectio ...
... • There are 5 major types of C regions which correspond to the 5 different classes of antibodies. • All plasma cells in the body are producing one of these classes of antibodies. • A particular plasma cell may switch the particular class of Antibody that it is producing in order to fight an infectio ...
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM How Do We Keep Our Bodies Healthy?
... Lymphocytes: (1 of 6 Types of White Blood Cells) • B cells: Notice antigens presented on the macrophage and produce ANTIBODIES which inactivate pathogens (that haven’t yet infected a body cell) • Helper T cells • Killer T cells: destroy body cells that are infected with pathogens ...
... Lymphocytes: (1 of 6 Types of White Blood Cells) • B cells: Notice antigens presented on the macrophage and produce ANTIBODIES which inactivate pathogens (that haven’t yet infected a body cell) • Helper T cells • Killer T cells: destroy body cells that are infected with pathogens ...
Evolutionary Genetics
... number of homology units? Which process would establish a new variant of the homology unit as part of the gene family? ...
... number of homology units? Which process would establish a new variant of the homology unit as part of the gene family? ...
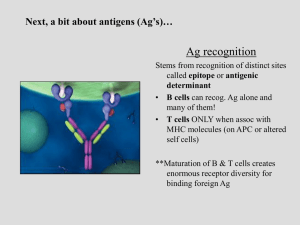
Next, a bit about antigens (Ag`s)…
... MHC molecules bind Antigenic peptides after Ag processing •Relation of Ag with MHC I or II appears to be determined by the route in which Ag enters the cell •Exogenous Ag is found OUTSIDE host cells and enters via phagocytosis in APC’s ONLY! •then APC digests Ag into peptide fragments, combines fra ...
... MHC molecules bind Antigenic peptides after Ag processing •Relation of Ag with MHC I or II appears to be determined by the route in which Ag enters the cell •Exogenous Ag is found OUTSIDE host cells and enters via phagocytosis in APC’s ONLY! •then APC digests Ag into peptide fragments, combines fra ...
Immune System
... • The Immune system must have the ability to distinguish between self and non-self molecules • Self Molecules- components of an organism’s body that can be distinguished from foreign substances by the immune system. Autoimmunity- immune reaction against self molecules • Non-self Molecules- recognize ...
... • The Immune system must have the ability to distinguish between self and non-self molecules • Self Molecules- components of an organism’s body that can be distinguished from foreign substances by the immune system. Autoimmunity- immune reaction against self molecules • Non-self Molecules- recognize ...
Monoclonal Antibody Immunotherapy - Society for Immunotherapy of
... Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) NCRs ...
... Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) NCRs ...
Cancer and the Immune System
... Prevent metastasis after surgical removal or primary melanoma in human patients ...
... Prevent metastasis after surgical removal or primary melanoma in human patients ...
Domain - Eukarya
... • This is because the trypanosome cell contains proteins in its cell membrane which the white blood cells recognise as ‘foreign’ (i.e. not belonging to the host). • These proteins in the trypanosome, that the white blood cells respond to, are called antigens. • The white blood cells make antibodies ...
... • This is because the trypanosome cell contains proteins in its cell membrane which the white blood cells recognise as ‘foreign’ (i.e. not belonging to the host). • These proteins in the trypanosome, that the white blood cells respond to, are called antigens. • The white blood cells make antibodies ...
Matching - use the key below to answer questions 1
... 2. What is the difference between a B & a T cell. B cells mark foreign cells, T cells destroy them. 3. Describe the different types of B and T cells. Memory cells: provides future immunity after first exposure Plasma cells: increases antibodies released into the blood Cytotoxic T cells: kill foreign ...
... 2. What is the difference between a B & a T cell. B cells mark foreign cells, T cells destroy them. 3. Describe the different types of B and T cells. Memory cells: provides future immunity after first exposure Plasma cells: increases antibodies released into the blood Cytotoxic T cells: kill foreign ...
Unit 10 p4
... _________________________________through placenta and/or breast milk (including colostrum) ARTIFICIALLY ACQUIRED PASSIVE IMMUNITY: person receives an injection of antiserum (antibodies) collected from a person who has already developed immunity against a particular disease TRANSPLANTATION and TISS ...
... _________________________________through placenta and/or breast milk (including colostrum) ARTIFICIALLY ACQUIRED PASSIVE IMMUNITY: person receives an injection of antiserum (antibodies) collected from a person who has already developed immunity against a particular disease TRANSPLANTATION and TISS ...
Cancer immunotherapy

Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncology) is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies fall into three main groups: cellular, antibody and cytokine. They exploit the fact that cancer cells often have subtly different molecules on their surface that can be detected by the immune system. These molecules, known as cancer antigens, are most commonly proteins, but also include molecules such as carbohydrates. Immunotherapy is used to provoke the immune system into attacking the tumor cells by using these antigens as targets.Antibody therapies are the most successful immunotherapy, treating a wide range of cancers. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that bind to a target antigen on the cell surface. In normal physiology the immune system uses them to fight pathogens. Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins. Those that bind to cancer antigens are used to treat cancer. Cell surface receptors are common targets for antibody therapies and include the CD20, CD274, and CD279. Once bound to a cancer antigen, antibodies can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, activate the complement system, or prevent a receptor from interacting with its ligand, all of which can lead to cell death. Multiple antibodies are approved to treat cancer, including Alemtuzumab, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, Ofatumumab, and Rituximab.Cellular therapies, also known as cancer vaccines, usually involve the removal of immune cells from the blood or from a tumor. Immune cells specific for the tumor are activated, cultured and returned to the patient where the immune cells attack the cancer. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells. The only cell-based therapy approved in the US is Dendreon's Provenge, for the treatment of prostate cancer.Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are examples of cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behaviour of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.