IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS)
... Cellular immunity (CI) functions to enhance antimicrobial actions of phagocytes to eliminate microbes. Cellular immunity manifests as delayed type cellular immune responses. This T-cell–mediated activation of phagocytes depends on interferon gamma (IFN-γ); a major cytokine produced by type 1 T-helpe ...
... Cellular immunity (CI) functions to enhance antimicrobial actions of phagocytes to eliminate microbes. Cellular immunity manifests as delayed type cellular immune responses. This T-cell–mediated activation of phagocytes depends on interferon gamma (IFN-γ); a major cytokine produced by type 1 T-helpe ...
Therapeutic strategies for targeting cancer stem cells
... It is hypothesized that CSCs are able to evade cancer immunosurveillance due to phenotypic and functional properties that allow them to survive in immunocompetent hosts. Antitumor immune cells are detectable and relevant to disease prognosis. Tumor associated antigens (TAA) are encoded by lineage sp ...
... It is hypothesized that CSCs are able to evade cancer immunosurveillance due to phenotypic and functional properties that allow them to survive in immunocompetent hosts. Antitumor immune cells are detectable and relevant to disease prognosis. Tumor associated antigens (TAA) are encoded by lineage sp ...
Activation by another means: role of immune system in Graves
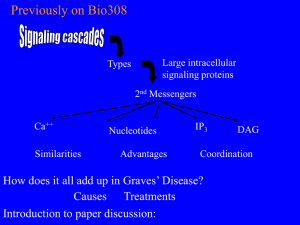
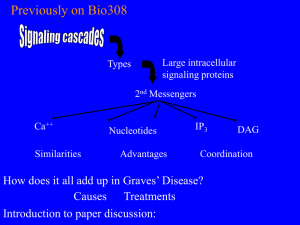
... What do they do? How are antibodies made? Fig 3-21 ...
... What do they do? How are antibodies made? Fig 3-21 ...
cd38 molecule-a multilineage glycoprotein and its unique
... associated marker. Western blot analysis indicated that the 6G5 MAb detected a single band with molecular weight of 41 KDa from cell lysates of two human B-cell lines, DAUDI and NALM6. Comparison of data obtained for 6G5 MAb with those of the MAb known as OKTIO indicated that both MAbs may have reac ...
... associated marker. Western blot analysis indicated that the 6G5 MAb detected a single band with molecular weight of 41 KDa from cell lysates of two human B-cell lines, DAUDI and NALM6. Comparison of data obtained for 6G5 MAb with those of the MAb known as OKTIO indicated that both MAbs may have reac ...
Chapter 3
... from people who have immunity to those that do not. The most common form of passive immunity is the transfer of antibodies from mother to baby across the placenta. Other less common forms of passive immunity include transfer of antibodies through transfusion of blood or blood products including immu ...
... from people who have immunity to those that do not. The most common form of passive immunity is the transfer of antibodies from mother to baby across the placenta. Other less common forms of passive immunity include transfer of antibodies through transfusion of blood or blood products including immu ...
(areolar) connective tissue
... * not attached directly to a core protein * attached to the core proteins via linker proteins B. chondroitin sulfate * attached directly to the core protein C. keratan sulfate * attached directly to the core protein 2. Proteoglycans - composed of a protein core covalently bound to many glycosaminogl ...
... * not attached directly to a core protein * attached to the core proteins via linker proteins B. chondroitin sulfate * attached directly to the core protein C. keratan sulfate * attached directly to the core protein 2. Proteoglycans - composed of a protein core covalently bound to many glycosaminogl ...
B cells - West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District
... It also can undergo latency People with AIDS are highly susceptible to infections and cancers that a healthy immune system would ...
... It also can undergo latency People with AIDS are highly susceptible to infections and cancers that a healthy immune system would ...
Seminar in PDF format
... eye protection, gowns) must be worn when performing procedures that may expose to infectious agents Hands must be washed before and after every patient contact and after glove removal “Touch” and “splash” surfaces must be precleaned and disinfected Critical instruments must be sterilized Inf ...
... eye protection, gowns) must be worn when performing procedures that may expose to infectious agents Hands must be washed before and after every patient contact and after glove removal “Touch” and “splash” surfaces must be precleaned and disinfected Critical instruments must be sterilized Inf ...
The Immune System
... bone marrow and complete their development there or in the spleen. B cells make antibodies. – T cells are cells that are made in the bone marrow but complete their development only after traveling to the thymus. T cells also participate in many immune reactions. ...
... bone marrow and complete their development there or in the spleen. B cells make antibodies. – T cells are cells that are made in the bone marrow but complete their development only after traveling to the thymus. T cells also participate in many immune reactions. ...
Characterization of Signal Transduction Pathways in
... thereby allowing for in vitro studies of cell function that previously were not feasible in these cells.1-3 We have derived such a permanent bone marrow endothelial cell line termed TrHBMEC from an adult female donor’s cells by transfection with the SV40 T antigen under the control of a truncated vi ...
... thereby allowing for in vitro studies of cell function that previously were not feasible in these cells.1-3 We have derived such a permanent bone marrow endothelial cell line termed TrHBMEC from an adult female donor’s cells by transfection with the SV40 T antigen under the control of a truncated vi ...
The role of IL-12/IL-23 in Crohn`s disease
... The immune system’s initial first line response, known as the innate immune system, will be activated; however, these short-term inflammatory processes may not be enough to deal with the invasion and the adaptive immune response will then become activated. This may result in acute intestinal inflamm ...
... The immune system’s initial first line response, known as the innate immune system, will be activated; however, these short-term inflammatory processes may not be enough to deal with the invasion and the adaptive immune response will then become activated. This may result in acute intestinal inflamm ...
CTLA-4
... Stimulates production of IgA antibodies by inducing B-cells to switch to this isotype. (IgA is the major antibody isotype required for mucosal immunity.) Promotes tissue repair after local inflammatory reactions (stimulate collagen synthesis and angiogenesis). Membrane-tethered TGF-β can also ...
... Stimulates production of IgA antibodies by inducing B-cells to switch to this isotype. (IgA is the major antibody isotype required for mucosal immunity.) Promotes tissue repair after local inflammatory reactions (stimulate collagen synthesis and angiogenesis). Membrane-tethered TGF-β can also ...
Sepsis-induced Innate and Adaptive Immune
... are the first cellular responders to invading organisms and are therefore vital to host defense. Cell types including monocytes (and their mature form, tissue macrophages), dendritic cells, and neutrophils recognize pathogens through constitutively expressed receptors including toll-like receptors ( ...
... are the first cellular responders to invading organisms and are therefore vital to host defense. Cell types including monocytes (and their mature form, tissue macrophages), dendritic cells, and neutrophils recognize pathogens through constitutively expressed receptors including toll-like receptors ( ...
Immune Response to Infectious Diseases
... • Recombinant subunit, DNA and vectored vaccines. i • Universal influenza virus vaccines. ...
... • Recombinant subunit, DNA and vectored vaccines. i • Universal influenza virus vaccines. ...
Immune suppression in cancer: Effects on immune cells
... cells that enable them to migrate using exactly the same mechanisms [31]. This phenomenon of “masquerading” provides yet another example of how tumors use the immune cells to their own advantage. At the same time, it is recognized that circulating tumor cells are particularly sensitive to lysis by n ...
... cells that enable them to migrate using exactly the same mechanisms [31]. This phenomenon of “masquerading” provides yet another example of how tumors use the immune cells to their own advantage. At the same time, it is recognized that circulating tumor cells are particularly sensitive to lysis by n ...
Cancer immunotherapy

Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncology) is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies fall into three main groups: cellular, antibody and cytokine. They exploit the fact that cancer cells often have subtly different molecules on their surface that can be detected by the immune system. These molecules, known as cancer antigens, are most commonly proteins, but also include molecules such as carbohydrates. Immunotherapy is used to provoke the immune system into attacking the tumor cells by using these antigens as targets.Antibody therapies are the most successful immunotherapy, treating a wide range of cancers. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that bind to a target antigen on the cell surface. In normal physiology the immune system uses them to fight pathogens. Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins. Those that bind to cancer antigens are used to treat cancer. Cell surface receptors are common targets for antibody therapies and include the CD20, CD274, and CD279. Once bound to a cancer antigen, antibodies can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, activate the complement system, or prevent a receptor from interacting with its ligand, all of which can lead to cell death. Multiple antibodies are approved to treat cancer, including Alemtuzumab, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, Ofatumumab, and Rituximab.Cellular therapies, also known as cancer vaccines, usually involve the removal of immune cells from the blood or from a tumor. Immune cells specific for the tumor are activated, cultured and returned to the patient where the immune cells attack the cancer. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells. The only cell-based therapy approved in the US is Dendreon's Provenge, for the treatment of prostate cancer.Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are examples of cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behaviour of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.