Preview - American Economic Association
... endogenous contract response (Einav, Finkelstein, and Levin 2010). Perhaps similar reasons may also explain why many (although not all) government interventions in insurance markets tend to focus on the pricing of contracts through taxes and subsidies, regulations, or mandates. The last part of the ...
... endogenous contract response (Einav, Finkelstein, and Levin 2010). Perhaps similar reasons may also explain why many (although not all) government interventions in insurance markets tend to focus on the pricing of contracts through taxes and subsidies, regulations, or mandates. The last part of the ...
Pure Exchange Economy
... 6 The first theorem of welfare economics The Walrasian equilibrium theory is very interesting from a positive perspective as long as we believe in the behavioural assumptions on which the model is based. Even if sometimes, the assumptions are not especially plausible, the Walrasian equilibrium theo ...
... 6 The first theorem of welfare economics The Walrasian equilibrium theory is very interesting from a positive perspective as long as we believe in the behavioural assumptions on which the model is based. Even if sometimes, the assumptions are not especially plausible, the Walrasian equilibrium theo ...
16-16R - University of Hawaii Economics Department
... the opportunity cost of holding money and price dispersion. In this paper, we revisit the classical question on welfare cost in a general equilibrium monetary model. We build on the New Monetarist framework of Lagos and Wright (2005), and integrate the analysis of endogenous price dispersion in a fr ...
... the opportunity cost of holding money and price dispersion. In this paper, we revisit the classical question on welfare cost in a general equilibrium monetary model. We build on the New Monetarist framework of Lagos and Wright (2005), and integrate the analysis of endogenous price dispersion in a fr ...
Microeconomics, 4e (Perloff)
... users purchase more cigarettes and are less sensitive to price changes relative to light users. To determine whether a heavy user suffers a greater loss of consumer surplus than a light user does when the price of cigarettes increases, one would need to know ...
... users purchase more cigarettes and are less sensitive to price changes relative to light users. To determine whether a heavy user suffers a greater loss of consumer surplus than a light user does when the price of cigarettes increases, one would need to know ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES MEASURING THE WELFARE GAIN FROM PERSONAL COMPUTERS:
... expenditure function, from which welfare measures can be obtained. The procedure was developed earlier in Hausman (1981). Analytical solutions for the expenditure function can be obtained when the demand equation is (ln) linear. When the demand equation is not linear the indirect utility function m ...
... expenditure function, from which welfare measures can be obtained. The procedure was developed earlier in Hausman (1981). Analytical solutions for the expenditure function can be obtained when the demand equation is (ln) linear. When the demand equation is not linear the indirect utility function m ...
Document
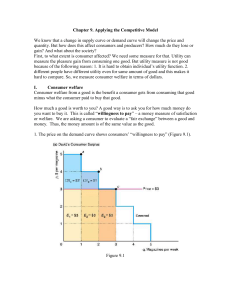
... PUTTING THE TOOLS TO WORK The effect of TANF on the budget constraint Assume that benefit guarantee, G, is $5,000 per year. Assume the benefit reduction rate, J, is 50%. Figure 13 illustrates this. ...
... PUTTING THE TOOLS TO WORK The effect of TANF on the budget constraint Assume that benefit guarantee, G, is $5,000 per year. Assume the benefit reduction rate, J, is 50%. Figure 13 illustrates this. ...
Public Finance and Public Policy
... how individuals and firms behave, we are able to address complicated questions such as how TANF benefits affect the labor supply of single mothers, and the implications of that response for social welfare. On the other hand, while we have answered these questions in a general sense, we have been ver ...
... how individuals and firms behave, we are able to address complicated questions such as how TANF benefits affect the labor supply of single mothers, and the implications of that response for social welfare. On the other hand, while we have answered these questions in a general sense, we have been ver ...
Second-Best Antitrust in General Equilibrium
... between the partial equilibrium demand curve and the marginal cost curve approximate the true welfare loss? The first issue is relevant for practical antitrust policy; there are always some unregulated industries in an ever changing world where old industries are replaced by new ones and where regul ...
... between the partial equilibrium demand curve and the marginal cost curve approximate the true welfare loss? The first issue is relevant for practical antitrust policy; there are always some unregulated industries in an ever changing world where old industries are replaced by new ones and where regul ...
The Expenditure Switching Effect, Welfare and Monetary Alan Sutherland
... when it has no future use (because there are no future periods). However, as previously stated, the model can easily be recast as an infinite horizon structure (where each period is identical in ex ante expected terms). In such a model, money held at the end of one period retains its value in future ...
... when it has no future use (because there are no future periods). However, as previously stated, the model can easily be recast as an infinite horizon structure (where each period is identical in ex ante expected terms). In such a model, money held at the end of one period retains its value in future ...
... Scanners, one of the most remarkable medical innovations of the last few decades. Even though CT Scanners are complex systems from a technological viewpoint, there are just a few attributes that characterize their performance (primarily scan speed and resolution). In the decade following the introdu ...
First Welfare Theorem
... Second Welfare Theorem: Preliminaries This is a converse to the First Welfare Theorem. The statement goes: under some conditions, any Pareto optimal allocation is part of a competitive equilibrium. Next, we try to understand what these conditions must be. We state and prove thw theorem next class. ...
... Second Welfare Theorem: Preliminaries This is a converse to the First Welfare Theorem. The statement goes: under some conditions, any Pareto optimal allocation is part of a competitive equilibrium. Next, we try to understand what these conditions must be. We state and prove thw theorem next class. ...
Welfare Economics
... Welfare Economics Welfare Economics – branch of economic theory concerned with the social desirability of alternative economic states Pure Economy Exchange • Assume a given amount of commodities exist – No Production – Two people and two commodities ...
... Welfare Economics Welfare Economics – branch of economic theory concerned with the social desirability of alternative economic states Pure Economy Exchange • Assume a given amount of commodities exist – No Production – Two people and two commodities ...
On the geometry of the consumer`s surplus line integral
... Since Dupuit (1844) consumer’s surplus has been proposed as a concept to measure the change in welfare in cases where the price of one good changes. In these cases the measure proposed, the consumer’s surplus change, is geometrically the area under the demand curve between the price in the initial s ...
... Since Dupuit (1844) consumer’s surplus has been proposed as a concept to measure the change in welfare in cases where the price of one good changes. In these cases the measure proposed, the consumer’s surplus change, is geometrically the area under the demand curve between the price in the initial s ...
Chp 9(6/30,7/1,7/2,7/6)
... Interpretation: By preventing other cab firms from entering the market, economic profit is created, the area . So the firms that are in the market benefit from the restriction; but consumers lose because of higher price. In most cities, permits can be rented or sold. So the owners of permits can c ...
... Interpretation: By preventing other cab firms from entering the market, economic profit is created, the area . So the firms that are in the market benefit from the restriction; but consumers lose because of higher price. In most cities, permits can be rented or sold. So the owners of permits can c ...
Lecture2b
... PUTTING THE TOOLS TO WORK The effect of TANF on the budget constraint Assume that benefit guarantee, G, is $5,000 per year. Assume the benefit reduction rate, θ, is 50%. Figure 13 illustrates this. ...
... PUTTING THE TOOLS TO WORK The effect of TANF on the budget constraint Assume that benefit guarantee, G, is $5,000 per year. Assume the benefit reduction rate, θ, is 50%. Figure 13 illustrates this. ...
A numerical example of the effects of an export subsidy
... The loss in consumer surplus is given by: - 0,5 (Pd - Pw) (Qd + Q'd) = -0.5(20(1000+900) = -19000 The increase in producer surplus is given by: 0,5 (Pd - Pw) (Qs + Q's) = 0,5 (20(2000+2400)) = +44000 The impact on the government budget (or the income of taxpayers) is the rectangle comprised of areas ...
... The loss in consumer surplus is given by: - 0,5 (Pd - Pw) (Qd + Q'd) = -0.5(20(1000+900) = -19000 The increase in producer surplus is given by: 0,5 (Pd - Pw) (Qs + Q's) = 0,5 (20(2000+2400)) = +44000 The impact on the government budget (or the income of taxpayers) is the rectangle comprised of areas ...
Theoretical Tools of Public Finance
... between the total size of the economic pie and its distribution among individuals. Social welfare function (SWF): A function that combines the utility functions of all individuals into an overall social utility function. ...
... between the total size of the economic pie and its distribution among individuals. Social welfare function (SWF): A function that combines the utility functions of all individuals into an overall social utility function. ...
Econ 210, Microeconomic Theory HW 7 Taxes, Subsidies, Tariffs
... M W T P = a − bQ M C = c + dQ Assume that 0 < c < a and b > 0 and d > 0. For each question below, where it says “describe the welfare effects”, a well-labeled graph is a good start. Don’t bother to make exact calculations. Focus on qualitative changes and identify winners and losers. If you making a ...
... M W T P = a − bQ M C = c + dQ Assume that 0 < c < a and b > 0 and d > 0. For each question below, where it says “describe the welfare effects”, a well-labeled graph is a good start. Don’t bother to make exact calculations. Focus on qualitative changes and identify winners and losers. If you making a ...
Government intervention in food markets
... • in which case the externality is on the person’s “future self” • children the most compelling case ...
... • in which case the externality is on the person’s “future self” • children the most compelling case ...
1.5 Welfare Economics: Consumer and Producer Surplus
... 1.5 Welfare Economics: Consumer and Producer Surplus 1.5.1 Introduction to Welfare Economics Welfare economics is concerned with how well off individuals and groups are. Welfare economics is not about government programs to assist the needy... that is a different type of welfare. In economics, welfa ...
... 1.5 Welfare Economics: Consumer and Producer Surplus 1.5.1 Introduction to Welfare Economics Welfare economics is concerned with how well off individuals and groups are. Welfare economics is not about government programs to assist the needy... that is a different type of welfare. In economics, welfa ...
Qs-ch7-9
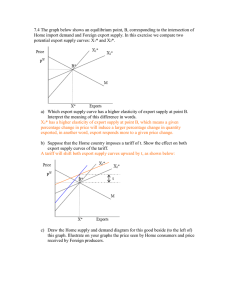
... overall welfare effect is ambiguous, though. Suppose a large food-importing country elsewhere reciprocates by lowering its tariffs on agricultural goods by the same amount. Are there gains or losses to this large country, or is it ambiguous? Is there a net overall gain? For a large food-importing co ...
... overall welfare effect is ambiguous, though. Suppose a large food-importing country elsewhere reciprocates by lowering its tariffs on agricultural goods by the same amount. Are there gains or losses to this large country, or is it ambiguous? Is there a net overall gain? For a large food-importing co ...