Innate immune recognition
... Antibody isotypes: IgM, IgG, IgD, IgA, IgE The advantages of multivalency effector functions of antibody isotypes ...
... Antibody isotypes: IgM, IgG, IgD, IgA, IgE The advantages of multivalency effector functions of antibody isotypes ...
t lyphocyte
... – End result: thousands of T lymphocytes each with different specific reactivities for different antigens – Insuring that each T lymphocyte will not react with the body’s own antigens (self antigen) • Then the preprocessed cells leave thymus to lymphoid tissues ...
... – End result: thousands of T lymphocytes each with different specific reactivities for different antigens – Insuring that each T lymphocyte will not react with the body’s own antigens (self antigen) • Then the preprocessed cells leave thymus to lymphoid tissues ...
How antifungal drugs kill fungi and cure disease
... cancer chemotherapy, bone marrow transplant, organ transplants, other immunotherapy, other immunecompromising disease High mortality: those people that get systemic infection are already sick; current drugs are not effective ...
... cancer chemotherapy, bone marrow transplant, organ transplants, other immunotherapy, other immunecompromising disease High mortality: those people that get systemic infection are already sick; current drugs are not effective ...
After-care for Liquid Nitrogen Treatment
... local destruction of damaged skin cells. In other conditions it may encourage your immune system to produce antibodies, to destroy warts for example. ...
... local destruction of damaged skin cells. In other conditions it may encourage your immune system to produce antibodies, to destroy warts for example. ...
Poster
... of fetal platelets due to maternal antibodies against a specific glycoprotein located on the platelet cell surface. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa has a region known as HPA1, which has a specific dimorphism linked to NAIT. If the mother’s platelet has a proline residue in position 33 (HPA1b), and the baby ha ...
... of fetal platelets due to maternal antibodies against a specific glycoprotein located on the platelet cell surface. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa has a region known as HPA1, which has a specific dimorphism linked to NAIT. If the mother’s platelet has a proline residue in position 33 (HPA1b), and the baby ha ...
ASCIA SCID Pamphlet - Immune Deficiencies Foundation Australia
... varies according to the: • severity of SCID • number of infections, especially around the time of the transplant • type of treatment the bone marrow has to receive to reduce the risk of rejection, such as removal of the T cells (or ‘T cell depletion’) - bone marrow contains T cells which can reco ...
... varies according to the: • severity of SCID • number of infections, especially around the time of the transplant • type of treatment the bone marrow has to receive to reduce the risk of rejection, such as removal of the T cells (or ‘T cell depletion’) - bone marrow contains T cells which can reco ...
Acquired Immunity Defends Against Infection of Body Cells and Fluids
... • They triggers release from mast cells and basophils of histamine and other chemicals that cause allergic reactions. ...
... • They triggers release from mast cells and basophils of histamine and other chemicals that cause allergic reactions. ...
AUTOIMMUNE ENDOCRINE DISEASES
... cells can be deleted before emigration. The autoreactive TSH clone, having emigrated from the thymus because the AIRE complex was not displaying TSH antigens, may be activated by sex hormones after puberty with or without the help of a viral infection. Other poorly understood tolerance mechanisms co ...
... cells can be deleted before emigration. The autoreactive TSH clone, having emigrated from the thymus because the AIRE complex was not displaying TSH antigens, may be activated by sex hormones after puberty with or without the help of a viral infection. Other poorly understood tolerance mechanisms co ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Social Circle City Schools
... Immune Responses Cell-mediated immunity: T cells are active against viruses and bacteria that have infected cells; also is crucial in the body’s response against transplanted tissues and cancerous cells - activated T cells become TH or TC; TH activate B cells that produce antibodies, TC destroy inf ...
... Immune Responses Cell-mediated immunity: T cells are active against viruses and bacteria that have infected cells; also is crucial in the body’s response against transplanted tissues and cancerous cells - activated T cells become TH or TC; TH activate B cells that produce antibodies, TC destroy inf ...
VMB 673 Comparative Immunology Syllabus 2013 Revised Cat 2
... Students will be expected to identify similarities and differences in immune system function between well studied systems (laboratory mice and human patients) to lesswell understood systems. Students will be able to comprehend common techniques used to study immune function and determine how tec ...
... Students will be expected to identify similarities and differences in immune system function between well studied systems (laboratory mice and human patients) to lesswell understood systems. Students will be able to comprehend common techniques used to study immune function and determine how tec ...
Immune System Concept Maps
... 2. IMMUNE RESPONSE, PRIMARY IMMUNE RESPONSE, PATHOGEN, ANTIGEN, TCELL, B-CELL, ANTIBODY, PLASMA CELLS, MEMORY B-CELLS, ANTIBODIES, PHAGOCYTES, KILLER T-CELL (CYTOTOXIC T-CELL), HELPER T-CELL, SECONDARY IMMUNE RESPONSE, SUPPRESSOR T-CELL (10 points) ...
... 2. IMMUNE RESPONSE, PRIMARY IMMUNE RESPONSE, PATHOGEN, ANTIGEN, TCELL, B-CELL, ANTIBODY, PLASMA CELLS, MEMORY B-CELLS, ANTIBODIES, PHAGOCYTES, KILLER T-CELL (CYTOTOXIC T-CELL), HELPER T-CELL, SECONDARY IMMUNE RESPONSE, SUPPRESSOR T-CELL (10 points) ...
Microbiology Review Guide Answers
... Microbiology Review Guide Answers Viruses 1. A virus is a small pathogen which causes many diseases. 2. Viruses are non-living because they don’t carry out life processes such as metabolism, growth, & development. All are parasitic – require hosts. 3. True: Viruses are specific as to what type of ho ...
... Microbiology Review Guide Answers Viruses 1. A virus is a small pathogen which causes many diseases. 2. Viruses are non-living because they don’t carry out life processes such as metabolism, growth, & development. All are parasitic – require hosts. 3. True: Viruses are specific as to what type of ho ...
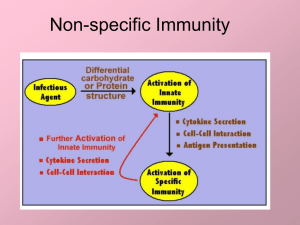
Non-specific Immunity
... • Pluses • Inhibit microbial growth • Enhance immune cell performance • Speed tissue repair ...
... • Pluses • Inhibit microbial growth • Enhance immune cell performance • Speed tissue repair ...