9-9 9.3 How Competition Maximizes Welfare
... • How should we measure society’s welfare? • If we are ok with weighting the well-being of consumers and producers equally, then welfare can be measured W = CS + PS • Producing the competitive quantity maximizes welfare. • Put another way, producing less than the competitive level of output lowers t ...
... • How should we measure society’s welfare? • If we are ok with weighting the well-being of consumers and producers equally, then welfare can be measured W = CS + PS • Producing the competitive quantity maximizes welfare. • Put another way, producing less than the competitive level of output lowers t ...
Lecture 07
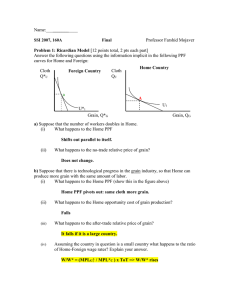
... You are trying to decide where to go on vacation. In country A, your risk of death is 1 in 10,000, and you would pay $600 to go on that vacation. In country B, your risk of death is 1 in 20,000, and you would pay $900 to go on that vacation. Suppose that you’re indifferent between these two destinat ...
... You are trying to decide where to go on vacation. In country A, your risk of death is 1 in 10,000, and you would pay $600 to go on that vacation. In country B, your risk of death is 1 in 20,000, and you would pay $900 to go on that vacation. Suppose that you’re indifferent between these two destinat ...
FinalSS-207 - UC Davis economics
... Here you goal to maximize the votes that you can get and not necessarily economic efficiency/welfare. In getting peoples vote you consider two factors: median voter and contribution of political lobbyists. The interests of the median voter and the lobbyists are against each other. The question is wh ...
... Here you goal to maximize the votes that you can get and not necessarily economic efficiency/welfare. In getting peoples vote you consider two factors: median voter and contribution of political lobbyists. The interests of the median voter and the lobbyists are against each other. The question is wh ...
Comparing Monopoly and Perfect Competition Comparing
... and charges PC, therefore earning a loss ...
... and charges PC, therefore earning a loss ...
Seminar 1 General Equilibrium and Welfare
... competitive market, that means the consumers are price taker ⇒ but the idea of competitive equilibrium make sense when there are enough agents. In the Edgeworth box there are only two agents, that can recognize their market power and use it to improve their position; ...
... competitive market, that means the consumers are price taker ⇒ but the idea of competitive equilibrium make sense when there are enough agents. In the Edgeworth box there are only two agents, that can recognize their market power and use it to improve their position; ...
Chapter 20: Welfare Economics
... 6. Majority voting, a mechanism design for determining social choice, can result in a social preference ranking that is not transitive. 7. By not revealing his or her true preferences, an agent can employ strategic voting to potentially alter a social choice toward improving his or her satisfaction. ...
... 6. Majority voting, a mechanism design for determining social choice, can result in a social preference ranking that is not transitive. 7. By not revealing his or her true preferences, an agent can employ strategic voting to potentially alter a social choice toward improving his or her satisfaction. ...
INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS ECON 30074 LECTURE 8 TRADE
... Warning!! These lecture notes are to help students during the lectures. Reading these notes without attending lectures can be misleading. © Estela Montado, University of Bristol ...
... Warning!! These lecture notes are to help students during the lectures. Reading these notes without attending lectures can be misleading. © Estela Montado, University of Bristol ...
Spatial Equilibrium - SOW-VU
... system in a transparent way. Nonetheless, it assumes that all transportation cost within counties are truly incurred. As explained in the previous lecture, this assumption would need to be relaxed. Therefore, as a background check on transport flows and price margins in CHINAGRO, and as a prototype ...
... system in a transparent way. Nonetheless, it assumes that all transportation cost within counties are truly incurred. As explained in the previous lecture, this assumption would need to be relaxed. Therefore, as a background check on transport flows and price margins in CHINAGRO, and as a prototype ...
Midterm 2 Summary Notes
... • Bertrand: firms set prices (instead of quantities) at the same time • Two firms may be enough to remove market power (i.e. restore competitive outcome) if products are identical • Recall proof from class that identical Bertrand duopolists drive price down to marginal cost • Also recall the Sta ...
... • Bertrand: firms set prices (instead of quantities) at the same time • Two firms may be enough to remove market power (i.e. restore competitive outcome) if products are identical • Recall proof from class that identical Bertrand duopolists drive price down to marginal cost • Also recall the Sta ...