Innate immunity
... ----- killing effect of NK cell is inhibited Abnormal condition: Non-HLA I molecules recognizing receptors (NCR NKG2D) Activation effect > inhibition effect -----NK cells kill target cells ...
... ----- killing effect of NK cell is inhibited Abnormal condition: Non-HLA I molecules recognizing receptors (NCR NKG2D) Activation effect > inhibition effect -----NK cells kill target cells ...
VL 08lecture2008
... Recognizes antigens (molecular signatures) specific for each pathogen Effective against both intra- and extracellular pathogens Two main components: Humoral immunity - Relies on Antibodies produced by B-lymphocytes - Fights pathogens outside of cells ...
... Recognizes antigens (molecular signatures) specific for each pathogen Effective against both intra- and extracellular pathogens Two main components: Humoral immunity - Relies on Antibodies produced by B-lymphocytes - Fights pathogens outside of cells ...
The Role of Regulatory T cell in HIV
... CD4CD25 T cells might be a key factor for the inefficiency of CD8 responses in viral persistence. The mechanisms of this suppression are not elucidated. Generation of CD8 T cell response following viral infection or vaccination is indispensable for infection control. In HIV infection the initial dec ...
... CD4CD25 T cells might be a key factor for the inefficiency of CD8 responses in viral persistence. The mechanisms of this suppression are not elucidated. Generation of CD8 T cell response following viral infection or vaccination is indispensable for infection control. In HIV infection the initial dec ...
Interferon Type II & III - Bite
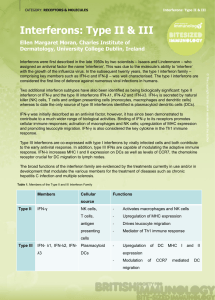
... cellular immune responses; activation of macrophages and NK cells; upregulation of MHC expression and promoting leucocyte migration. IFN-γ is also considered the key cytokine in the Th1 immune response. Type III interferons are co-expressed with type I interferons by virally infected cells and both ...
... cellular immune responses; activation of macrophages and NK cells; upregulation of MHC expression and promoting leucocyte migration. IFN-γ is also considered the key cytokine in the Th1 immune response. Type III interferons are co-expressed with type I interferons by virally infected cells and both ...
Monoclonal Antibodies In Hematology
... necessitating close monitoring and observation. These adverse events have been summarized in Table IV . Though uncommon, severe or life threatening events have also been reported after rituximab administration with 2.9% deaths attributable to rituximab8. Respiratory complications are the commonest c ...
... necessitating close monitoring and observation. These adverse events have been summarized in Table IV . Though uncommon, severe or life threatening events have also been reported after rituximab administration with 2.9% deaths attributable to rituximab8. Respiratory complications are the commonest c ...
... Histamine is secreted by basophils, white blood cells found in connective tissue. Vasodilation(dilation of blood vessels), stimulated by histamine, increases blood supply to the damaged area and allows for easier movement of white blood cells through blood vessel walls. This also causes redness, an ...
IMMUNO-Immunology Instant
... There is probably a genetic link as patients with AD have increased serum levels of IgE and are deficient in a cell-mediated TH1 response. What immunological process is disrupted or altered: Patients have both IgE and Th2 cells specific for the allergen. Allergen at the site of entry causes cytokine ...
... There is probably a genetic link as patients with AD have increased serum levels of IgE and are deficient in a cell-mediated TH1 response. What immunological process is disrupted or altered: Patients have both IgE and Th2 cells specific for the allergen. Allergen at the site of entry causes cytokine ...
Name - Medical Mastermind Community
... A. Differentiation of B cells into plasma cells B. Affinity maturation C. Switching from IgM to IgA1 expression D. Coexpresson of surface 1gM and IgD E. Somatic hypermutation 21. In the process of antigen presentation, CD8+ T cells recognize: A. Exogenous peptides associated with MHC class II molecu ...
... A. Differentiation of B cells into plasma cells B. Affinity maturation C. Switching from IgM to IgA1 expression D. Coexpresson of surface 1gM and IgD E. Somatic hypermutation 21. In the process of antigen presentation, CD8+ T cells recognize: A. Exogenous peptides associated with MHC class II molecu ...
Slide Presentation (Powerpoint)
... •Can block fusion(neutralizing) if antibody (Ab) binds to fusion protein such as gp41 of HIV. •Can effect clearance of virus if it binds the virus and then binds Fc receptors on monocytes and macrophages. •Can also bind complement and kill enveloped viruses. •Most effective if they are present at th ...
... •Can block fusion(neutralizing) if antibody (Ab) binds to fusion protein such as gp41 of HIV. •Can effect clearance of virus if it binds the virus and then binds Fc receptors on monocytes and macrophages. •Can also bind complement and kill enveloped viruses. •Most effective if they are present at th ...
Recurrent miscarriage – if a woman has experienced a sereise of at
... Recurrent miscarriage and stress About 1 in a hundred couples experience recurrent miscarriages (RM). RM is defined as a series of at least three involuntary losses of seemingly normal pregnancies before the 29 th week of pregnancy. . The percentage of RM that may be attributed to known biological c ...
... Recurrent miscarriage and stress About 1 in a hundred couples experience recurrent miscarriages (RM). RM is defined as a series of at least three involuntary losses of seemingly normal pregnancies before the 29 th week of pregnancy. . The percentage of RM that may be attributed to known biological c ...
MEGAMIN ACTIV on Viral Deseases
... diverse response of the immune system. Such unusual antigens are termed superantigens. Superantigens (SAG) are a class of immunostimulatory and disease causing proteins of bacterial or viral origin with the ability to stimulate and activate large fractions (5-20%) of the T cell population. Activatio ...
... diverse response of the immune system. Such unusual antigens are termed superantigens. Superantigens (SAG) are a class of immunostimulatory and disease causing proteins of bacterial or viral origin with the ability to stimulate and activate large fractions (5-20%) of the T cell population. Activatio ...
Dendritic Cell Vaccines Against Non- small Cell Lung Cancer
... DCs pulsed with tumor epitopes derived from newly identified tumor-associated peptides, RNA, apoptotic bodies or genetically modified with cDNAs encoding, for example, immunostimulatory cytokines, such as IL-12 to augment the generation of effective anti-tumor CTL responses, or with full-length cDNA ...
... DCs pulsed with tumor epitopes derived from newly identified tumor-associated peptides, RNA, apoptotic bodies or genetically modified with cDNAs encoding, for example, immunostimulatory cytokines, such as IL-12 to augment the generation of effective anti-tumor CTL responses, or with full-length cDNA ...
PowerPoint to accompany - Current University of Rio Grande
... • resistance to particular pathogens or to their toxins or metabolic by-products • based on the ability to distinguish “self” from “non-self” ...
... • resistance to particular pathogens or to their toxins or metabolic by-products • based on the ability to distinguish “self” from “non-self” ...
Lecture Notes
... with surface constituents of other cells and this interaction triggers the killer activity of the NK cells. However, they also express another set of receptors whose interactions induce inhibitory signals that prevent target cell killing, and these inhibitory signals are normally dominant over the a ...
... with surface constituents of other cells and this interaction triggers the killer activity of the NK cells. However, they also express another set of receptors whose interactions induce inhibitory signals that prevent target cell killing, and these inhibitory signals are normally dominant over the a ...
Pneumonitis
... toxicity by causing apoptosis of epithelial cells and/ or by inhibiting recovery during the organizing phase. ...
... toxicity by causing apoptosis of epithelial cells and/ or by inhibiting recovery during the organizing phase. ...
Directed Reading
... which resist the virus’s initial attempts to bind with healthy cells. Vaccines are used to prevent measles, hepatitis, mumps, polio, and influenza, among other viral diseases. Answers to Student Worksheet 1. The small yellowish ovals surrounding the blue and green circle show the protective shell. 2 ...
... which resist the virus’s initial attempts to bind with healthy cells. Vaccines are used to prevent measles, hepatitis, mumps, polio, and influenza, among other viral diseases. Answers to Student Worksheet 1. The small yellowish ovals surrounding the blue and green circle show the protective shell. 2 ...
1. dia
... Complete absence of T-cell help. No interactions no cytokines. At high concentration B-cell mitogens. Simultaneous activation of BCR and other receptors on B cells (i.e. LPS binding protein /CD14/TLR4) induces the B cells to proliferate and differentiate ...
... Complete absence of T-cell help. No interactions no cytokines. At high concentration B-cell mitogens. Simultaneous activation of BCR and other receptors on B cells (i.e. LPS binding protein /CD14/TLR4) induces the B cells to proliferate and differentiate ...
Immunology 2
... 3. To understand how defects in tolerance lead to autoimmune disease There are over 70 chronic autoimmune diseases affecting 5-8% of the population (80% of which are women). The major ones are: - Rheumatoid Arthritis: 2.1 million cases 30-50,000 children, 2.1 million lost ...
... 3. To understand how defects in tolerance lead to autoimmune disease There are over 70 chronic autoimmune diseases affecting 5-8% of the population (80% of which are women). The major ones are: - Rheumatoid Arthritis: 2.1 million cases 30-50,000 children, 2.1 million lost ...
Two branches of immune system
... dendritic cells • Pathogen destruction by phagocytosis: – Neutrophils, macrophages ...
... dendritic cells • Pathogen destruction by phagocytosis: – Neutrophils, macrophages ...
3. Immunology
... Through its ability to cross the placenta, maternal IgG provides the major line of defense against infection for the first few weeks of a baby's life. ...
... Through its ability to cross the placenta, maternal IgG provides the major line of defense against infection for the first few weeks of a baby's life. ...
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1
... Perforin - A major component of structures called cytolytic granules within T cells and NK cells. One of the main ways in which T cells and NK cells destroy other cells is to transport and secrete these cytolytic granules, which contain cell-killing proteins, onto the membranes of the target cell ...
... Perforin - A major component of structures called cytolytic granules within T cells and NK cells. One of the main ways in which T cells and NK cells destroy other cells is to transport and secrete these cytolytic granules, which contain cell-killing proteins, onto the membranes of the target cell ...
Activity: What is an allergy?
... examiners could test your recall and understanding of (a), (b) and (c). The Eduqas specification does not explicitly include these concepts. 2 The release of antibodies and the formation of an antigen–antibody complex is clearly stated in the A-level specifications of AQA, Edexcel and OCR, so examin ...
... examiners could test your recall and understanding of (a), (b) and (c). The Eduqas specification does not explicitly include these concepts. 2 The release of antibodies and the formation of an antigen–antibody complex is clearly stated in the A-level specifications of AQA, Edexcel and OCR, so examin ...
PHA 321 - Biosciences II
... 6. An immune complex is defined as A) complement combined with LPS. B) antigen combined with antigen. ...
... 6. An immune complex is defined as A) complement combined with LPS. B) antigen combined with antigen. ...
Cancer immunotherapy

Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncology) is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies fall into three main groups: cellular, antibody and cytokine. They exploit the fact that cancer cells often have subtly different molecules on their surface that can be detected by the immune system. These molecules, known as cancer antigens, are most commonly proteins, but also include molecules such as carbohydrates. Immunotherapy is used to provoke the immune system into attacking the tumor cells by using these antigens as targets.Antibody therapies are the most successful immunotherapy, treating a wide range of cancers. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that bind to a target antigen on the cell surface. In normal physiology the immune system uses them to fight pathogens. Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins. Those that bind to cancer antigens are used to treat cancer. Cell surface receptors are common targets for antibody therapies and include the CD20, CD274, and CD279. Once bound to a cancer antigen, antibodies can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, activate the complement system, or prevent a receptor from interacting with its ligand, all of which can lead to cell death. Multiple antibodies are approved to treat cancer, including Alemtuzumab, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, Ofatumumab, and Rituximab.Cellular therapies, also known as cancer vaccines, usually involve the removal of immune cells from the blood or from a tumor. Immune cells specific for the tumor are activated, cultured and returned to the patient where the immune cells attack the cancer. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells. The only cell-based therapy approved in the US is Dendreon's Provenge, for the treatment of prostate cancer.Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are examples of cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behaviour of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.