Anatomy chapter 14 (Lymphatic and immunity)
... •The medulla – inner area where macrophages and T-cells are. •They are covered with connective tissue that extends inside the node and divides it into nodules and spaces called sinuses. •These contain both lymphocytes and macrophages which clean the lymph as it flows through the node. •Lymph nodes a ...
... •The medulla – inner area where macrophages and T-cells are. •They are covered with connective tissue that extends inside the node and divides it into nodules and spaces called sinuses. •These contain both lymphocytes and macrophages which clean the lymph as it flows through the node. •Lymph nodes a ...
Immunity and Immune Response
... • Act on antigens appearing on the surface of individual cells. • Over a million different kinds of T-cells – Each produces a different receptor in the cell membrane – Each receptor is composed of 1 molecule each of two different proteins – Each receptor binds a specific antigen but has only one bin ...
... • Act on antigens appearing on the surface of individual cells. • Over a million different kinds of T-cells – Each produces a different receptor in the cell membrane – Each receptor is composed of 1 molecule each of two different proteins – Each receptor binds a specific antigen but has only one bin ...
Chapter 27: Communicable Diseases
... _____ to _____ the open _______. b. ________ System is an _____ of individual _______, ______ and ______ that work _____ to fight against __________. ...
... _____ to _____ the open _______. b. ________ System is an _____ of individual _______, ______ and ______ that work _____ to fight against __________. ...
Type of Innate immune
... Key Molecules in immune response : Antigens , antibodies , MHC, TCR, adhesion molecules (CD), Cytokines. Several types of molecules play vital roles in immune responses. Antibodies are substances which provoke an immune response. Antibodies are not only the surface receptors of B cells that recogniz ...
... Key Molecules in immune response : Antigens , antibodies , MHC, TCR, adhesion molecules (CD), Cytokines. Several types of molecules play vital roles in immune responses. Antibodies are substances which provoke an immune response. Antibodies are not only the surface receptors of B cells that recogniz ...
Exam 4 review key - Iowa State University
... a.) Expresses several different antigen receptors b.) May mature in bone marrow to a cytotoxic T cell c.) May mature in the thymus to a helper T cell d.) Is phagocytic and participates in the inflammatory response B cells mature in the bone marrow, T cells mature in the thymus Which of the following ...
... a.) Expresses several different antigen receptors b.) May mature in bone marrow to a cytotoxic T cell c.) May mature in the thymus to a helper T cell d.) Is phagocytic and participates in the inflammatory response B cells mature in the bone marrow, T cells mature in the thymus Which of the following ...
Ectopie Synthesis and Paraneoplastic
... gests that some materials produced are ectopie in place (since, for example, a lung cell should not be making ACTH) or are ectopie in time, since a liver cell should not be making a-fetoglobulin after fetal life. From the point of view of the partially differentiated lung or liver cell that is produ ...
... gests that some materials produced are ectopie in place (since, for example, a lung cell should not be making ACTH) or are ectopie in time, since a liver cell should not be making a-fetoglobulin after fetal life. From the point of view of the partially differentiated lung or liver cell that is produ ...
CYTOKINE AND LYMPHOCYTE SUBSETS SMALL GROUPS
... Leprosy can incite either a Th1 (helper) or Th2 subset dominant response. The dominant subset is influenced by route and dose of antigens (M. Leprae), status of the patient, especially nutritional (malnutrition is associated with depressed Th function), and MHC/TLR dictation of the immune response. ...
... Leprosy can incite either a Th1 (helper) or Th2 subset dominant response. The dominant subset is influenced by route and dose of antigens (M. Leprae), status of the patient, especially nutritional (malnutrition is associated with depressed Th function), and MHC/TLR dictation of the immune response. ...
Evolutionary Genetics
... • A Gene Superfamily is a large set of related genes that is divisible into smaller sets or families • Genes in each family are more closely related to each other than to genes in other families • Multigene families within this Superfamily – Antibody Genes – T cell receptor genes – MHC protein genes ...
... • A Gene Superfamily is a large set of related genes that is divisible into smaller sets or families • Genes in each family are more closely related to each other than to genes in other families • Multigene families within this Superfamily – Antibody Genes – T cell receptor genes – MHC protein genes ...
The Specific/Adaptive Immune Response
... –APC internalizes the invading pathogen and enzymatically digests it into smaller antigenic fragments which are contained within a phagolysosome –Phagolysosome fuses with a vesicle containing MHCII molecules –Each fragment binds to the antigen-binding groove of a complementary MHCII molecule –The fu ...
... –APC internalizes the invading pathogen and enzymatically digests it into smaller antigenic fragments which are contained within a phagolysosome –Phagolysosome fuses with a vesicle containing MHCII molecules –Each fragment binds to the antigen-binding groove of a complementary MHCII molecule –The fu ...
1 - Homeschooling is Fun
... __________ 27. B and T cells are named after what they are trained to fight. __________ 28. Bacteria can become immune to antibiotics. __________ 29. The spleen is about the size of your liver. __________ 30. Antigens are special chemicals sent to injured to increase blood flow. __________ 31. A per ...
... __________ 27. B and T cells are named after what they are trained to fight. __________ 28. Bacteria can become immune to antibiotics. __________ 29. The spleen is about the size of your liver. __________ 30. Antigens are special chemicals sent to injured to increase blood flow. __________ 31. A per ...
Life Processes and Living things
... • Doughnut shape to allow maximum O2 absorbed by the haemoglobin they contain. The function is similar the the Palisade Cells . They are doughnut shaped rather than tall to allow smooth passage through the capillaries • They are so packed with Haemoglobin that they have no room for a Nucleus ...
... • Doughnut shape to allow maximum O2 absorbed by the haemoglobin they contain. The function is similar the the Palisade Cells . They are doughnut shaped rather than tall to allow smooth passage through the capillaries • They are so packed with Haemoglobin that they have no room for a Nucleus ...
Hematopathology
... • Lymphocytes are much more common in the lymphatic system. • Lymphocytes are distinguished by having a deeply staining nucleus which may be eccentric in location. • B cells make antibodies that bind to pathogens to enable their destruction. • CD4+ (helper) T cells co-ordinate the immune response an ...
... • Lymphocytes are much more common in the lymphatic system. • Lymphocytes are distinguished by having a deeply staining nucleus which may be eccentric in location. • B cells make antibodies that bind to pathogens to enable their destruction. • CD4+ (helper) T cells co-ordinate the immune response an ...
NUR127 Unit 1 Lecture 2 Immunology
... Helper T-Cells: Stimulate other helper Tcells, cytotoxic T-cells, and B cells. Suppressor T-Cells: Help regulate the attack & prevent tissue destruction. Memory T-Cells: Remain as an immune response and stimulate faster responses if the same antigen invades again. ...
... Helper T-Cells: Stimulate other helper Tcells, cytotoxic T-cells, and B cells. Suppressor T-Cells: Help regulate the attack & prevent tissue destruction. Memory T-Cells: Remain as an immune response and stimulate faster responses if the same antigen invades again. ...
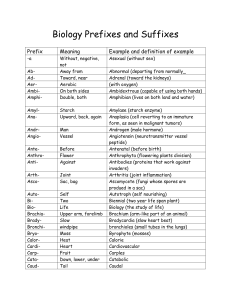
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... nutrients from dead or decaying matter) schizocarp (fruit that splits into several closed one-seeded portions upon maturation) ...
... nutrients from dead or decaying matter) schizocarp (fruit that splits into several closed one-seeded portions upon maturation) ...
Recombinant Human LIF (Carrier-free) - Data Sheets
... Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a member of the IL-6 family of cytokines, based on its helical structure. LIF expression has been observed in various tissues including thymus, lung, and neuronal tissue. Expression has also been reported in T cells, monocytes, astrocytes, osteoblasts, keratinocyt ...
... Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a member of the IL-6 family of cytokines, based on its helical structure. LIF expression has been observed in various tissues including thymus, lung, and neuronal tissue. Expression has also been reported in T cells, monocytes, astrocytes, osteoblasts, keratinocyt ...
Non-specific (innate) immune system Specific (adaptive) immune
... immune system Includes chemical and physical barriers (the first line of defence) and responses such as inflammation (the second line of defence). Its effects are rapid, shortlived and non-specific. Found in all ...
... immune system Includes chemical and physical barriers (the first line of defence) and responses such as inflammation (the second line of defence). Its effects are rapid, shortlived and non-specific. Found in all ...
Blood Groups and Immunogenetics
... "Acquired immunity" refers to the fact that we can respond to invasion by a "foreign" organism only after exposure; our system is able to recognize "antigens" as foreign. Antigens are molecules (usually proteins) that differ in some way from our own natural proteins. The proteins on one persons' cel ...
... "Acquired immunity" refers to the fact that we can respond to invasion by a "foreign" organism only after exposure; our system is able to recognize "antigens" as foreign. Antigens are molecules (usually proteins) that differ in some way from our own natural proteins. The proteins on one persons' cel ...
Innate immune responses to cationic antimicrobial peptides in the lung
... least partially due to pre-existing inflammation. In addition there is no question that inflammatory response plays an important role in late stage CF lung disease. Cationic antimicrobial peptides have been proposed as a therapeutic option for the treatment of CF. The ability of peptides to kill P. ...
... least partially due to pre-existing inflammation. In addition there is no question that inflammatory response plays an important role in late stage CF lung disease. Cationic antimicrobial peptides have been proposed as a therapeutic option for the treatment of CF. The ability of peptides to kill P. ...
Lecture 5
... – T cells are key cellular component of immunity. – T cells have an antigen receptor that recognizes and reacts to a specific antigen (T cell receptor). – T cell receptor only recognize antigens combined with major histocompatability (MHC) proteins on the surface of cells. • MHC Class I: Found on al ...
... – T cells are key cellular component of immunity. – T cells have an antigen receptor that recognizes and reacts to a specific antigen (T cell receptor). – T cell receptor only recognize antigens combined with major histocompatability (MHC) proteins on the surface of cells. • MHC Class I: Found on al ...
3) ALL LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO A STIMULUS
... To grow means to get bigger and to get bigger; more cells must be added. To increase numbers of cells, cell division must occur. Develop means to change into an adult form (mature). ...
... To grow means to get bigger and to get bigger; more cells must be added. To increase numbers of cells, cell division must occur. Develop means to change into an adult form (mature). ...
(b) activate the adaptive immune response
... of histologically apparent cytologic changes, cellular infiltration, and mediator release that occurs in the affected blood vessels and adjacent tissues in response to an injury or abnormal stimulation caused by a physical, chemical, or biologic agent, including the local reactions and resulting mor ...
... of histologically apparent cytologic changes, cellular infiltration, and mediator release that occurs in the affected blood vessels and adjacent tissues in response to an injury or abnormal stimulation caused by a physical, chemical, or biologic agent, including the local reactions and resulting mor ...