Bitter Taste Bodyguards
... dispersed widely throughout the nasal cavity and making up about only 1 percent of the cells there. The cells have both T2R bitter receptors and T1R sweet receptors. When T2Rs in these cells get stimulated, we have found, the solitary cells release a signal to surrounding cells that prompts them to ...
... dispersed widely throughout the nasal cavity and making up about only 1 percent of the cells there. The cells have both T2R bitter receptors and T1R sweet receptors. When T2Rs in these cells get stimulated, we have found, the solitary cells release a signal to surrounding cells that prompts them to ...
[Science] 22 NOVEMBER 2013 VOL 342, ISSUE 6161, PAGES 901
... demonstration of the profound tolerance-inducing ability of i.v. administered Ag-coupled splenocytes (Ag-SP) in mice, which has been demonstrated to treat T cell–mediated disorders including autoimmunity, allergy, and transplant rejection. Recent studies have defined the intricate interplay between ...
... demonstration of the profound tolerance-inducing ability of i.v. administered Ag-coupled splenocytes (Ag-SP) in mice, which has been demonstrated to treat T cell–mediated disorders including autoimmunity, allergy, and transplant rejection. Recent studies have defined the intricate interplay between ...
Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Mucosal Infection by Highly
... cellular peptides generated by the proteasome from endogenous proteins that are translocated by the transporter associated with Ag processing into the ER for subsequent selection and trimming for MHC class I loading. When released from necrotic cells, gp96 functions as a danger associated molecular ...
... cellular peptides generated by the proteasome from endogenous proteins that are translocated by the transporter associated with Ag processing into the ER for subsequent selection and trimming for MHC class I loading. When released from necrotic cells, gp96 functions as a danger associated molecular ...
CD4+ Vbx T cell
... inflammation of the synovial joints and infiltration by blood-derived cells, chiefly memory T cells, macrophages, and plasma cells, all of which show signs of activation. This leads in most cases to progressive destruction of cartilage and bone, which occurs after invasion of these tissues by the ce ...
... inflammation of the synovial joints and infiltration by blood-derived cells, chiefly memory T cells, macrophages, and plasma cells, all of which show signs of activation. This leads in most cases to progressive destruction of cartilage and bone, which occurs after invasion of these tissues by the ce ...
Center Reaction Development of the Anti
... stained with anti-idiotypic Abs E4 or AD8 (blue) is shown in Figure 1, B and C, respectively. Ars-specific GCs were usually accompanied by scattered Id-positive cells in adjacent regions of the white and red pulp, some of which were brightly staining and could be AFCs (Fig. 1, B and C). The vast maj ...
... stained with anti-idiotypic Abs E4 or AD8 (blue) is shown in Figure 1, B and C, respectively. Ars-specific GCs were usually accompanied by scattered Id-positive cells in adjacent regions of the white and red pulp, some of which were brightly staining and could be AFCs (Fig. 1, B and C). The vast maj ...
Group_4_Abstract - Mast Cell
... In the field of mast cell and basophil research, the most used experimental tools are based on murine models. Regarding basophils not much research on animal models has been carried out as yet. In general, we can distinguish between two types of mast cell deficient mouse models: c-Kitdependent model ...
... In the field of mast cell and basophil research, the most used experimental tools are based on murine models. Regarding basophils not much research on animal models has been carried out as yet. In general, we can distinguish between two types of mast cell deficient mouse models: c-Kitdependent model ...
Inflammatory bowel disease related innate immunity and adaptive
... of which was significantly higher than that produced by DCs co-cultured with homologous or heterologous spleen T cells [15]. In colonic mucosa of IBD patients, interactions between DCs and T cells promote production of inflammatory cytokines and cause inflammation [15]. In addition, there is a regul ...
... of which was significantly higher than that produced by DCs co-cultured with homologous or heterologous spleen T cells [15]. In colonic mucosa of IBD patients, interactions between DCs and T cells promote production of inflammatory cytokines and cause inflammation [15]. In addition, there is a regul ...
No Slide Title
... • Final diagnosis is based on extensive clinicopathologic diagnosis • More than one insult can contribute to the injury and diagnostic hierarchy should be assigned, if possible. • Pathophysiologic approach usually trumps morphological approach, but combination is best ...
... • Final diagnosis is based on extensive clinicopathologic diagnosis • More than one insult can contribute to the injury and diagnostic hierarchy should be assigned, if possible. • Pathophysiologic approach usually trumps morphological approach, but combination is best ...
I. BACTERIA Percent Shift from Gram Positive (facultative) to Gram
... host response against them may contribute to the pathogenesis of CHD. Pussinen PJ, Nyyssonen K, Alfthan G, Salonen R, Laukkanen JA, Salonen JT. Serum antibody levels to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans predict the risk for coronary heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc ...
... host response against them may contribute to the pathogenesis of CHD. Pussinen PJ, Nyyssonen K, Alfthan G, Salonen R, Laukkanen JA, Salonen JT. Serum antibody levels to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans predict the risk for coronary heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc ...
evaluation the immune status of the burn patients infected with
... immunological criteria for patients with these bacteria Was clearly evident and clear rise in the number of white blood cells in patients where proportional rise with the degree of burning and intensity, reaching the preparation of cells to mm3) / 103) 10.44, 13.222 and 15.955 for each of the patien ...
... immunological criteria for patients with these bacteria Was clearly evident and clear rise in the number of white blood cells in patients where proportional rise with the degree of burning and intensity, reaching the preparation of cells to mm3) / 103) 10.44, 13.222 and 15.955 for each of the patien ...
Introduction - Philsci
... the mother, the fetus does not trigger any maternal immune response, or is protected against such a response. Induction of tolerance mechanisms, such as those due to HLA-G (20) and regulatory T cells (21) have been proved to play a critical role in this tolerance. (iv) Chimerism, that is, the proces ...
... the mother, the fetus does not trigger any maternal immune response, or is protected against such a response. Induction of tolerance mechanisms, such as those due to HLA-G (20) and regulatory T cells (21) have been proved to play a critical role in this tolerance. (iv) Chimerism, that is, the proces ...
1 We discussed function of white blood cells ,different type of white
... Know we are going to take about ABO system: as I told you some people on their RBC the have only A antigen, so their blood type is A. at the same time these people who have only A, they have antibodies to the antigen that is not presented on their body (so they have anti B). So in ABO system, the bo ...
... Know we are going to take about ABO system: as I told you some people on their RBC the have only A antigen, so their blood type is A. at the same time these people who have only A, they have antibodies to the antigen that is not presented on their body (so they have anti B). So in ABO system, the bo ...
Chapter 21 review questions
... Cytotoxic T cells activate B cells to produce antibodies. Cytotoxic T cells induce cell lysis with perforin, a protein similar to complement's MAC. Cytotoxic T cells secrete the proteins that activate complement. Cytotoxic T cells are antigen-presenting cells similar to the complement proteins found ...
... Cytotoxic T cells activate B cells to produce antibodies. Cytotoxic T cells induce cell lysis with perforin, a protein similar to complement's MAC. Cytotoxic T cells secrete the proteins that activate complement. Cytotoxic T cells are antigen-presenting cells similar to the complement proteins found ...
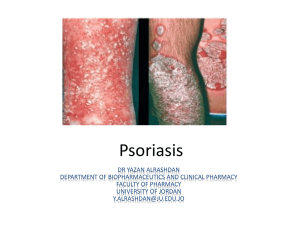
Diagnosis
... the area affected into a single score in the range 0 (no disease) to 72 (maximal disease). ...
... the area affected into a single score in the range 0 (no disease) to 72 (maximal disease). ...
Immune System and Parkinson`s Disease
... active disease state and is believed to actually cause an effect leading to further neurodegeneration by inducing cell death in dopaminergic neurons [30]. Once microglia become activated by a stimulus such as α-synuclein, they may remain activated and respond atypically to subsequent stimuli thereby ...
... active disease state and is believed to actually cause an effect leading to further neurodegeneration by inducing cell death in dopaminergic neurons [30]. Once microglia become activated by a stimulus such as α-synuclein, they may remain activated and respond atypically to subsequent stimuli thereby ...
Immune system
... LN in dimensions, sometimes with modification of their consistence. Polyadenia – increasing of number of ...
... LN in dimensions, sometimes with modification of their consistence. Polyadenia – increasing of number of ...
IMMUNITY TO BACTERIAL INFECTIONS Bacterial
... • prevent CR on phagocytes from binding activated complement on ...
... • prevent CR on phagocytes from binding activated complement on ...
Document
... MARKED THICKENING OF THE BASEMENT MEMBRANE OF BRONCHIAL MUCOSA, HYPERTROPHY OF BRONCHIAL SMOOTH MUSCLE, HYPERTROPHY OF BRONCHIAL MUCOUS GLANDS, EOSINOPHILS AND CHRONIC INFLAMMATORY CELLS IN THE BRONCHIAL WALL, INC. NUMBER OF MAST CELLS, PRESENCE OF MUCOUS IN BRONCHI CONTAINING LARGE NUMBERS OF EOSIN ...
... MARKED THICKENING OF THE BASEMENT MEMBRANE OF BRONCHIAL MUCOSA, HYPERTROPHY OF BRONCHIAL SMOOTH MUSCLE, HYPERTROPHY OF BRONCHIAL MUCOUS GLANDS, EOSINOPHILS AND CHRONIC INFLAMMATORY CELLS IN THE BRONCHIAL WALL, INC. NUMBER OF MAST CELLS, PRESENCE OF MUCOUS IN BRONCHI CONTAINING LARGE NUMBERS OF EOSIN ...
New Oral Treatments for Multiple Sclerosis
... Hvizdos, A.J., and Mosler, C.R. (2016). Current Perspectives on Multiple Sclerosis. US Pharmacist, 41(1): 22 - 26. Mehling, M., Kappos, L. & Derfuss, T. (2011). Fingolimod for multiple sclerosis: mechanism of action, clinical outcomes, and future directions. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. ...
... Hvizdos, A.J., and Mosler, C.R. (2016). Current Perspectives on Multiple Sclerosis. US Pharmacist, 41(1): 22 - 26. Mehling, M., Kappos, L. & Derfuss, T. (2011). Fingolimod for multiple sclerosis: mechanism of action, clinical outcomes, and future directions. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. ...
Lect 03 - Connective Tissue
... B-cells (adaptive immune system) Activation of B-cells ─ 1. B cells produce ‘immunoglobulin-receptors’ that are inserted on surface membrane ─ 2. antigens bind to receptors & induce B-cell differentiation into plasma and memory cells ─ 3. memory cells are long lived and allow quick attack against sa ...
... B-cells (adaptive immune system) Activation of B-cells ─ 1. B cells produce ‘immunoglobulin-receptors’ that are inserted on surface membrane ─ 2. antigens bind to receptors & induce B-cell differentiation into plasma and memory cells ─ 3. memory cells are long lived and allow quick attack against sa ...
Eicosanoids: an emerging role in dendritic cell biology
... such as prostaglandins (PGs) and leukotrienes (LTs) are produced predominately by antigen–presenting cells (APC), including macrophages and dendritic cells (DC). DC constitue a family of bone marrow-derived professional APC that play a critical role in the induction and modulation of both innate and ...
... such as prostaglandins (PGs) and leukotrienes (LTs) are produced predominately by antigen–presenting cells (APC), including macrophages and dendritic cells (DC). DC constitue a family of bone marrow-derived professional APC that play a critical role in the induction and modulation of both innate and ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.



![[Science] 22 NOVEMBER 2013 VOL 342, ISSUE 6161, PAGES 901](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001637839_1-ba508aab372cae0b1264fbbed354b56b-300x300.png)